* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 25.
Survey
Document related concepts
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative comparative linguistics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Maximum parsimony (phylogenetics) wikipedia , lookup
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
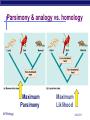
Chapter 25. Phylogeny & Systematics AP Biology An unexpected family tree. What are the evolutionary relationships among a human, a mushroom, and a tulip? Molecular systematics has revealed that— despite appearances—animals, including humans, and fungi, such as mushrooms, are more closely related to each other than either are to plants. 4/30/2017 Building phylogenies Morphological & molecular homologies similarities based on shared ancestries bone structure DNA sequences beware of analogous structures convergent evolution “Homoplasies” AP Biology marsupial mole 4/30/2017 placental mole Evaluating molecular homologies Aligning DNA sequences more bases in common = more closely related analyzed by software AP Biology beware of molecular homologies 4/30/2017 Orthologous genes Common genes: differences due to speciation; diverged after a speciation event AP Biology 4/30/2017 Paralogous Genes Common genes; differences due to a duplication event Examples: next page AP Biology 4/30/2017 Ortho/Para Genes example: AP Biology 4/30/2017 Building trees Connection between classification & phylogeny Tracing possible evolutionary relationships between some of the taxa of the order Carnivora, a branch of the AP Biology class Mammalia. 4/30/2017 Illustrating phylogeny Cladograms patterns of shared characteristics Classify organisms according to the order in time at which branches arise along a phylogenetic tree AP Biology 4/30/2017 Illustrating phylogeny Cladograms patterns of shared characteristics Shared Primitive Character AP Biology 4/30/2017 Illustrating phylogeny Cladograms patterns of shared characteristics Shared Derived Character AP Biology 4/30/2017 Parsimony & analogy vs. homology Phylogenetic trees are hypotheses Which is the most parsimonious tree? AP Biology 4/30/2017 Parsimony & analogy vs. homology Maximum Parsimony AP Biology Maximum Liklihood 4/30/2017 Modern Systematics Shaking up some trees! Crocodiles are now thought to be closer to birds than other reptiles AP Biology 4/30/2017 Molecular clocks Trace variations in genomes to date evolutionary changes HIV-1M samples were collected from patients between early 1980s & late 1990s. The gene evolved at a relatively constant rate. Concluded that HIV-1M strain first infected humans in 1930s. Rate of change is calculated and then extrapolate back What does this assume? AP Biology 4/30/2017 Trees: Phylogram (Primates) AP Biology 4/30/2017 Tree: Phylogram (Giraffe species) AP Biology 4/30/2017 Tree: Ultrametric AP Biology 4/30/2017 Universal Tree of Life 3 Domains Bacteria Eukarya Archaea AP Biology 4/30/2017