Several brain structures contribute to “mind time,”
... splits— some guests converse in the living room in front of the camera, while others repair to the dining room to look at rare books— we sensibly attribute a longer duration to this offscreen episode than the few minutes it takes up in the actual film. Another factor may also contribute to the decel ...
... splits— some guests converse in the living room in front of the camera, while others repair to the dining room to look at rare books— we sensibly attribute a longer duration to this offscreen episode than the few minutes it takes up in the actual film. Another factor may also contribute to the decel ...
Pharmacoresistant Epilepsy: How..!? How to define? How to
... There has been relatively little improvement in AED efficacy since the introduction of phenobarbital in 1912, so that still more than 30% of epilepsy patients are resistant to AEDs with up to 90% with certain types of focal epilepsies. Failure of past drug developments is likely because of a neur ...
... There has been relatively little improvement in AED efficacy since the introduction of phenobarbital in 1912, so that still more than 30% of epilepsy patients are resistant to AEDs with up to 90% with certain types of focal epilepsies. Failure of past drug developments is likely because of a neur ...
∂ u /∂ t = u(x,t) +∫ w(x,y)f(u(y,t)) + I(x) + L(x)
... antennal lobe. The initial work focused on the spatial aspect of odor representation in the honeybee antennal lobe. Two types of models were used for hypothesis testing: a more biophysicallydetailed network of spiking cells, and a more abstract model in the form of an ...
... antennal lobe. The initial work focused on the spatial aspect of odor representation in the honeybee antennal lobe. Two types of models were used for hypothesis testing: a more biophysicallydetailed network of spiking cells, and a more abstract model in the form of an ...
Case Study 55
... neuronal cortical dysplasia within the glioneuronal neoplastic element as well as numerous scattered neurons in the subcortical white matter. This is further confirmed by the reduced synaptophysin staining in the affected regions. Furthermore, the GFAP staining highlights the glial component of the ...
... neuronal cortical dysplasia within the glioneuronal neoplastic element as well as numerous scattered neurons in the subcortical white matter. This is further confirmed by the reduced synaptophysin staining in the affected regions. Furthermore, the GFAP staining highlights the glial component of the ...
Seizure Disorder PowerPoint.2014-02-04
... generalized seizure (partial seizures that spread throughout the brain to become a generalized), implement the response for tonic-clonic seizures. ...
... generalized seizure (partial seizures that spread throughout the brain to become a generalized), implement the response for tonic-clonic seizures. ...
AP Psychology Brain Review- Have A Ball! Learning Target: Identify
... 35. This is made up of the axons of neurons and glial cells and is called white matter - cerebrum 36. This outer layer is made up of the cell bodies of neurons called gray matter - cerebral cortex 37. This area directs messages to the opposite site of the brain - brainstem 38. Damage to one of these ...
... 35. This is made up of the axons of neurons and glial cells and is called white matter - cerebrum 36. This outer layer is made up of the cell bodies of neurons called gray matter - cerebral cortex 37. This area directs messages to the opposite site of the brain - brainstem 38. Damage to one of these ...
Lecture 52-Epilepsy
... of urine or faeces. The clonic phase then begins, with generalized convulsing, frothing at the mouth and bilateral, rhythmic jerking of muscles. This lasts from a few seconds to several minutes. Seizures are usually self-limiting, followed by drowsiness, confusion or coma for several hours. ...
... of urine or faeces. The clonic phase then begins, with generalized convulsing, frothing at the mouth and bilateral, rhythmic jerking of muscles. This lasts from a few seconds to several minutes. Seizures are usually self-limiting, followed by drowsiness, confusion or coma for several hours. ...
L
... secondarily generalized. There are many causes of partial seizures, including head injuries, tumors, infection, and stroke (Table 1). Many people with partial seizures recall having a “warning” or “aura” just prior to losing consciousness. The aura is the simple partial portion of the seizure. As th ...
... secondarily generalized. There are many causes of partial seizures, including head injuries, tumors, infection, and stroke (Table 1). Many people with partial seizures recall having a “warning” or “aura” just prior to losing consciousness. The aura is the simple partial portion of the seizure. As th ...
Occipital Lobe
... other fast moving lights. Scientists are trying to find out the cause of epilepsy by studying the Occipital Lobe. They are also trying to find out how to better treat those with epilepsy. ...
... other fast moving lights. Scientists are trying to find out the cause of epilepsy by studying the Occipital Lobe. They are also trying to find out how to better treat those with epilepsy. ...
Epilepsy and Seizure Mangament
... Epilepsy is also known as a “seizure disorder” A seizure is the physical manifestation of a sudden disruption of orderly communication between neurons in the brain A seizure can take a variety of forms, depending on where the disruption occurs and how far the resulting abnormal electrical activi ...
... Epilepsy is also known as a “seizure disorder” A seizure is the physical manifestation of a sudden disruption of orderly communication between neurons in the brain A seizure can take a variety of forms, depending on where the disruption occurs and how far the resulting abnormal electrical activi ...
Understand why continuous EEG is being requested in certain
... may not need Many of these patients have been on medicine for years for presumed seizures For patients with epilepsy and NES we can minimize medicine by not treating NES with additional epilepsy drugs ...
... may not need Many of these patients have been on medicine for years for presumed seizures For patients with epilepsy and NES we can minimize medicine by not treating NES with additional epilepsy drugs ...
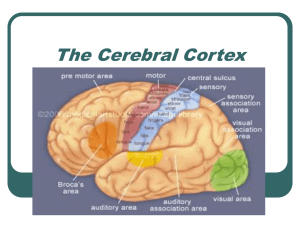
The Cerebral Cortex
... Interprets auditory code Damage to the Wernicke’s Area (Wernicke’s Aphasia): loss of the ability to understand language person can speak clearly, but the words that are put together make no sense. This way of speaking has been called "word salad" because it appears that the words are all mixed up li ...
... Interprets auditory code Damage to the Wernicke’s Area (Wernicke’s Aphasia): loss of the ability to understand language person can speak clearly, but the words that are put together make no sense. This way of speaking has been called "word salad" because it appears that the words are all mixed up li ...
Learning and the Brain - Santa Clara County Office of
... 2. Mid section of your knuckles is your Parietal Lobe. 3. The back part of your fist is the Occipital Lobe 4. The hand part of the fist is the Temporal Lobe. 5. The Cerebellum as at heel of the hand. ...
... 2. Mid section of your knuckles is your Parietal Lobe. 3. The back part of your fist is the Occipital Lobe 4. The hand part of the fist is the Temporal Lobe. 5. The Cerebellum as at heel of the hand. ...
Neurology for Psychiatrists - the Peninsula MRCPsych Course
... Right temporal lobe lesions - interpret nonverbal auditory stimuli (e.g. music) ...
... Right temporal lobe lesions - interpret nonverbal auditory stimuli (e.g. music) ...
Temporal Lobe Function and Dysfunction
... • TLE = Most common form of epilepsy (3-6 per 1000 of the population); ...
... • TLE = Most common form of epilepsy (3-6 per 1000 of the population); ...
what is a seizure? - Patient Focused Neurology!
... "Myo" means "muscle" and a myoclonic jerk is a brief, shock-like jerk of a group of muscles. People who do not have epilepsy may experience a jerk like this while falling asleep. That's considered normal. Myoclonic seizures in epilepsy involve sudden jerks of the arms, shoulders, neck, body, or uppe ...
... "Myo" means "muscle" and a myoclonic jerk is a brief, shock-like jerk of a group of muscles. People who do not have epilepsy may experience a jerk like this while falling asleep. That's considered normal. Myoclonic seizures in epilepsy involve sudden jerks of the arms, shoulders, neck, body, or uppe ...
WHAT IS A SEIZURE?
... "Myo" means "muscle" and a myoclonic jerk is a brief, shock-like jerk of a group of muscles. People who do not have epilepsy may experience a jerk like this while falling asleep. That's considered normal. Myoclonic seizures in epilepsy involve sudden jerks of the arms, shoulders, neck, body, or uppe ...
... "Myo" means "muscle" and a myoclonic jerk is a brief, shock-like jerk of a group of muscles. People who do not have epilepsy may experience a jerk like this while falling asleep. That's considered normal. Myoclonic seizures in epilepsy involve sudden jerks of the arms, shoulders, neck, body, or uppe ...
Document
... extremely serious. It is fatal in one in ten cases and in one in seven survivors is left with severe handicap, such as deafness or brain injury. The bacteria that causes both meningococcal and and pneummococcal meningitis are vary common and live in the back of the nose and throat. People of any age ...
... extremely serious. It is fatal in one in ten cases and in one in seven survivors is left with severe handicap, such as deafness or brain injury. The bacteria that causes both meningococcal and and pneummococcal meningitis are vary common and live in the back of the nose and throat. People of any age ...
Brain Sturcture and Function
... The Cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain. Its is also known to be associated with higher brain functions such as thought and action. It is divided into 4 lobes. These are called: ...
... The Cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain. Its is also known to be associated with higher brain functions such as thought and action. It is divided into 4 lobes. These are called: ...
Pathophysiology of Epilepsy
... The Hippocampal Model In sections from epileptic areas, neurons from specific regions (CA1) are lost or damaged Synaptic reorganization (mossy fiber sprouting) causes recurrent hyperexcitability Variety of brain insults can lead to the phenomena of mossy fiber sprouting ...
... The Hippocampal Model In sections from epileptic areas, neurons from specific regions (CA1) are lost or damaged Synaptic reorganization (mossy fiber sprouting) causes recurrent hyperexcitability Variety of brain insults can lead to the phenomena of mossy fiber sprouting ...
Neuroanatomy 18 [4-20
... 34. How can a febrile seizure cause temporal lobe epilepsy? How does it develop in time? Complex febrile seizure (longer than 15 minutes or multiple in a day) cause medial temporal sclerosis or hippocampal sclerosis Latent period of up to a few years before onset of complex partial seizures 35. ...
... 34. How can a febrile seizure cause temporal lobe epilepsy? How does it develop in time? Complex febrile seizure (longer than 15 minutes or multiple in a day) cause medial temporal sclerosis or hippocampal sclerosis Latent period of up to a few years before onset of complex partial seizures 35. ...
Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders
... smells, sights, tastes Forced thinking Physical sensations – nausea, headaches, dizziness Unusual feelings ...
... smells, sights, tastes Forced thinking Physical sensations – nausea, headaches, dizziness Unusual feelings ...
What is a Seizure?
... quickly, causing an “electrical storm”. These uncontrolled electrical impulses can cause a change in awareness or movement. There are over 20 different types of seizures. Some seizures cause people to shake, fall or have convulsions. Other seizures involve staring, confusion, muscle spasms, aiml ...
... quickly, causing an “electrical storm”. These uncontrolled electrical impulses can cause a change in awareness or movement. There are over 20 different types of seizures. Some seizures cause people to shake, fall or have convulsions. Other seizures involve staring, confusion, muscle spasms, aiml ...
Temporal lobe epilepsy
Temporal lobe epilepsy is a chronic neurological condition characterized by recurrent, unprovoked epileptic seizures (epilepsy) which originate in the temporal lobe of the brain. The seizures involve sensory changes; for example, smelling an unusual odor that is not there (an olfactory illusion), or a memory disturbance. The most common cause is mesial temporal sclerosis. Treatment is through medication or surgery and prognosis is variable.