* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Chromosomes Mr. Alvarez March 15, 2013
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
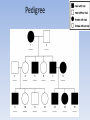
Human Chromosomes Mr. Alvarez March 15, 2013 DNA • Each diploid cell contains 6 billion base pairs • An Average Human Gene is 3,000 base pairs • Largest gene in human genome has more than 2 million base pairs Lou Gehrig’s Disease • Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)- Causes a progressive loss of muscle control due to the destruction of nerves in the brain and spinal cord. – Caused by a mutation on Chromosome 21 Sex-Linked Genes Sex-Linked Genes- Genes found on either the X or Y chromosome Color-Blindness • Human genes associated with color vision are located on the X chromosome • Most common type of color blindness is RedGreen color blindness – Effects 1 in 10 males – Effects 1 in 100 females Sex-Linked Disorders KEY: C =Normal Vision c = Color Blind Normal Female Carrier Female Affected Female Normal Male Affected Male Why Can’t Males Be Carriers? • Males have just one X chromosome • All X-linked alleles are expressed in males, even if they are recessive In humans, normal vision (XC) is dominant to colorblindness (Xc) and is sex-linked. A normal-visioned man marries a colorblind woman. What are the chances that a son will be colorblind. A daughter? A normal male (not colorblind) marries a female carrier. What are the offspring genotypes and phenotypes? Hemophilia is due to a sex-linked recessive gene (Xh) and the normal condition to the gene (XH). A hemophiliac man marries a woman who is not. Their first son has hemophilia. What are the chances that their daughter, if they had one, will be hemophilic? Hemophilia Hemophilia- Sex-linked heredity disorder in which the blood fails to clot properly, resulting in excessive bleeding Duchene Muscular Dystrophy Duchene Muscular Dystrophy- Sex-linked disorders that results in the progressive weakening and loss of skeletal muscle Pedigree