* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells: The Basic Unit of Life
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
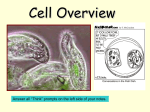
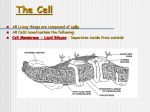
Cells: The Basic Unit of Life Cells, the most basic unit of a living thing, were discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke. Hooke contributed greatly to The Cell Theory. The Cell Theory 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the most basic unit of life in all living things. 3. All cells come from existing cells. Cells can be found living alone or grouped with other cells: Unicellular: made of a single cell. Must carry out all functions needed to survive in one cell. Multicellular: made of many cells. Are able to have groups of cells that specialize for certain functions (muscle, nerves, etc) Some cells are simpler in structure than other cells. Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells No Nucleus Nucleus No membrane-covered organelles Membrane-covered organelles Circular DNA Linear DNA Bacteria All cells other than bacteria Cells have many components called organelles that enable the cell to live, grow, & reproduce. Cytoplasm: cellular fluid surrounding a cell’s organelles Cell Membrane: phospholipid barrier that controls what enters & exits a cell Cell Wall: provides strength & support to the cell membrane in a plant cell and bacterial cell. Plant cell walls are made from cellulose. Nucleus: stores the cell’s DNA which stores the information for how to make proteins. Ribosome: small organelles that make proteins from amino acids Endoplasmic Reticulum: makes lipids & breaks down drugs and other chemicals. Mitochondria: makes the ATP through cellular respiration that the cell uses for energy. Chloroplast: found in plants & algae, this organelle takes the energy from sunlight and is used to make sugar through the process of photosynthesis Golgi Complex: modifies & packages lipids & proteins for export from the cell. Vacuole: large chamber to store water while supporting the cell in plant cells Lysosome: digest food particles, wastes, cell parts, & foreign invaders Types of Cells Eukaryotic/Plant Prokaryotic/Bacteria Eukaryotic/Animal