* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 20 Study Guide – The United States
Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
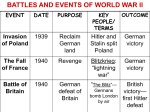
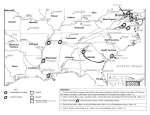
Chapter 24 Study Guide – The World War II Era (1935-1945) In addition to the Blue terms in Chapter 22 in the textbook, you should know: 1. Section 1 – Aggression Leads to War a. The Rise of Dictators 1. Mussolini, Stalin, Hitler – types of government – fascist, totalitarian, etc. 2. Militarism, racism, extreme nationalism in Japan b. Military aggression 1. Japan invades Manchuria 2. Italy invades Ethiopia 3. Ineffectiveness of the League of Nations 4. Hitler’s defiance of Treaty of Versailles 5. Treaty of Munich – appeasement c. United States Foreign Policy 1. Isolationism 2. Neutrality Act 3. Good Neighbor Policy – purpose onlyy d. War Begins in Europe 1. Failure of appeasement 2. The Invasion of Poland - Nazi-Soviet Pact 3. Britain and France declare war on Germany – beginning of WWII 4. Fall of France – retreat to Dunkirk, surrender to Germany 5. Battle of Britain – British victory 6. Hitler invades the Soviet Union – breaks pact, Soviet Union joins Allies 2. Section 2 – The United States at War a. FDR wins reelection 1. Lend Lease 2. How US prepared for war 3. Atlantic Charter b. The US Enters the War 1. Events in Asia – American Response 2. Japan plans to attack the US 3. The attack at Pearl Harbor c. Know Axis powers and Allied Powers d. Turning points in Europe and North Africa 1. The Battle of Stalingrad 2. El Alamein e. Japan takes islands in the Pacific 1. Philippines – Americans/Filipinos trapped on Bataan Peninsula / Bataan Death March f. Turning points in the Pacific – Battle of Midway 3. Section 4 – Toward Victory a. Victory in Europe 1. Removing Italy 2. D-Day – would assure victory in Europe – location, challenges, victory 3. Battle of the Bulge – Germany running out of soldiers, opened Germany from the East and the West (1945) 4. Who replaces FDR after his death 5. Collapse of Germany – unconditional surrender 6. V-E Day – May 8. 1945 b. Victory in the Pacific 1. Island hopping strategy – stepping stones to Japan 2. Japan’s kamikaze strategy 3. US decides on full-scale invasion 4. Japan would not give up 5. Truman’s decision to use the atomic bomb to end the war. 6. Hiroshima/Nagasaki c. The Holocaust – liberation of the death camps d. Trials for War Crimes – Nuremberg 4. Map of Europe and Africa a. Main Axis and Allied Powers – Britain, b. Poland, Czechoslovakia, Russia c. Important countries in North Africa