* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cell division cs
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
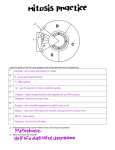
Eukaryotic cell DNA Gene Histone Chromatin Centromere Chromatid Chromosome Cytokinesis Protein Organelle Enzyme Mutation Prokaryotic cell Eukaryote Interphase Mitosis Meiosis Metabolism Prokaryote Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Centriole Spindle Meristem cells Homologous Clones Binary fission Asexual reproduction Sexual reproduction Cells that have a nucleus inside a nuclear envelope, and other membrane-bound organelles. Deoxyribonucleic acid – a polymer of nucleotide molecules that form the instructions for the synthesis of proteins found within organisms. These nucleotides contain the 5-carbon sugar deoxyribose. A length of DNA that carries the code for the synthesis of one (or more) specific polypeptide. Type of protein associated with DNA in eukaryotes. DNA is wound around histone proteins to form chromatin. Material staining dark red in the nucleus during interphase of mitosis and meiosis. It consists of nucleic acids and proteins. Chromatin condenses into chromosomes during prophase of nuclear division. The region of a chromosome where two sister chromatids are joined together, and where the spindle fibre attaches during cell division. A replicated chromosome appears as two strands in early stages of cell division. Each strand is a chromatid. A linear DNA molecule wrapped around histone proteins found in the nucleus. Chromosomes become visible in prophase of cell division. The division of the cell, following nuclear division, to form two new cells. A polymer consisting of many amino acid monomers covalently bonded together. Structure inside a cell. Each organelle has a specific function. A protein molecule that acts as a biological catalyst. A cell lacking a membrane-bound nucleus. A change in the structure of DNA, or in the Prokaryotic genetic material exists as a structure and number of chromosomes. single circular DNA molecule called a plasmid. An organism having cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. The phase of the cell cycle where synthesis of new DNA and organelles takes place. Nuclear division that results in the formation of cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. Nuclear division that results in the formation of cells containing half the number of chromosomes of the adult cell. All the chemical reactions that take place in an organism. An organism with cells that do not contain a true nucleus. The phase of mitosis where the chromosomes become visible as a pair of sister chromatids joined at the centromere. The phase of mitosis where the chromosomes line up at the equator of the spindle. In mitosis, the stage when the newly separated chromatids are pulled towards opposite poles of the nuclear spindle. Final phase of mitosis. Two new nuclear envelopes form around the two new nuclei. An organelle from which the spindle fibres develop during cell division in animal cells. A structure consisting of protein fibres found in eukaryotic cells during cell division. Chromosomes become attached to the spindle at their centromeres, and spindle fibres guide the movement of chromosomes to opposite end of the cell at telophase. Undifferentiated plant cells capable of rapid cell division. Chromosomes that have the same genes at the same loci. Members of a homologous pair of chromosomes pair up during meiosis. Diploid organisms, produced by sexual reproduction, have homologous pairs of chromosomes – one member of each pair from the male parent and the other member from the female parent. (Can also be used to refer to structures that have different functions but have a common evolutionary origin, such as human arm and a bird wing.) Genetically identical cells or individuals. Method of cell division in bacteria. The DNA replicates and the cell divides into two, each having the same DNA as the parent cell. It does not involve mitosis. The production of a new individual formed by the fusing of gametes from two The production of genetically identical new different parent organisms. The offspring organisms by a single ‘parent’ organism. have unique combinations of alleles inherited from both parents.