* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Possible Next Steps –S1 Cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
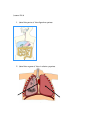
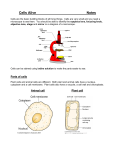
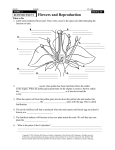
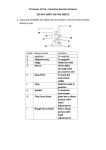
Next Steps Lesson 1 1. Label parts A-C C A E E y e p ie c e B 2. Complete the following table Magnification of Magnification of Total eyepiece lens objective lens magnification of microscope Low power 10 X 4X (a) Medium power 10 X 10 X (b) High power 10 X 40 X (c) 3. How do you work out the total magnification of the object you place under the microscope? Lesson 2 1. Label the parts of the animal cell. Lesson 3 1. Complete the description function using the words below Cell Structure Description/Function Nucleus Contains _____________ information and controls cell activities Cell membrane Forms the thin, outer layer of animal cells and controls _____ and ______ of materials Cytoplasm Jelly-like material, site of __________ reactions Cell Wall The outer layer of all plants cells which is made of cellulose and helps ________the cell. Vacuole Membrane bounded ___which ________ a solution of water, salts and sugars and helps support the cell Chloroplasts Makes food using _____energy in the process of ___________ Wordbank entry, chemical, support, photosynthesis, stores, genetic, light, sac, exit 2. Label parts A-F A B C D E F Structure and Function of Plant and Animal Cells Draw an arrow to match the correct structure to function Structure Function Cell wall controls the activities of the cell Vacuole contains chlorophyll for photosynthesis Cytoplasm controls what can get in and out of the cell Nucleus gives plant cells support and shape Chloroplasts store full of plant cell sap Cell membrane jelly like substance where all the chemical reactions happen 2. In each box place a tick if the structure is present or a cross if the structure is not present in each type of cell Structure Plant cell Animal cell nucleus cell wall cell membrane chloroplast vacuole cytoplasm Lesson 4 1. Match the cell type below to the correct structure and function Cell type Specialised structural feature Streamline shape with a tail Function Biconcave shape giving a large surface area To transport oxygen to the body cells Long thin fibres To carry a message from one part of the body to another Long extended cell with a large surface area Absorbs the water from the soil Swim in a fluid to fertilise female egg Columnar shaped cells Absorbs sunlight to be containing chloroplasts used in photosynthesis Box-like shape allowing Protection cells to fit together like a brick wall. Long thin shape with pointed ends To allow the cells to slide over each other easily when the muscles contract and relax palisade cell, nerve cell, sperm cell, epidermal cell, red blood cell, muscle cell, root hair Lesson 5 & 6 1. Label the parts of the digestive system F A B E C 2. Label the organs of the circulatory system Lesson 7 1. What is the definition of fertilisation? 2. What is the scientific name for a sex cell? 2. What is the female sex cell called? 3. What is the male sex cell called? 4. Where are sperm produced? 5. Where are eggs/ovum produced? 6. What is formed when an egg joins with a sperm? 7. Where does fertilisation take place? 8. The onset of puberty in males is between the ages of _______ and females between the ages of ________ 9. Label the parts of the male and female reproductive system Lesson 8 & 9 1. Beginning with puberty, put the rest of the steps of the human life cycle below in the correct order . 1. Puberty 2. Sexual Intercourse 3. Growth of the child 4. Pregnancy 5. Male – sperm produced by testes/ Female – egg released by ovary 6. Birth 7. Fertilisation 1. Puberty___________ 2. _________________ 3. _________________ 4. _________________ 5. _________________ 6. _________________ 7. _________________ 2. Read the paragraph and fill in the blanks using the wordbank below. Human pregnancy lasts ______ months, these are divided into the first, second and third trimesters. During the time of development, the fertilised egg becomes an ________ in the first trimester, then a_________, then finally becoming a ______ at birth. Know that the _________ becomes fully developed in the first trimester of pregnancy. The placenta is an organ attached to the _______ _______ that transfers food and _______ to the growing embryo from the mother’s blood. The placenta connects to the foetus via the________________. The placenta controls the movement of __________ into and out of the foetus and produces essential_________. Wordbank baby, substances, embryo, umbilical cord, hormones, placenta, nine, uterus wall, oxygen, foetus. Lesson 11 1. Label the parts of the flower A Label parts A-F of the flower: B A: B: C: D: E: F: C F D E 2. Fill in the correct structure and functions Part Function petals Where pollen grains land sepal Produces the male gametes ovary Lesson 12 & 13 1. Fill in the blanks using the statements below Part of plant wind Petals Petals small and green Pollen grains Small, light pollen Scent No scent Anther Stigma insect Found inside the plant Feathery and hangs outside plant Statements Sticky and is found inside the plant Large and brightly coloured Scented Hang outside the plant Sticky, spiky pollen 2. Complete the following table Part of seed function Seed coat Grows into new plant Food store 3.What is the name given to the growth of a seed into a new plant