* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grade 9 Light-emitting diode
Survey
Document related concepts
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Manchester Mark 1 wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
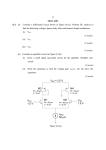
Educator and Tagging Information Learning Area: Technology Resource Name: Technology Assessment Exemplar Number: TECHN9.109 Item/s: 1 Phase: Senior Phase Grade: 9 Tags: Technology, systems and control, electrical systems, electronic circuits, output, input, light-emitting diode, LED, anode, cathode, circuit symbol, barrier potential, advantages, forward-biased, reversebiased, resistors, drawing, worksheet, Formative Assessment Assessment Type: Formative Assessment Form/s: Drawing, worksheet Copyright for included material: N/A Duration: 60 min Learning Outcome(s) and Assessment Standard(s): Learning Outcome 1: Technological Processes and Skills The learner will be able to apply technological processes and skills ethically and responsibly using appropriate information and communication technology. Assessment Standards We know this when the learner 5 Communicates 5.1 Presents ideas (in a project portfolio) using formal drawing techniques, in two-dimensional or three-dimensional sketches, circuit diagrams or systems diagrams that include all of the following features: Use of South African conventional drawing standards (e.g. scale, outline, dimension lines, first and third angle projection); Notes to clarify design reasoning and key choices; Impressive enhancements of significant sketches (e.g. colour, texture, shade, thick and thin lines, shadow). Learning Outcome 2: Technological Knowledge and Understanding The learner will be able to understand and apply relevant technological knowledge ethically and responsibly. Assessment Standards We know this when the learner 3 Systems and Control 3.2 Demonstrates knowledge and understanding of how simple electronic circuits and devices are used to make an output respond to an input signal (e.g. resistors, light-emitting diodes, transistors, push or magnetic switches, thermistors, light-dependent resistors). Learning Space: Assessment Hyperlinks: To be completed later. Rating: Number of questions for exemplar: 1 Easy questions: Medium questions: Question 1 Difficult questions: Assessment Task Light-emitting diode (LED) 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 How do you determine the anode and cathode of an LED? [2 marks] Draw the circuit symbol for an LED. [2 marks] What is meant by the barrier potential of an LED? [1 mark] Name four advantages to the use of LEDs. [4 marks] Look at the two circuits below. Identify the circuit which is forward-biased and the circuit which is reverse-biased. [2 marks] i. ii. 1.6 1.7 Why is it advisable to use a fixed resistor with an LED? [1 mark] Which of the following resistors are more suitable to use with an LED if there is a supply voltage greater than 3V: 180Ω or 230Ω? [1 mark] Give two examples of where we could find LEDs in our everyday lives. [2 marks] [15 marks] 1.8 Suggested Solutions Question number 1. Possible marks 2 marks Answers 1.1 The anode is positive and has a longer lead than the cathode. The cathode also has a ‘flat’ side on the rim of the lens. 2 marks 1.2 1 mark 4 marks 1 mark 1 mark 1.3 The barrier potential is the minimum voltage with which an LED will light up. 1.4 It only needs a small current to function. It will function at a low voltage, as long as the voltage is more than the barrier potential. It is very robust; they do not break when dropped. It lasts a very long time . i. reversed-biased 1 mark ii. forward-biased 2 marks 1.6 An LED’s function is destroyed by heavy currents. A fixed resistor will help to protect the LED against the current. 1.7 180Ω 1.8 Traffic lights, pilot lights in TVs, radios, computers, remotes etc. Learners might have other answers. [15 marks] Appendix of Assessment Tools 1 mark 1.5