* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch8
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
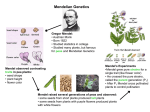
BIOLOGY Ch -8 notes MENDEL AND HEREDITY Heredity – Genetics – Mendel worked with the Pea plant – Useful Features in Peas: Several traits of the garden pea exist in two clearly different forms. 1. The flower color is either purple or white— there are no intermediate forms. Table 1 shows the seven traits that Mendel chose to study. 2. The male and female reproductive parts of garden peas are enclosed within the same flower. You can control mating by allowing a flower to fertilize itself (self-fertilization), or you can transfer the pollen to another flower on a different plant (crosspollination). 3. The garden pea is small, grows easily, matures quickly, and produces many offspring. Thus, results can be obtained quickly, and there are plenty of subjects to count. The Seven Traits Mendel Studied and Their Contrasting Forms: 1 MONOHYBRID CROSS – True Breeding – Three steps of Mendel’s experiments: Draw figure ___ 2 MENDEL’s HYPOTHESIS 1. For each inherited trait, an individual has two copies of the gene—one from each parent. 2. There are alternative versions of genes. For example, the gene for flower color in peas can exist in a “purple” version or a “white” version. Today the different versions of a gene are called its ____________ 3. When two different alleles occur together, one of them may be completely expressed, while the other may have no observable effect on the organism’s appearance. Mendel described the expressed form of the trait as __________________. The trait that was not expressed when the dominant form of the trait was present was described as _____________ 4. When gametes are formed, the alleles for each gene in an individual separate independently of one another. Thus, gametes carry only one allele for each inherited trait. When gametes unite during fertilization, each gamete contributes one allele. Homozygous – Heterozygous – Genotype – Phenotype – Dominant trait Recessive trait THE LAWS OF HEREDITY The Law of segregation – 3 The Law of independent assortment – Studying heredity: PUNNETT SQUARES One pair of contrasting traits: Monohybrid Cross –homozygous plants Monohybrid Cross –heterozygous plants 4 TEST CROSS - Probability- Pedigree- Autosomal trait- Sex linked trait - Two pairs of contrasting traits: DIHYBRID CROSS 5 COMPLEX PATTERNS OF HEREDITY Polygenic trait Incomplete dominance Multiple alleles Codominance Traits influenced by the environment 6 GENETIC DISORDER DOMINANT OR RECESSIVE SYMPTOMS Sickle cell anemia Hypercholesterolemia Tay Sachs disease Cystic fibrosis Hemophilia A Huntington's disease GENE THERAPY 7