Quantum-assisted biomolecular modelling
... like a protein interacting with a drug, or even an entire cell, it is worth considering the nature of computer simulation and what we achieve by its use. Essentially, we are testing our most accurate models of the real world by calculating, in detail, what they predict, and comparing this with our o ...
... like a protein interacting with a drug, or even an entire cell, it is worth considering the nature of computer simulation and what we achieve by its use. Essentially, we are testing our most accurate models of the real world by calculating, in detail, what they predict, and comparing this with our o ...
Spin Hall Effect in
... Rashba term induces an energy level crossing in the lowest heavy hole sub-band, which gives rise to a resonant spin Hall conductance. The resonance may be used to identify the intrinsic spin Hall effect. In collaboration with X. Dai, Z. Fang, Y. G. Yao ...
... Rashba term induces an energy level crossing in the lowest heavy hole sub-band, which gives rise to a resonant spin Hall conductance. The resonance may be used to identify the intrinsic spin Hall effect. In collaboration with X. Dai, Z. Fang, Y. G. Yao ...
Chapter 7 The Collapse of the Wave Function
... At this point, it’s worth taking a step back and reviewing where we are. We started with some observations about how electron spins function, and how it’s very different from what you’d expect for little spinning balls operating under the laws of classical physics. These observations are: ...
... At this point, it’s worth taking a step back and reviewing where we are. We started with some observations about how electron spins function, and how it’s very different from what you’d expect for little spinning balls operating under the laws of classical physics. These observations are: ...
A Aberration The apparent change in position of a light
... Bode's law had no theoretical justification when it was first introduced; it did, however, agree with the soon-tobe-discovered planet Uranus' orbit (19.2 au actual; 19.7 au predicted). Similarly, it predicted a missing planet between Mars and Jupiter, and shortly thereafter the asteroids were found ...
... Bode's law had no theoretical justification when it was first introduced; it did, however, agree with the soon-tobe-discovered planet Uranus' orbit (19.2 au actual; 19.7 au predicted). Similarly, it predicted a missing planet between Mars and Jupiter, and shortly thereafter the asteroids were found ...
Single and Entangled Photon Sources
... quantum dot causes its energy levels to shift to higher values, much like a particle confined to a box will have its energy levels shifted higher if the box is made smaller [4]. Thus different wavelength light can be achieved by preparing samples of quantum dots with varying sizes. Many quantum dots ...
... quantum dot causes its energy levels to shift to higher values, much like a particle confined to a box will have its energy levels shifted higher if the box is made smaller [4]. Thus different wavelength light can be achieved by preparing samples of quantum dots with varying sizes. Many quantum dots ...
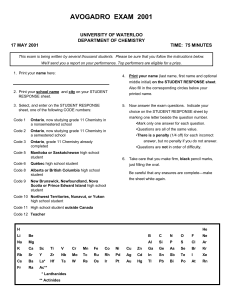
avogadro exam 2001 - University of Waterloo
... The results of Student A are more accurate but less precise. ...
... The results of Student A are more accurate but less precise. ...
Hidden Variable Theory
... brought into being by the very act of measurement. There are two reasons why we say this: 1. Measurements disturb the system If we want to measure the position of an atom we must shine light on it. The wavelength of the light must be about the atom’s size: λ . ∆x. But the light imparts a momentum to ...
... brought into being by the very act of measurement. There are two reasons why we say this: 1. Measurements disturb the system If we want to measure the position of an atom we must shine light on it. The wavelength of the light must be about the atom’s size: λ . ∆x. But the light imparts a momentum to ...
II. Electrons and Their Interaction with Matter
... An electron in a circular orbit in the xy plane is equivalent to a linear oscillator along the x-axis and one along y, and should consequently radiate twice as fast. This energy loss is a simple way of understanding Bohr’s dilemma. In order to retain the orbit’s stability, Bohr suggested that the el ...
... An electron in a circular orbit in the xy plane is equivalent to a linear oscillator along the x-axis and one along y, and should consequently radiate twice as fast. This energy loss is a simple way of understanding Bohr’s dilemma. In order to retain the orbit’s stability, Bohr suggested that the el ...
4 Theory of quantum scattering and chemical reactions
... chemical reactions Quantum scattering theory plays an essential role in describing chemical reactions and photoionization. Although all of these phenomena are time dependent, scattering theory is most accessible from a time-independent perspective. We will however introduce the concept of scattering ...
... chemical reactions Quantum scattering theory plays an essential role in describing chemical reactions and photoionization. Although all of these phenomena are time dependent, scattering theory is most accessible from a time-independent perspective. We will however introduce the concept of scattering ...
Chapter 40
... simplification model that is a result of the recognition of the dual nature of light and of material particles In this model, entities have both particle and wave characteristics We much choose one appropriate behavior in order to understand a ...
... simplification model that is a result of the recognition of the dual nature of light and of material particles In this model, entities have both particle and wave characteristics We much choose one appropriate behavior in order to understand a ...
Dephasing and the Orthogonality Catastrophe in Tunneling through a Quantum... The “Which Path?” Interferometer
... because it cannot be externally controlled.) In the proposed experiment, the transmission coefficient across the ring Tring can be obtained from the appropriate combination of measurements in a multiprobe geometry [3]. According to the Aharonov-Bohm effect, i.e., the phase difference of 2pFyF0 betwe ...
... because it cannot be externally controlled.) In the proposed experiment, the transmission coefficient across the ring Tring can be obtained from the appropriate combination of measurements in a multiprobe geometry [3]. According to the Aharonov-Bohm effect, i.e., the phase difference of 2pFyF0 betwe ...
... same, I have complete confidence in the reliability of the method used here.” The emergence of field quantization Once quantum theory had been developed by Heisenberg, Schrödinger and others, it was obvious that electromagnetic fields should be quantized. It was known how to map the electromagnetic ...
Document
... • Alice sends Bob a stream of photons which have been randomly polarized to one of four states (0o,45o,90o,135o). • Bob measures the photons in a random sequence of basis. • Alice and Bob publicly announces the sequence of basis they used. • Alice and Bob discard the results that have been measured ...
... • Alice sends Bob a stream of photons which have been randomly polarized to one of four states (0o,45o,90o,135o). • Bob measures the photons in a random sequence of basis. • Alice and Bob publicly announces the sequence of basis they used. • Alice and Bob discard the results that have been measured ...
talk by Paul McGuirk
... within a certain probability. Multiple runs can be performed to increase the probability that the answer is correct. This increases the complexity to n3 log 2 n A Quantum Computer with 7 Qubits was developed in 2001 to implement Shor’s algorithm to factor 15. ...
... within a certain probability. Multiple runs can be performed to increase the probability that the answer is correct. This increases the complexity to n3 log 2 n A Quantum Computer with 7 Qubits was developed in 2001 to implement Shor’s algorithm to factor 15. ...
Problem Set 7
... peak at δ = 6.5 to 8. The two methylene protons will yield a quartet centered at δ = 2.6. The methyl proton will give a triplet at δ = 1.1. (c) i-butane-(CH3)3CH The nine methyl protons should appear as a doublet at δ = 0.9. The single proton will appear as ten peaks centered at about δ = 1.5. 19-31 ...
... peak at δ = 6.5 to 8. The two methylene protons will yield a quartet centered at δ = 2.6. The methyl proton will give a triplet at δ = 1.1. (c) i-butane-(CH3)3CH The nine methyl protons should appear as a doublet at δ = 0.9. The single proton will appear as ten peaks centered at about δ = 1.5. 19-31 ...
Unitary time evolution
... preparing another system. But it is impossible to copy an unknown quantum state. This means that many techniques of classical information theory (such as protecting information by making redundant copies, or having a fanout gate from a single bit) are impossible in quantum information theory. ...
... preparing another system. But it is impossible to copy an unknown quantum state. This means that many techniques of classical information theory (such as protecting information by making redundant copies, or having a fanout gate from a single bit) are impossible in quantum information theory. ...
review of experimental concepts for studying the quantum vacuum
... several tens of orders of magnitude greater than the energy density of matter-antimatter annihilation reactions. Even if we are constrained to integrate over all frequency modes only up to the nucleon Compton frequency (~ 1023 Hz), this energy density will still be enormous (~ 1035 J/m3). And we hav ...
... several tens of orders of magnitude greater than the energy density of matter-antimatter annihilation reactions. Even if we are constrained to integrate over all frequency modes only up to the nucleon Compton frequency (~ 1023 Hz), this energy density will still be enormous (~ 1035 J/m3). And we hav ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).