BIOL 103 Ch 5 Carbohydrates for Students F15
... reduce risk for heart disease and cancer • Cons: excess sugar weight gain, poor nutrient intake, tooth decay • Sugar and dental caries (cavities) promoted by: – Sugar eaten by bacteria in teeth acids tooth decay cavities – Chocolate or Candy? – “Natural toothbrushes” ...
... reduce risk for heart disease and cancer • Cons: excess sugar weight gain, poor nutrient intake, tooth decay • Sugar and dental caries (cavities) promoted by: – Sugar eaten by bacteria in teeth acids tooth decay cavities – Chocolate or Candy? – “Natural toothbrushes” ...
Glucose
... Glycemic Index way of classifying food according to their ability to raise blood glucose much controversy ...
... Glycemic Index way of classifying food according to their ability to raise blood glucose much controversy ...
Fiber
... Glycemic Index way of classifying food according to their ability to raise blood glucose much controversy ...
... Glycemic Index way of classifying food according to their ability to raise blood glucose much controversy ...
BIOL 103 Ch 5 Carbohydrates for Students F15
... • Safe for diabeHcs • Nearly as sweet as sugar à “I can eat more” ...
... • Safe for diabeHcs • Nearly as sweet as sugar à “I can eat more” ...
Carbohydrates
... D-glucitol, commonly called D-sorbitol. • Reduction of D-fructose produces a mixture of D-glucitol and D-mannitol. ...
... D-glucitol, commonly called D-sorbitol. • Reduction of D-fructose produces a mixture of D-glucitol and D-mannitol. ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Five carbon backbones are pentoses and three carbon sugars are trioses. ...
... • Five carbon backbones are pentoses and three carbon sugars are trioses. ...
Structure and Function of Carbohydrates
... carbon, along with hydrogen and oxygen - usually in the same ratio as that found in water (H2O). Typical carbohydrates are composed of strings or chains of monosaccharides - that is, chains of individual sugars. A monosaccharide (mono = one, saccharide = sugar) is the smallest carbohydrate unit. The ...
... carbon, along with hydrogen and oxygen - usually in the same ratio as that found in water (H2O). Typical carbohydrates are composed of strings or chains of monosaccharides - that is, chains of individual sugars. A monosaccharide (mono = one, saccharide = sugar) is the smallest carbohydrate unit. The ...
Unit 1/Carbohydrates Fall 2011.pdf
... produced during the germination of seeds and fermentation. Sucrose is fructose and glucose combined. It is refined from sugarcane and sugar beets, tastes sweet, and is readily available. Lactose is galactose and glucose combined. It is found in milk and milk products. © 2009 Cengage - Wadsworth ...
... produced during the germination of seeds and fermentation. Sucrose is fructose and glucose combined. It is refined from sugarcane and sugar beets, tastes sweet, and is readily available. Lactose is galactose and glucose combined. It is found in milk and milk products. © 2009 Cengage - Wadsworth ...
3_Carbohydrate - WordPress.com
... starches of cereals, roots and tubers, sugars of fruits and milk are examples of carbohydrates. Animal tissues contain glycogen (animal starch). They are the major sources of energy and play key role in many biochemical processes including energy generation. DEFINITION Chemically all the carbohydrat ...
... starches of cereals, roots and tubers, sugars of fruits and milk are examples of carbohydrates. Animal tissues contain glycogen (animal starch). They are the major sources of energy and play key role in many biochemical processes including energy generation. DEFINITION Chemically all the carbohydrat ...
3_carbohydrate - WordPress.com
... starches of cereals, roots and tubers, sugars of fruits and milk are examples of carbohydrates. Animal tissues contain glycogen (animal starch). They are the major sources of energy and play key role in many biochemical processes including energy generation. DEFINITION Chemically all the carbohydrat ...
... starches of cereals, roots and tubers, sugars of fruits and milk are examples of carbohydrates. Animal tissues contain glycogen (animal starch). They are the major sources of energy and play key role in many biochemical processes including energy generation. DEFINITION Chemically all the carbohydrat ...
Chapter 5 Carbohydrates
... Grams of sugars listed on a Nutrition Facts panel include both naturally occurring and added sugars—you need to do some further reading to identify foods that are high in refined sugars. •Read list of ingredients on label—ingredients are listed in order of weight, with the most predominant ingredien ...
... Grams of sugars listed on a Nutrition Facts panel include both naturally occurring and added sugars—you need to do some further reading to identify foods that are high in refined sugars. •Read list of ingredients on label—ingredients are listed in order of weight, with the most predominant ingredien ...
Carbohydrates
... blood glucose levels – Foods with a low glycemic index: • Don’t produce dramatic fluctuations in blood glucose • May increase HDL/LDL ratio (good cholesterol) • Are generally higher in fiber • May reduce the risk of heart disease and colon ...
... blood glucose levels – Foods with a low glycemic index: • Don’t produce dramatic fluctuations in blood glucose • May increase HDL/LDL ratio (good cholesterol) • Are generally higher in fiber • May reduce the risk of heart disease and colon ...
CARBOHYDRATES
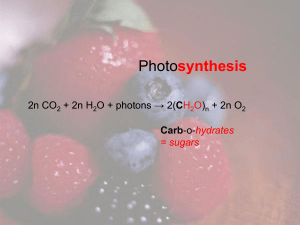
... Glucose is the preferred fuel for many of our cells including our brain and the rest of the nervous system. Carbohydrates (includes fiber) often occur in food (fruits and vegetables) with water, vitamins, minerals, phytochemicals, and no fat. They are also relatively cheap! ...
... Glucose is the preferred fuel for many of our cells including our brain and the rest of the nervous system. Carbohydrates (includes fiber) often occur in food (fruits and vegetables) with water, vitamins, minerals, phytochemicals, and no fat. They are also relatively cheap! ...
Chapter 8: Carbohydrates energy
... Anomers are two stereoisomers of a monosaccharide that differ only at the configuration at C-1 for aldoses and C-2 for ketoses ...
... Anomers are two stereoisomers of a monosaccharide that differ only at the configuration at C-1 for aldoses and C-2 for ketoses ...
Chemdraw B&W
... • Current terminology: natural materials that contain many hydroxyls and other oxygen-containing groups ...
... • Current terminology: natural materials that contain many hydroxyls and other oxygen-containing groups ...
PPT CH 16
... • In order for lactose to be used as an energy source, galactose must be converted to a phosphorylated glucose molecule • When enzymes necessary for this conversion are absent, the genetic disease galactosemia results • People who lack the enzyme lactase (~20%) are unable to digest lactose and have ...
... • In order for lactose to be used as an energy source, galactose must be converted to a phosphorylated glucose molecule • When enzymes necessary for this conversion are absent, the genetic disease galactosemia results • People who lack the enzyme lactase (~20%) are unable to digest lactose and have ...
Chapter 5 Ans
... chemically bonded to glucose to form lactose. When a food label lists sugar as an ingredient, the term refers to sucrose. Human milk tastes sweeter than cow’s milk because it has a higher concentration of lactose. When digestive enzymes break down starch in the mouth, a sweet taste is sensed. This s ...
... chemically bonded to glucose to form lactose. When a food label lists sugar as an ingredient, the term refers to sucrose. Human milk tastes sweeter than cow’s milk because it has a higher concentration of lactose. When digestive enzymes break down starch in the mouth, a sweet taste is sensed. This s ...
Name:
... (n is the number of repeating glucose units and ranges in the 1,000's) Starch is the principal polysaccharide used by plants to store glucose for later use as energy. Plants often store starch in seeds or other specialized organs; for example, common sources of starch include rice, beans, wheat, cor ...
... (n is the number of repeating glucose units and ranges in the 1,000's) Starch is the principal polysaccharide used by plants to store glucose for later use as energy. Plants often store starch in seeds or other specialized organs; for example, common sources of starch include rice, beans, wheat, cor ...
Food chemistry slides
... and lower HDL (good) cholesterol when used instead of cis fatty acids or natural oils. These changes may increase the risk of heart disease. Because there are no standard methods, it's difficult to estimate the TFA content of food items. It's also difficult to estimate intake, especially long-term i ...
... and lower HDL (good) cholesterol when used instead of cis fatty acids or natural oils. These changes may increase the risk of heart disease. Because there are no standard methods, it's difficult to estimate the TFA content of food items. It's also difficult to estimate intake, especially long-term i ...
glucose galactose
... of the polyhydric alcohols and their derivatives In animal cells, this biomolecule serves as an important source of energy for vital activities in the form of glucose and glycogen Some carbohydrates have specific functions ...
... of the polyhydric alcohols and their derivatives In animal cells, this biomolecule serves as an important source of energy for vital activities in the form of glucose and glycogen Some carbohydrates have specific functions ...
Carbohydrates
... • Formula CnH2nOn • One carbon is either an aldehyde or ketone • The suffix ose indicates that the molecule is a carbohydrate • Use prefix to indicate number of carbons tri , tetr, pent, hex • Aldose – contain an aldehyde group • Ketose – contain a ketone group ...
... • Formula CnH2nOn • One carbon is either an aldehyde or ketone • The suffix ose indicates that the molecule is a carbohydrate • Use prefix to indicate number of carbons tri , tetr, pent, hex • Aldose – contain an aldehyde group • Ketose – contain a ketone group ...
Lecture 3 Carbs
... • D-ribose when heated with concentrated HCl yields furfural (commercial route for the production of THF (tetrahydrofuran) • D-glucose under the same conditions yields 5-hydroxymethyl furfural ...
... • D-ribose when heated with concentrated HCl yields furfural (commercial route for the production of THF (tetrahydrofuran) • D-glucose under the same conditions yields 5-hydroxymethyl furfural ...
Sweetened beverage
A sweetened beverage is any beverage with added sugar. They have been described as ""liquid candy."" Consumption of sweetened beverages has been linked to weight gain, obesity, and associated health risks.