* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download famous mathematicians
Mathematical proof wikipedia , lookup
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
John Wallis wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and architecture wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
List of first-order theories wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Discrete mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and art wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Laws of Form wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical logic wikipedia , lookup
Secondary School Mathematics Curriculum Improvement Study wikipedia , lookup
Principia Mathematica wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
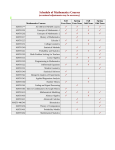
FAMOUS MATHEMATICIANS EUCLID (300 BC – 275 BC) *(1) *(2) (3) Known as “the father of geometry” His Elements is the most successful textbook in the history of mathematics. In it, the principles of Euclidean geometry are deduced from a small set of axioms. His contemporaries nicknamed him “beta” (Greek for “number two”) because he supposedly proved himself to be the second in the ancient Mediterranean region in many fields. ARCHIMEDES (287 BC – 212 BC) (1) *(2) *(3) (4) (5) (6) His early advances in Calculus included the first known summation of an infinite series with a method that is still used today. (Method of Exhaustion) At his request, his tomb carried a carving of his favorite mathematic proof. (a sphere inside a cylinder of the same height and diameter) Quote : “Eureka! “ I have found it!” said after finding the density of an object after submerging it in water. In The Measurement of a circle, he gave an approximate value for the square root of 3 which was very accurate. In The Quadrature of the Parabola, Archimedes proved that the area enclosed by a parabola and a straight line is 4/3 multiplied by the area of a triangle with equal base and height. In The Sand Reckoner, he set out to calculate the number of grains of sand that the universe could contain. ERASTOTHENES (276 BC – 194 BC) (1) (2) *(3) *(4) Contemporaries nicknamed him “beta” (Greek for “number two”) because he supposedly proved himself to be the second in the ancient Mediterranean region in many fields. Devised a system of latitude and longitude. First known to have calculated the circumference of the Earth. He is remembered for his prime number sieve, the “Sieve of Erathosthenes”. CLAUDIUS PTOLEMY (BORN ABOUT 85 AD) *(1) Wrote Almagest (gives in detail the mathematical theory of the motions of the Sun, Moon, and planets). DIOPHANTUS (born between 200 and 214 AD and died between 284 and 298 AD_ *(1) *(2) (3) Sometimes called “the father of algebra” Wrote “Arithmetica” He was the first person to use algebraic notation and symbolism. Before him everyone wrote out equations completely. HYPATIA (370 AD – 415 AD) (1) She edited the work On the Conics of Apollonius, which divided cones into different parts of the plane. *(2) The first notable woman in mathematics JOHN NAPIER (1550 – 1617) (1) *(2) Nicknamed “Marvellous Merchiston” He is most remembered as the inventor of logarithms and Napier’s bones (a multiplication tool using a set of numbered rods) and for popularizing the decimal point. RENE DESCARTES (1596 – 1650) (1) *(2) *(3) (4) *(5) (6) (7) Father of Modern Philosophy Father of Modern Mathematics Cartesian coordinate system used in plane geometry and algebra named for him Descartes Rule of signs is also a commonly used method in modern mathematics to determine possible quantities of positive and negative zeros of a function. He created Analytical Geometry One of Descartes most enduring legacies was his development of Cartesian geometry, the algebraic system taught in schools today. He also created exponential notation, indicated by numbers written in what is now referred to as superscript (x 2 ) LEONARD EULER (1707 – 1783) (1) *(2) (3) *(4) He introduced much of the modern mathematical terminology and notation, particularly for mathematical analysis, such as the notion of a mathematical function. Introduced the notation f(x). He published more papers than any other mathematician of his time. The letter “e” which is used in natural logarithms was named after him (Euler’s number). MARIA AGNESI (1718 – 1799) (1) *(2) Analytical Institutions (differential and integral Calculus) Book was one of the first and most complete works on finite and infinitesimal analysis Best know from the curve called the “Witch of Agnesi) yx 2 = a 2 (a - y) SOPHIE GERMAIN (1776 – 1831) *(1) *(2) Submitted papers and assignments under the pseudonym “Mondieur Le Blanc: One of her major contributions to number theory was the following theorem : if x, y, and z are integers and x 5 + y 5 = z 5 then either x, y, or z has to be divisible by 5. ADA LOVELACE (1815 – 1852) (1) *(2) (3) *(4) Her birth name was August Ada Byron. is mainly known for having written a description of Charles Babbage;s early mechanical general-purpose computer, the analytical engine. Her father called her “the princess of parallelograms” Credited with be the first computer programmer. GEORGE BOOLE (1815 – 1864) *(1) (2) Inventor of Boolean Algebra, which is the basis of all modern computer arithmetic. Regarded as one of founders of the field of computer science, although computers did not exist in his day. JOHN VENN (1834 – 1923) *(1) (2) Famous for conceiving the Venn diagrams, which are used in many fields, including set theory, probability, logic, statistics, and computer science. Wrote The Logic of Chance which introduced the frequency interpretation of probability; Symbolic Logic which introduced the Venn diagrams and Principles of Empirical Logic. SONYA KOVALEVSKY (1850 – 1891) *(1) *(2) (3) First woman member of Russian Academy of Sciences. Established first significant result in general theory of partial differential equations. In her memoir, On the Problem of the Rotationo of a Solid Body about a Fixed Pointshe completely settled a problem whose solution had long eluded mathematicians.