* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Algebra 1 Chapter 1-6 Study Guide 2015
Survey
Document related concepts
BKL singularity wikipedia , lookup
Unification (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Euler equations (fluid dynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Equation of state wikipedia , lookup
Itô diffusion wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Calculus of variations wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Schwarzschild geodesics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Study Guide - Chapter 6 Cumulative Test
Chapters 1-6
Name_________________________________
CHAPTER 1
1.1 Variables and Expressions
1.2 Adding and Subtracting Real Numbers
1.3 Multiplying and Dividing Real Numbers
1.4 Powers and Exponents
1.5 Roots and Real Numbers
Ex 1. List all possible classifications for each number.
a. -4
b. ¼
c. √37
d. 7
1.6 Order of Operations
Ex 2. Simplify. 8(9) – 4 + 3{[5 + 2] − 1}
1.7 Simplifying Expressions
Ex 3. Simplify.
6𝑥 + 10 − 7𝑦 − 3(𝑥 + 5𝑦) + 5
Ex 4. Simplify. −3𝑥 2 + 5𝑥 − 4𝑥 + 5𝑥 2 + 10 − 2(𝑥 + 4)
CHAPTER 2
2.1 Solving Equations by Adding or Subtracting
2.2 Solving Equations by Multiplying or Dividing
2.3 Solving Two-Step and Multi-Step Equations
Ex 5. −4𝑥 + 3𝑥 = 7 + 5(𝑥 + 1)
Ex 6.
−5𝑥 + 7 = 1 + 3(𝑥 + 2)
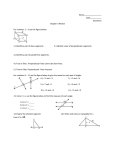
Ex 7. The sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. Find the value of x and
the measure of each angle.
2.4 Solving Equations with Variables on Both Sides
When do you have all real number (infinitely many) solutions?
When do you have no solution?
When do you have exactly one solution?
Ex 8. −4𝑥 + 3𝑥 = 7 + 5(𝑥 + 1)
Ex 9.
Ex 10. 10 − 3𝑥 + 5 = −3(𝑥 + 1)
Ex 11.
−5𝑥 + 7 = 1 + 3(𝑥 + 2)
5(2𝑥 + 4) − 𝑥 = 9(𝑥 + 1) + 11
2.5 Solving for a Variable
How do you solve for h when the equation contains only variables?
Ex 12. Solve ℎ𝑘 − 𝑗 = 𝑙 for h.
Ex 13. Solve 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑏 for x.
CHAPTER 3
3.1 Graphing and Writing Inequalities
3.2 Solving Inequalities by Adding or Subtracting
3.3 Solving Inequalities by Multiplying or Dividing
3.4 Solving Two-Step and Multi-Step Inequalities
3.5 Solving Inequalities with Variables on Both Sides
When do you have all real number (infinitely many) solutions?
When do you have no solution?
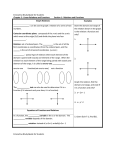
Ex 14. 𝑆𝑜𝑙𝑣𝑒 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑝ℎ. − 4𝑥 + 𝑥 < 10 + 2𝑥
Ex 15. 𝑆𝑜𝑙𝑣𝑒 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑝ℎ. 𝑚 + 5 ≤ 7(𝑚 − 1)
Ex 16. 10 − 3𝑥 + 5 > −3(𝑥 + 1)
Ex 17.
2𝑥 − 5 ≥ 2(𝑥 + 1)
CHAPTER 4
4.1 Graphing Relationships
4.2 Relations and Functions
How can you identify whether or not a relation is a function?
Ex 18. Circle each relation below that is a function.
{(-6, 6), (6, -6), (4, 5), (5,4)}
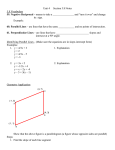
Ex 19. Write relation described by the mapping diagram below as a list of ordered pairs.
Ex 20. Evaluate 𝑓(𝑥) = 2𝑥 2 − 5 for 𝑥 = −3.
Ex 21. Evaluate 𝑔(𝑡) = −𝑡 2 + 𝑡 − 4 for 𝑥 = −2.
4.3 Writing Functions
Ex 22. Application
a. Write a function rule to model the situation below USING FUNCTION NOTATION!
“A fitness center charges a $100 initiation fee plus $40 per month. Write a rule to describe the total cost of
membership after m months.”
b. Use your rule to determine how much an 8 month membership would cost.
Ex 23. Identifying Independent and Dependent Variables
a. Movie sales increase as more tickets are sold.
b. Each cupcake costs $4.50.
Independent:____________________
Independent:____________________
Dependent: _________________________
Dependent: _________________________
4.4 Graphing Functions
CHAPTER 5
5.1 Identifying Linear Functions
Ex 24. Circle each relation below that is linear. Explain how you made your decision for each problem.
a.
Explain:
b.
Explain:
c. 𝑦 = 6𝑥 + 3
Explain:
d. 𝑦 = 6𝑥 2 + 3
Explain:
5.2 Using Intercepts
Ex 25. Calculate the x-and y-intercepts and graph the equation using the
intercepts.
5𝑥 − 4𝑦 = 20
5.3 Rate of Change and Slope
How do you determine the rate of change and slope given a graph, a linear equation, a list of points or a table of
values?
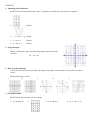
Ex 26. Find the slope of each.
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
5.4 The Slope Formula
Ex 27. Find the slope between each set of points.
a. (4, -4) and (9,-3)
b.
c. (4, 8) and (4,-3)
d. (2, -3) and (-7, -3)
5.7 Slope-Intercept Form
Ex 28. Write the equation for the line graphed below in slope-intercept form.
a.
b.
c.
5.8 Point-Slope Form
1
Ex 29. Rewrite 𝑦 − 6 = 2 (𝑥 − 4)in slope intercept form.
1
Ex 30. Rewrite 𝑦 − 6 = 2 (𝑥 − 4)in standard form.
Ex 31. Write the equation that goes through (6, -4) and (2,1) in all three forms.
Find m:
PS:
SI:
S:
5.9 Slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines
How are slopes related for parallel and perpendicular lines?
Ex 32. Vocabulary. Fill in the blanks with parallel and perpendicular.
______________________ lines have the same slope but different y-intercepts.
______________________ lines have opposite reciprocal slopes.
Ex 33. Writing Equations of parallel and perpendicular lines in slope-intercept form.
a. Find the equation of a line parallel to 𝑦 =
1
− 3 𝑥 + 6 that goes through (3,4).
b. Find the equation of a line perpendicular to
1
𝑦 = − 𝑥 + 6 that goes through (3,4).
3
CHAPTER 6
6.1 Solving Systems by Graphing
Graphically, how can I identify the special cases?
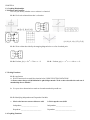
Ex 34. Solve by graphing.
a.
6.2 Solve Systems using Substitution
Ex 35. Solve by substitution.
a.
6.3 Solve Systems using Elimination
Ex 36. Solve by elimination.
a.
b.
b.
b.
How to prepare for the Cumulative Exam:
Start now! Don’t wait until the night before to prepare!
Read through the study guide! Identify the topics that you need to revisit.
Ask Questions! Utilize Flex or Lunch Time to get extra help!
Revisit old class materials like past quizzes and homework assignments.
Exam will take place on January 27, 2016.