* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Learning About Soil
Survey
Document related concepts
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Soil respiration wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Terra preta wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
Soil horizon wikipedia , lookup
Canadian system of soil classification wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Soil contamination wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
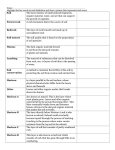
4.7 Learning About Soil Page 210-211 Rocks can be broken down by weathering These particles of rock are the beginning of a process that leads to the formation of soil in which plants can grow The soil can be views as a series of thin layers called horizons Each layer can be identified by a distinct color, thickness, and texture Mature soils in different biomes or geographic regions vary in color, porosity, acidity, and depth These characteristics can be used to classify different soil types Litter The surface of the soil is usually covered with leaves, broken branches, and fallen trees This layer keeps the ground damp by preventing too much water from evaporating Topsoil Beneath the litter Topsoil usually contains dark, decaying plant and animal matter called humus Humus contains the rich supply of nutrients and minerals that new plants need for growth Subsoil Contains larger pieces of rock and clay Usually lighter in color as it contains little humus Bedrock A layer of solid, unbroken rock This layer is still subject to biological weathering Bedrock to Topsoil As bedrock is weathered, small rocks break off and become subsoil The subsoil is also being weathered by plant roots, and small burrowing animals, which brings humus down into the subsoil As a result, the top of the subsoil, slowly becomes topsoil Page 211 #1, 2, 3