* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NAME: CHAPTER 14 – THE CIVIL WAR (DISCUSSION POINTS
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
Photographers of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Forts Jackson and St. Philip wikipedia , lookup
Fort Washington Park wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Donelson wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Big Bethel wikipedia , lookup
Missouri secession wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Fort Monroe wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fort Stanton (Washington, D.C.) wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Fort Pulaski wikipedia , lookup
Galvanized Yankees wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Jubal Early wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Henry wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hatteras Inlet Batteries wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
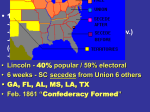
NAME: ________________________________________________________________________ CHAPTER 14 – THE CIVIL WAR (DISCUSSION POINTS) CHAPTER INTRODUCTION *A young nation once so full of promise now faced its most daunting challenge ever. *The romantic vision of America's great national destiny had at this point ceased to be a unifying force among all Americans. *The United States was beginning to embark on a downhill slide into domestic chaos and war. If the decades of the 1840s and 1850s had proven to be divisive and complicated, the 1860s had more to offer on a more grand scale. The election of Abraham Lincoln was the so-called nail in the coffin. Once and for all the south would give up its call to compromise, put down the pen, and pick up the sword. THE SECESSION CRISIS *A surge of nationalism among Southerners spread like wildfire soon after the news of Abraham Lincoln's victory had become national knowledge. Known as the “fire-eaters,” Southern nationalists began to prepare for secession. *South Carolina, long a hotbed of southern separatism, seceded first. On December 20, 1860, South Carolina's special convention voted unanimously to withdraw from the Union. *By the time Abraham Lincoln took office, six other states (so 7 in all) had seceded. *These states included Mississippi (January 9, 1861), Florida (January 10, 1861), Alabama (January 11, 1861), Georgia (January 19, 1861), Louisiana (January 26, 1861), and Texas (February 1, 1861). *Representatives from all seven of these states met in Montgomery Alabama to form the new Confederate states of America in February of 1861. Almost immediately the Confederacy stopped at nothing to take control of federal property inclusive of forts, arsenals, and government offices within their boundaries. *South Carolina sent commissioners to Washington DC to ask for the peaceful surrender of Fort Sumter. However, Pres. Buchanan refused to give it up. When an unarmed merchant ship was sent by the government of the United States of America to supply Fort Sumter with additional troops and supplies it was fired upon by Confederate gunmen onshore. *Obviously, the Fort Sumter incident was an act of war. However, Pres. Buchanan still worked to come up with a compromise with the South. THE FAILURE OF COMPROMISE *Kentucky Sen. John J. Crittenden submitted a new compromise. *This compromise called for several constitutional amendments, which would guarantee the permanent existence of slavery in the slave states and would satisfy Southern demands on such issues as fugitive slaves and slavery in the District of Columbia. Crittenden's plan also called for a reestablishment of the Missouri compromise line in all present and future territory of the United States. *The Republicans in Congress refused to accept the compromise. This was due to the fact that they were not going to go back on their word which said that slavery would not be allowed to expand within the borders of the United States of America. FORT SUMTER *The situation at Fort Sumter was not good. Federal troops there were running out of supplies. The new president of the United States, Abraham Lincoln, had a huge decision to make. If he allowed the Confederacy to take control of Fort Sumter, he would look weak and submissive to the goals of the Confederate States of America. *The president therefore let South Carolinians authorities know that he was shipping in supplies to federal troops occupying Fort Sumter. According to the president he had no intent of going on the offensive against Confederate military forces. Federal shipping to Fort Sumter was merely for supply reasons and nothing else. *Like Lincoln, the Confederacy knew that if it did not take a strong stance against Lincoln's shipments it would be perceived as being weak. Gen. PGT Beauregard who was the commander of Confederate forces at Charleston South Carolina was ordered to seek out surrender from the Union’s General Anderson who controlled Fort Sumter. When Anderson refused to surrender Confederate soldiers bombarded Fort Sumter for two days (April 12 through the 13th of 1861). *On April 14, 1861, Gen. Anderson surrendered Fort Sumter to Confederate forces. *This marked the beginning of the American Civil War! *The president began to mobilize the Union for war. *Four more slave states immediately secede from the union. These states included Virginia (April 17, 1861), Arkansas (May 6, 1861), Tennessee (June 8, 1861), and North Carolina (May 20, 1861). *Now there were only four remaining slave states who had not seceded and joined the Confederacy. These four states included Maryland, Delaware, Kentucky, and Missouri. Under heavy political and even military pressure from Washington these four states decided against secession and promised to remain part of the United States of America. *Compromise had failed and war had begun. THE OPPOSING SIDES *At the beginning of the war, it seemed as if the North had the upper hand. They had an industrial infrastructure that was capable of manufacturing the war machine the Union would need to achieve victory. Their population was twice as large as that of the South and nearly 4 times as large as the non-slave population of the South. *The South had almost no industry at all and would therefore have to rely on imports from Europe. The transportation system the North was also better than the one in the south. *Despite all of these material advantages that the North enjoyed, the South was fighting a guerrilla war on their own turf which could help them achieve small victories. MOBILIZATION OF THE NORTH (ECONOMIC MEASURES) *Homestead Act of 1862 *Morrill Land Grant Act P. 474 *With Southern representation gone from Congress, the North pursued an aggressive legislative program intended to benefit themselves. *the United States government passed legislation to promote economic growth as well as financial stability for the war itself. The government made a valiant effort to finance the war by levying taxes, issuing paper currency, and borrowing. In 1861 the government levied an income tax for the first time. *The printing of “greenbacks”. *War bonds