* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Part III – the workshop
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Electronic musical instrument wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
National Electrical Code wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
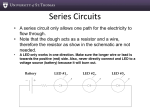
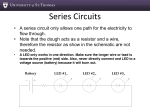
Part III – The Workshop I. Identifying basic TOOLS and EQUIPMENT for circuit work 1. This is a zippered carry case containing the basic electronic tool kit for both – the electronics professional or hobbiest. Label the picture with the expressions from the box. wire cutters multimeter long nose pliers wire strippers proto board screwdriver 2. Match the items on the left with the definitions on the right. TOOL / INSTRUMENT Long nose pliers IS / ARE Wire strippers USED TO Wire cutters Soldering iron Multimeter © Marija Šubic, prof. USE measure voltage, current and resistance. solder the components to a printed circuit board. cut wire to a particular length. strip the end of wire, removing the insulation part, leaving the copper. hold wire while it is been cut or to hold small components. PROJEKTNI TEDEN Part III II. Identifying ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS 1. Label the pictures with the expressions from the box. diode transistor resistor capacitor LED diode 2. Complete the definitions of electronic components. a. A …………………………… is a semiconductor device which amplifies current. b. A …………………………… is a two-terminal component which restricts the flow of current. c. A …………………………… is a passive electronic component which stores electric charge. d. A ……………………...…… is a device which only allows current to flow in one direction. e. A ……………………...…… is a transducer which converts electrical energy to light. 3. QUIZ – Resistor colour code http://www.funtrivia.com/playquiz/quiz2664721e821c8.html The Resistor Colour Code Colour Number BLACK 0 BROWN 1 RED 2 ORANGE 3 YELLOW 4 GREEN 5 BLUE 6 VIOLET 7 GREY 8 WHITE 9 © Marija Šubic, prof. PROJEKTNI TEDEN Part III III. SOLDERING 1. Definition Soldering is a process in which two or more metal items are joined together by melting and flowing a filler metal (solder) into the joint. 2. Tools Label the picture → soldering iron soldering iron stand sponge wire strippers switch 3. How to solder a. Complete the SOLDERING GUIDE (the first letter of the word may help you). 4. Interactive exercise - Soldering © Marija Šubic, prof. http://www2.arnes.si/~sspmsubi/soldering2.htm PROJEKTNI TEDEN Part III IV. Creating MY FIRST IC 1. Below is a picture of a solderless breadboard ZY-204 with the attached components. You created this IC during your workshop. a. Label the picture with the following expressions: resistor, LED diode, proto board, microchip, switch b. Draw the diagram of your IC. ↓ 2. Below are the diagrams of the first integrated circuit (pic. in Part I) created by Jack Kilby. a. Label the picture on the left with components and compare Kilby’s IC and diagram to yours. Use and / but / however. Source: http://www.google.com/patents/about?id=O89pAAAAEBAJ&dq © Marija Šubic, prof. PROJEKTNI TEDEN Part III 3. Series circuit or parallel circuit? Circuits are generally very complex combinations of series and parallel circuits. Have the components in your circuit been connected in series (along a single path, so the same current flows through all the components) or in parallel (the same voltage is applied to each component)? Answer: ________________________________________________________________ Think of a string of Christmas lights. If any of the bulbs is missing or burned out, no current will flow and none of the lights will go on. Which circuit has been used – series or parallel? 4. HOMEWORK Write a short report how you created your IC (tools, components and functioning). Interactive exercise - Electronic components and symbols http://www2.arnes.si/~sspmsubi/ELSYMBOLS.htm *V. IC e-DICTIONARY Create a Slovene – English e-Dictionary. © Marija Šubic, prof. PROJEKTNI TEDEN Part III