* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Cell unit
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
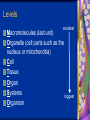
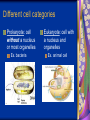
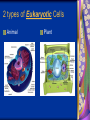
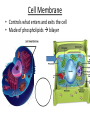
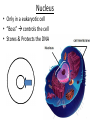
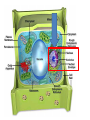
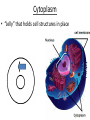
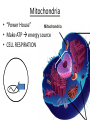
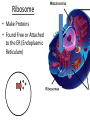
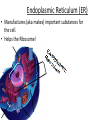
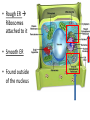
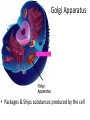
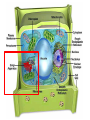
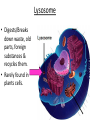
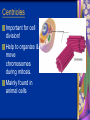
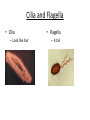
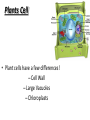
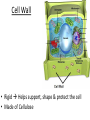
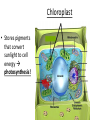
Chapter 7: Cell Structure & Function 7.1 & 7.2 Discovering the Cell For a long time, we didn’t know cells existed. They were too small to see with the naked eye! What invention changed this? Discovering the Cell The invention of the microscope changed how we look at living things We use a compound light microscope. Can see the Cell Membrane & Nucleus Can not study internal structures of organelles Electron Microscope Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke: saw a honeycomb structure when examining cork under the microscope Named these structures cells, meaning “storage rooms” Discovery of the cell Van Leeuwenhoek Observed microorganisms in pond water, tooth scrapings, and saliva Cell Theory Three parts Cells are the smallest/basic units of life All living things are made up of cells All cells come from preexisting cells http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-wackyhistory-of-cell-theory Levels smallest Macromolecules (last unit) Organelle (cell parts such as the nucleus or mitochondria) Cell Tissue Organ Systems biggest Organism Different cell categories Prokaryote: cell without a nucleus or most organelles Ex. bacteria Eukaryote: cell with a nucleus and organelles Ex. animal cell 2 types of Eukaryotic Cells Animal Plant Cell Membrane • Controls what enters and exits the cell • Made of phospholipids bilayer Nucleus • Only in a eukaryotic cell • “Boss” controls the cell • Stores & Protects the DNA Cytoplasm • “Jelly” that holds cell structures in place Mitochondria • “Power House” • Make ATP energy source • CELL RESPIRATION Cell Respiration Converts chemical energy in food to usable energy in the form of ATP Ribosome • Make Proteins • Found Free or Attached to the ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum) Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • Manufactures (aka makes) important substances for the cell. • Helps the Ribosome! • Rough ER Ribosomes attached to it • Smooth ER • Found outside of the nucleus Golgi Apparatus • Packages & Ships substances produced by the cell Lysosome • Digests/Breaks down waste, old parts, foreign substances & recycles them. • Rarely found in plants cells. Centrioles Important for cell division! Help to organize & move chromosomes during mitosis. Mainly found in animal cells Cilia and Flagella • Cilia – Look like hair • Flagella – A tail Plants Cell • Plant cells have a few differences! – Cell Wall – Large Vacuoles – Chloroplasts Cell Wall • Rigid Helps support, shape & protect the cell • Made of Cellulose Vacuole • Fluid filled sac • Stores enzymes, waste, & water • Also found in animal cells but they are much smaller Chloroplast • Stores pigments that convert sunlight to cell energy photosynthesis!