* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download and View
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
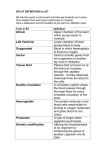
CHAPTER 8 7TH GRADE SECTION 1 PG 214-217 I Living Things A organism- any living thing B all have similar traits II Organizing living things A cell- smallest unit of an organism that carries on functions of lifeC:\Documents and Settings\admin\My Documents\My Pictures 1. orderly structure and contains instructions for cellular organisms 2. heredity DNA tells cells what to do III Growth and Development A. increase in the number of cells-multicelled organism B. growth of a cell larger—1 celled organism C. development- all changes that take place in a lifespan D. lifespan- how long an organism is expected to live IV Living things must do to live A. respond- interactive with surroundings a. stimulus- causes a response B. maintain homeostasis- regulation of an organisms life-maintaining condition despite change in environment C. use energy a. from the sun b. from food c. from chemicals D. reproduce a. keeps organisms group alive V Living things needs A. shelter B. water C. food SECTION 2 PG 218-220 I Classification A. Carolus Linnaeus- developed a new system of grouping organisms B. binomial nomenclature- two word naming system that Linneaus used to name various organisms C. Genus- group of similar species D. Species- describes a feature of the species E. Scientific names are always used so that: 1. avoid mistakes 2. organisms with similar evolutionary history are put together 3. descriptive information is given in the name 4. helps us organize species II Modern classification A. phylogeny- evolutionary history of an organism and how it has changes over time B. used to help classify C. kingdom- largest grouping of organisms and then becomes more specific Ex: pg 219 fig. 6 III Tools for identification A. field guides B. dichotomous keys- key of identifying characteristics that includes scientific names Ex: pg 220 Table 1 SECTION 3 PG 221- 230 I Cell Theory A. Robert Hooke (1165) Look at a cork under microscope and discovered small box-like structures— called them cells. B. Matthias Schleiden (1830) studied plants and said cells made up plants C. Theodor Schwann- animals are made of cells. D. Virchow- cells divide into more new cells. E. Cell theory1. all living things are made up of cells. 2. the cell is the basic unit of organization in organisms 3. all cells come from cells (microscopes page 222-223) II cell organization (page 224 fig 8) A. prokaryotic cells- cell without membrane—bound structures B. eukaryotic cells -with a membrane—bound structure III cell parts (plants, algae, fungi, bacteria) A. cell wall- tough, rigid outer coverings that protect cells and give shape 1. cellulose- long thread-like fibers allows nutrients in and out 2. pectin and lignini. pectin- aids in cell growth, development, defense, and strength ii. lignin- makes cell wall rigid B. cell membrane- protective layer surrounding every cell 1. outer most covering of a cell unless a cell wall is there 2. regulates interactions between cell and its environment 3. nutrients in----wastes out C. cytoplasm- gelatin-like substance that flows in a cell. 1. most life processes occur here 2. cytoskeleton- framework made of tubes of protein D. ribosomes- structures that make proteins 1. float freely in cytoplasm 2. DNA tells ribosomes how, when and what order to make proteins E. organelles- found only in eukaryotic cells F. nucleus- directs all cell activities of the cell 1. contains the DNA G. chloroplasts- contain chlorophyll- a green pigment 1. found only in plant cells 2. changes sunlight, water, and CO ---- O and sugar H. mitochondria- store and release energy 1. contain ribosomes I. endoplasmic reticulum- a series of folded membranes so materials can be processed and move around the cell 1. extends from the nucleus to cell membrane 2. ribosomes are attached to it K. golgi body- sorts proteins and other cellular substances and packages them into vesicles 1. vesicles deliver cellular substances to areas inside the cell L. vacuoles- stores cell material, water, wastes, and food. 1. vacuoles make up most of a plant cell volume M. lysosomes- breakdown food molecules, wastes, and old cell parts 1. recycles parts 2. kills viruses and bacteria that enter The cell IV Organization of organisms (many-celled) A. cell B. tissue- group of similar cells C. organ- made of 2 or more tissues that work together D. organ system- group of organs that work to perform a specific function I Virus A. a strand of hereditary material surrounded by a protein coating B. It will replicate itself with the help of a living cell C. have no nucleus, organelles, or cell membrane II 2 types of viruses A. active virus a. enters cell and causes host cell to make new virus b. kills host cell (page 232 fig. 17) B. latent virus a. inactive virus b. enters the cell, and its hereditary material becomes part of the cell’s hereditary material c. the virus is copied along when new cells are made d. lays dormant or quiet until something triggers it Ex: cold sore III Virus affect A. Can only infect certain cells (human or animal) B. A few can affect more than 1 type of cell C. Bateriaphages- viruses that infect bacteria IV Treatment A. antibiotics- treat bacterial infections but don’t work on viruses B. anti-virals- used on viruses- side effects are terrible C. Prevention a. Vaccination b. Sanitation c. Quarantine d. Animal control D. Natural immunity- making interferonsproteins that protect cells from viruses a. Proteins are produced rapidly by infected cells and move noninfected cells host—noninfected produced protective substances E. Vaccines-cause the body to make interferons-usually weakened virus is given (Jenner 1796) F. Gene therapy- fixes cells that are defective because of heredity a. virus injected that have correct heredity b. Ex: AIDs/HIV currently being studied this way