* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit1continetaldrift 3.40MB 2017-03-29 12:41:28
Survey
Document related concepts
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
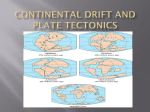
Unit 1: Physical Environments 1.1 Earth Systems – The Earth’s crust is part of a dynamic system. Continental Drift: Continental drift is the theory that the continental landmasses have changed position over time, attributed to Alfred Wegener (A German meteorologist) in 1912. The evidence for this movement falls into three categories – Geological / Biological / Climatological. Evidence for Continental Drift: Geological: The “fit” of the continents – similar to a jigsaw. o comparing continents either side of the Atlantic – South America and Africa o Especially when using the edges of the continental shelves rather than present coastline. Rock types / structures are similar on the two sides of the Atlantic. o Sequence of sedimentary and igneous rocks from the Appalachian Mountains of North America match the Caledonian Mountains of Scotland. o Ancient Shield Mountains can be traced from East Brazil to West Africa. Biological: Fossils found in South America and West Africa, suggests these continents were once together. o Mesosaurus – a small freshwater reptile o Glossopteris – small fern o Cynagnathus – Triassic reptile Plant / animal species diversification. o Mammals found in South America, Africa and Australia are uniquely different – developed under different circumstances – continental drift. o As continents join – the Americas – species of plants / animals shared. Climatological: Coal / Oil found in Antarctica Glacial characteristics in warm regions o Glacial striations in Brazil match those in West Africa. o Glacial deposits in India, South America and the Vaal Valley in South Africa are similar. Students Notes – Lesson 1 Plate Tectonics: As Wegener developed his ideas on the movement of continents it became clear that about 300 million years ago the continents were a single landmass called Pangaea. Over the next 100 million years this landmass drifted apart forming two distinct regions: Laurasia – In the Northern Hemisphere, made up of Eurasia and North America Gondwanaland – In the Southern Hemisphere, made up of Africa, Australasia, India, South America and Antarctica. See clip on Pangaea – Make annotated diagram/s on Pangaea and movement. http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a000000/a000000/a000073/a000073.mpg http://whs.moodledo.co.uk/file.php/1365/EarthSystems/Earth%20Systems/The%20Break-up%20of%20Pangaea.swf http://whs.moodledo.co.uk/file.php/1365/EarthSystems/Earth%20Systems/The%20Break%20up%20of%20Pangaea.swf Wegener’s studies eventually led to the formulation of the PLATE TECTONIC theory. This states that the Earth’s crust is not a continuous skin but a series of rigid, spherical caps about 100km thick. Of these seven are very large and five carry continents. See diagram A on the next sheet. The plates ride on a weak, soft, partially upper mantle. The main evidence to support this idea comes from investigations into sea-floor spreading, which is occurring in the Atlantic Ocean. Palaeomagnetism of the basalts. o When magma solidifies the iron particles are orientated to magnetic north. o The North & South Poles move considerably during geological time – even reversing. o This is known as Polar Wandering. o The pattern of magnetism is reflected either side of the Atlantic Ridge, and relates to the alternating pattern of Northerly & Southerly magnetism. o http://whs.moodledo.co.uk/file.php/1365/EarthSystems/Earth%20Sys tems/Magnetic%20Reversal.swf Age of rocks on the sea-floor. o Near the mid-Atlantic ridge the basaltic rocks of the sea floor are much younger than those found towards the continental shelves at the edge of the ocean. o The age of the rocks either side of the mid-Atlantic ridge mirror each other, suggesting they were once touching. Diagram A