* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 17: Transcription, RNA Processing, and Translation
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Hammerhead ribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
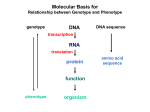
Chapter 17: Transcription, RNA Processing, and Translation Text Vocabulary: RNA Polymerases Template Strand Coding Strand Initiation Sigma Holoenzyme Core Enzyme Promoters Downstream Upstream Elongation Termination TATA box Basal Transcription Factors Poly(A) Signal Primary Transcript Pre-mRNA Exons Introns Splicing Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) Spliceosome Poly(A) tail RNA Processing Ribosomes Polyribosome Transfer RNA (tRNA) Anticodon Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases Aminoacyl-tRNA Wobble Hypothesis Ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) Shine-Dalgarno Sequence Initiation Factors Translocation Elongation Factors Release Factor Molecular Chaperones Lecture 22 “Transcription of Genes: Production of RNA” Review: 1.) What is the function of RNA Polymerase? What is the template strand and what is the coding strand? What direction does RNA Polymerase perform its template-directed synthesis (strand polarity here)? 2.) Does RNA Polymerase require a primer? What is the name for the region of DNA that RNA Polymerases interact with during transcription initiation? 3.) What are the components that make up the bacterial RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme? What is the function of each component? 4.) What is the significance of the -35 box, -10 box, and +1 box? In bacteria, what component of the RNA Polymerase holoenzyme interacts with the DNA initially during transcription initiation? Where does the component bind and how is this assisting the RNA Pol core enzyme? 5.) Once the holoenzyme is bound to the DNA, what change must occur in the DNA helix in order for RNA Pol to transcribe a single RNA strand? What enzyme causes this change? 6.) Is the reaction catalyzed by RNA Polymerase exergonic or endergonic? Why? 7.) What is the step that ends initiation? What is the name of the second step? What is happening during this step?(—think about what the RNA Pol is physically doing during this step) 8.) What is the final step in bacterial transcription? What causes this to occur? What happens to the orientation of the RNA molecule immediately after this final step? 9.) What is the RNA Polymerase that transcribes protein-coding genes in eukaryotes? How does the promoter sequence differ in eukaryotes compared to bacteria? What proteins in eukaryotes serve the same function as sigma factor did for bacteria? How does termination of eukaryotic protein-coding genes differ from bacteria? 10.) What are exons? What are introns? Does the primary RNA transcript contain both exons and introns? 11.) What are the proteins that make up the spliceosome? What is the function of the spliceosome? 12.) During RNA processing, what must occur to the 5’ end and the 3’ ends of the RNA transcript? What is the function of both of these processing steps? Lecture 23 “Translation of mRNA: Protein Synthesis & Post Translation Modifications” Review: 1.) What is the site of translation in both eukaryotes and bacteria? What does it mean to say that transcription and translation are tightly coupled? Are they coupled in both bacteria and eukaryotes? Explain why. 2.) What is the function of a polyribosome? 3.) What facilitates the interaction between amino acids and mRNA in ribosomes? Within the ‘facilitator’, what type of structure does the AA interact with? What does the mRNA interact with? Think back to RNAs with tertiary structure. 4.) What catalyzes the addition of amino acids to the tRNA? How is the molecule able to do this? (What within its structure allows it and what is it recognizing). 5.) What is the term used to describe a tRNA molecule covalently linked to an AA? 6.) What is the wobble hypothesis? What paradox does it resolve? 7.) Where in the cell are ribosomes assembled? What are the substructures of the ribosomes and what are their basic functions? 8.) What are the three sites in ribosomes that tRNA occupies during translation? What are the basic interactions occurring at each? 9.) What are the steps of translation initiation (from the PPT)? 10.) What are the steps of translation elongation? 11.) What type of enzyme is a ribosome? What part(s) of the ribosome is/are composed of rRNA? 12.) What are the steps in translation termination? 13.) What is the primary difference between the release factor and the aminoacyl tRNA that bind before it? How does the binding of the release factor cause the separation of the polypeptide from the ribosome? 14.) What is the function of a molecular chaperone? 15.) Why might a protein need to undergo a post-translational modification? What are the 4 posttranslational modifications that were discussed in lecture? **I don’t know yet whether or not Dr. Kerscher’s sumoylation material will be on test.