* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure and Function of Cells – Glossary
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
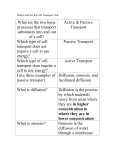
Structure and Function of Cells – Glossary Alcohol gas that makes dough rise during baking, Antibiotic unicellular fungus used in baking and brewing Bacteria mesh of cellulose fibres that surrounds and supports a plant Carbon Dioxide product of anaerobic respiration used as an alternative fuel Cell Membrane spherical structure that controls cellular activities Cell Wall sugar from cereal grains used in the brewing of beer Chloroplast the first antibiotic to be isolated and used to fight disease Cytoplasm thin layer that controls entry and exit of materials into and out of the cell Fermentation unicellular organism used for making yoghurt Lactic Acid process on which wine and beer making depend Lactose describes a microbe that is neither inhibited nor killed by a certain antibiotic Maltose describes a microbe that is inhibited by a certain antibiotic Nucleus jelly-like material in which biochemical reactions occur in a living cell Penicillin sugar in milk acted on by yoghurt forming bacteria Resistant large sac like structure in a plant cell that regulates water content of the cell Sensitive Chemical substance produced by bacterial action on lactose Vacuole general name for a substance formed by one micro-organism that inhibits the growth of other micro-organisms. Yeast discus- shaped structure containing chlorophyll for photosynthesis. Diffusion and Osmosis- Glossary Concentration Gradient structure that allows rapid passage through it of small molecules ( eg. water) but not large molecules Contractile Vacuole term used to describe a solution with a higher water concentration than a comparable solution Diffusion term used to describe a solution with a lower water concentration than a comparable solution Flaccid term used to describe two solutions that are of equal water concentrations Freely Permeable the difference in concentration that exists between two regions, resulting in diffusion Hypertonic structure used by unicellular animal to remove excess water gained by osmosis Hypotonic shrinkage of plant cells contents away from cell walls as a result of excessive water loss Isotonic term used to describe a structure that allows rapid passage through of all molecules in a solution Osmosis term used to describe a plant cell swollen with water taken in by osmosis Plasmolysis term used to describe a plant cell that has lost water by osmosis and become soft Selectively Permeable Membrane movement of molecules of a substance from high to low concentration Turgid process of increased movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane to a more concentrated solution.