* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Phy123 Exam2 review
Survey
Document related concepts
Image intensifier wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Ray tracing (graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Lens (optics) wikipedia , lookup
Reflecting telescope wikipedia , lookup
Schneider Kreuznach wikipedia , lookup
Micro Four Thirds system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
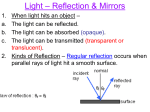
Exam 2: Phy 123 Study Guide (These are guidelines only, you are expected to know all material coveredin assignments, lecture, readings, labs, and tutorials. 1. Reflection and Ray Optics a. Understand how images and objects can be located by: • Parallax • Ray-Tracing b. State the Law of Reflection and give examples to illustrate its meaning. c. Use Ray-Tracing to show the following characteristics of an image in a curved mirror (concave and convex): • Image Location • Image Type • Image Size compared to the Object Size (Magnification) • Image Orientation 2. Refraction and Ray Optics a. State the Snell’s Law and give examples to illustrate its meaning. b. Use the concept of refraction to predict the path (and speed) of light as it moves from one substance to another. c. Use Snell’s Law and the concept of Refraction to explain the function of a lens. d. Apply Snell’s law to the explain the operation of such devices as: • Optical Fiber • Our eyes • Glasses • Prisms • Cameras • Telescopes • Microscopes 3. Calculation related to image formation: a. Understand the sign conventions with each of the following: • Concave mirrors • Convex mirrors • Diverging lenses • Converging lenses b. Use the mirror equation or the thin-lens equation to calculate the following for single or multiple optical devices: • Object location • Image location • Focal length • Magnification Phys. 123: Exam2_Study Guide Eyres: 2010 Review Mirrors and Lenses: • The worksheet we did in class with the object at locations within various standard zones in front of curved mirrors and lenses. You were asked for ray diagrams, coordinate systems to find whether xi, xo, si, so were positive or negative. • Equations relating to curved mirrors and lenses. • The similar triangles that gave us the equations. • Parallax • Lab on Lenses Review Snell’s Law: • Lab on Snell’s Law • You should be able to predict the direction of propagation when a wave travels from one medium to another. Review the relationship of v, f, , n, for these situations. Do You Understand Outcomes 4-6? • • • • You should be able to predict image location and characteristics from a verbal description of the situation, from ray diagrams and from equations. You should also be able to explain the coordinate system(s). Can you describe in words or by drawing a picture what one would see when looking into a mirror or through a lens for different situations and materials? What would you predict when light (or other waves) pass from one medium to another. Could you predict relationships (equations and graphs) between variables such as v, f, , n, Or between xi, x0, si, s0, f for lenses and mirrors? 4. Light as a Wave a. Use the concept of wave superposition to explain the fringe pattern resulting from: • Thin film interference b. Explain polarization in terms of vector components Review: • Do you remember looking at the Polaroid filters? • Thin-film Demos Phys. 123: Exam2_Study Guide Eyres: 2010