* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plasma = a fluid of free charged particles
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Gauge fixing wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Search for the Higgs boson wikipedia , lookup
Higgs boson wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Theory of everything wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
ALICE experiment wikipedia , lookup
Weakly-interacting massive particles wikipedia , lookup
Yang–Mills theory wikipedia , lookup
Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Strangeness production wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Technicolor (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chromodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Higgs mechanism wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
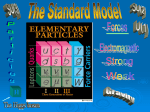
Plasma = a fluid of free charged particles Maxwell’s eqn’s: + Newton’s laws Î Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) “Frozen in” fields: • • • Field lines and charged particles move together. Takes energy to squish field lines closer together Takes energy to stretch field lines. The Sun’s magnetic field Charged particles in magnetic field feel Lorenz force: Magnetic Field Lines Force B (mag field) velocity X-ray flare movie http://farside.ph.utexas.edu/teaching/plasma/lectures/node60.html 1 The History of the Universe Nucleosynthesis Planck Galaxy of H, He, Li time Formation Decoupling Inflation of CMB Now Hot Cool High density Low density Interactions Four forces in Nature 1 Gravity 3 Weak Interaction Newton Beta (radioactive) decay Muon decay Time scales: 10-12 ~ 103 sec 2 Electromagnetism Faraday 4 Strong Interaction Hold nuclei together Particle collision Time scales: 10-23 sec (These slides compliments of Prof. Yuan) 2 Leptons • Don’t feel the strong force • Integer or Zero charge • Flavours: e− “electron” (1897) In atoms (1937) First seen in Cosmic Ray (1975) Seen at SLAC (0.511 MeV) µ− “Muon” (206 me) τ− “Tau” (17 mµ) νe ( Stanford Linear Accelerator Center) “electron neutrino” (1956) Pauli’s explanation of Beta Decay (1930) Mass νµ “Muon neutrino” (1962) ντ ν e < 3 eV ν µ < 0.19 MeV “Tau neutrino” (2000) ν τ < 18.2 MeV Quarks • Feel the strong force • Fractionally charged 2 3 Q= × Proton charge − 1 3 • Constituents of neutron and proton (udd) ( ) u d • Flavors: u d s c b t (uud) “up” “down” “up” “down” “strange” “charmed” “bottom” “top” Baryon A strongly interacting particle that is composed of quarks and has a spin that is an integer multiple of ħ (e.g., a quark, neutron, or proton). 3 The Standard Model of Particle Physics Matter fields (make up all visible matter in the universe) Fermions (Spin 1/2) Lepton ( No Strong Interaction Quarks (q) ) u d L νe − e L νµ − µ L ντ − τ L eR− µ −R τ−R u d L c c c s L s L s L u d L t b L t b L t b L uR uR uR c R c R cR tR tR tR dR dR dR sR sR sR bR bR bR 14444444244444443 3 families Scalar (Spin 0) Higgs Boson ( Not yet found! ) ( From Higgs Mechanism Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking) The Standard Model of Particle Physics Interactions ( mediated by interchanging Gauge Bosons, spin-1 force carrier ) 1) Electromagnetic Interaction (QED) Photon (massless) 2) Strong Interaction (QCD) Gluon (massless) (1979) 3) Weak Interaction W + , W − and ( Z Gauge Bosons massive M W = 80.4 GeV M Z = 91.187 GeV In SM, the Mass of W-boson, either W ± (1983) 1 GeV = 109 eV ) or Z , arises from the Higgs Mechanism ( Without it, Gauge Bosons have to be massless from gauge principle.) 4 “Freezing out” of the four forces: Theory of Everything Grand Unified Theory • Massless gauge bosons. • Many additional massive particles (dark matter candidates) • Quarks • Massive gauge bosons • Leptons • Gluons • Photons 5