M. Shiga and W. Shinoda, heat capacity of water from quantum nuclear dynamics
... and becomes 9kB ⯝ 1 cal/ 共g K兲. Beyond the boiling point, the heat capacity of vapor drops to about 3kB, but increases gradually as the vapor is more heated. High heat capacity in the liquid state is said to be one of the anomalous properties of water, and this is mainly ascribed to the configuratio ...
... and becomes 9kB ⯝ 1 cal/ 共g K兲. Beyond the boiling point, the heat capacity of vapor drops to about 3kB, but increases gradually as the vapor is more heated. High heat capacity in the liquid state is said to be one of the anomalous properties of water, and this is mainly ascribed to the configuratio ...
Two-dimensional electron gas in InGaAs/ InAlAs quantum wells E. Diez
... 关DOI: 10.1063/1.2168666兴 In this Letter we report the characterization of electronic properties of two-dimensional electron gas 共2DEG兲 in a series of lattice-matched InGaAs/ InAlAs quantum wells 共QWs兲 grown by molecular beam epitaxy 共MBE兲 on an InP substrate 共here and after in our paper we use abbre ...
... 关DOI: 10.1063/1.2168666兴 In this Letter we report the characterization of electronic properties of two-dimensional electron gas 共2DEG兲 in a series of lattice-matched InGaAs/ InAlAs quantum wells 共QWs兲 grown by molecular beam epitaxy 共MBE兲 on an InP substrate 共here and after in our paper we use abbre ...
On the Reality of the Quantum State
... by German electric companies, who at the time were attempting to produce the brightest light bulbs possible given minimum energy input, an optimisation problem that would be solved by a correct blackbody theory. By the end of 1893 Wien had discovered [7] what is now known as Wien’s law, giving the b ...
... by German electric companies, who at the time were attempting to produce the brightest light bulbs possible given minimum energy input, an optimisation problem that would be solved by a correct blackbody theory. By the end of 1893 Wien had discovered [7] what is now known as Wien’s law, giving the b ...
Nonparametric estimation of the purity of a quantum state in
... probabilities of its measurable properties, or "observables" (examples of observables include energy, position, momentum and angular momentum). Generally, quantum mechanics does not assign deterministic values to observables. Instead, it makes predictions about probability distributions; that is, th ...
... probabilities of its measurable properties, or "observables" (examples of observables include energy, position, momentum and angular momentum). Generally, quantum mechanics does not assign deterministic values to observables. Instead, it makes predictions about probability distributions; that is, th ...
gunify - Paradigm Shift Now
... Einstein noted that the “special theory of relativity” does not compel us to deny the aether, and in fact employed an aether for his gravitational “special theory of relativity.” Since there is only one fundamental EM field; the magnetic vector potential field A, the web site Montalk.net argues that ...
... Einstein noted that the “special theory of relativity” does not compel us to deny the aether, and in fact employed an aether for his gravitational “special theory of relativity.” Since there is only one fundamental EM field; the magnetic vector potential field A, the web site Montalk.net argues that ...
1. Given the balanced equation
... the mixture to remove impurities in the ore. The carbon monoxide is formed by the oxidation of carbon(coke), as shown in the reaction below: 2 C + O2 - 2 CO + energy Liquid iron flows from the bottom of the blast furnace and is processed into different alloys of iron. Balance the equation for the re ...
... the mixture to remove impurities in the ore. The carbon monoxide is formed by the oxidation of carbon(coke), as shown in the reaction below: 2 C + O2 - 2 CO + energy Liquid iron flows from the bottom of the blast furnace and is processed into different alloys of iron. Balance the equation for the re ...
Powerpoint 7/13
... be computed, how fast, and with use of how much memory. With quantum computers, as with classical stochastic computers, one must also ask ‘and with what probability?’ We have seen that the minimum computation time for certain tasks can be lower for Q than for T . Complexity theory for Q deserves fur ...
... be computed, how fast, and with use of how much memory. With quantum computers, as with classical stochastic computers, one must also ask ‘and with what probability?’ We have seen that the minimum computation time for certain tasks can be lower for Q than for T . Complexity theory for Q deserves fur ...
force - Resonance DLP
... Suppose a toy car can move on its wheels along eastwest direction. If we push the car with our left hand, it moves towards east. If we push the car with our right hand, it will move towards west. If we push the car with our left hand towards east and with right hand towards west simultaneously, it i ...
... Suppose a toy car can move on its wheels along eastwest direction. If we push the car with our left hand, it moves towards east. If we push the car with our right hand, it will move towards west. If we push the car with our left hand towards east and with right hand towards west simultaneously, it i ...
Quantum Mechanical Path Integrals with Wiener Measures for all
... This result achieves our stated goal of a path-integral representation. It is important to compare our results here with those obtained earlier. In Ref. 3 we were able to find an expression for quadratic Hamiltonians which involves the function H(p, q) = (p, q lHlp, q) as the Hamiltonidrift an funct ...
... This result achieves our stated goal of a path-integral representation. It is important to compare our results here with those obtained earlier. In Ref. 3 we were able to find an expression for quadratic Hamiltonians which involves the function H(p, q) = (p, q lHlp, q) as the Hamiltonidrift an funct ...
An Introduction to Density Functional Theory
... expanding field of research. There are now many different flavours of functional available which are more or less appropriate for any particular study. Ultimately such judgments must be made in terms of results (i.e.: the direct comparison with more accurate theory or experimental data, which will b ...
... expanding field of research. There are now many different flavours of functional available which are more or less appropriate for any particular study. Ultimately such judgments must be made in terms of results (i.e.: the direct comparison with more accurate theory or experimental data, which will b ...
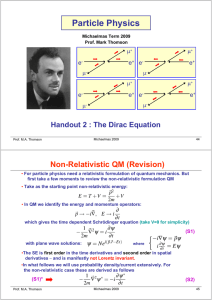
Dirac Equation
... The Dirac Equation Historically, it was thought that there were two main problems with the Klein-Gordon equation: Negative energy solutions The negative particle densities associated with these solutions We now know that in Quantum Field Theory these problems are overcome and the KG equation i ...
... The Dirac Equation Historically, it was thought that there were two main problems with the Klein-Gordon equation: Negative energy solutions The negative particle densities associated with these solutions We now know that in Quantum Field Theory these problems are overcome and the KG equation i ...
Lattice waves - Binghamton University
... wave-like phenomena in classical mechanics, they acquire certain particle-like properties when the lattice is analyzed using quantum mechanics (see wave-particle duality.) They are then known as phonons. There have been many excellent textbooks on the physics of lattice waves. Typical books1-14 whic ...
... wave-like phenomena in classical mechanics, they acquire certain particle-like properties when the lattice is analyzed using quantum mechanics (see wave-particle duality.) They are then known as phonons. There have been many excellent textbooks on the physics of lattice waves. Typical books1-14 whic ...
Laszlo and McTaggart
... days of quantum physics when theorists looked for the quantum equivalent of an oscillator - such as a weight bouncing up and down on a spring. In classical physics the electromagnetic field was described as being made up of superimposed magnetic and electric fields which also ‘oscillated’ in the se ...
... days of quantum physics when theorists looked for the quantum equivalent of an oscillator - such as a weight bouncing up and down on a spring. In classical physics the electromagnetic field was described as being made up of superimposed magnetic and electric fields which also ‘oscillated’ in the se ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).