* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IUSTI Australia MAMEF poster
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Maurice Wilkins wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Surround optical-fiber immunoassay wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
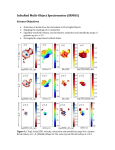
Optimization and Clinical Testing of a Microwave-Accelerated Metal-Enhanced Fluorescence (MAMEF) Assay for the Detection of Chlamydia trachomatis Melendez 1 JH , Gaydos 2 CA , Geddes 1 CD * 1Institute of Fluorescence and Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, UMBC, Baltimore, MD 21202, USA 2Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Division of Infectious Diseases, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA *[email protected] Background Results In the present study, detection of CT DNA is mediated by a two-step process. First, CT cells are rapidly lysed and the DNA fragmented using lysing chambers composed of gold or aluminum triangles deposited on glass slides and heated using conventional microwave irradiation (Figure 2). After a centrifugation step, detection of CT genomic DNA is carried in silver island-covered wells known as fire-in-the-hole plates (Figure 2) which have been shown to enhance the fluorescence signal. Detection of genomic DNA is mediated by the complementary binding of two probes to the target sequence as shown in figure 1. For increased sensitivity and specificity, two sets of probes targeting the 16S rRNA gene and the Cryptic plasmid of CT has been designed and optimized. 2 3 4 5 Figure 3. A) Fragmentation of CT DNA following 15 seconds microwave irradiation 1) DNA Ladder; 2) gold triangles (50% power); 3) aluminum triangles (50% power); 4) gold triangles 70% power); 5) aluminum triangles (70% power). B) MAMEF signals of samples # 4 and # 5 from Figure A showing identical fluorescence signal suggestive of similar concentration of DNA. Au = gold; Al = aluminum. 2. Rapid and sensitive detection of CT DNA Fluorescence Intensity (AU) Methods 1 Fluorescence Intensity (AU) Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) is the most commonly reported sexually-transmitted infections (STI). In 2009, there were 1.2 million cases of chlamydia reported to the CDC. This infection has serious sequelae among women: PID, tubal factor infertility, chronic pelvic pain, and ectopic pregnancy. Chlamydia infections can increase HIV transmission 3-5 fold. Often persons who present to a clinic for STI testing never return to the clinic to receive their STI test results. Thus the availability of a point-of-care test which can be resulted to them immediately is highly desirable. In the present study, we report on the optimization of an ultra-rapid and sensitive point of care assay for detection of CT, and discuss clinical testing with vaginal specimens. 1. Efficiency of lysing triangles 10^6 ifu/ml 10^5 ifu/ml 10^4 ifu/ml 10^3 ifu/ml 10^2 ifu/ml 10^1 ifu/ml 0 ifu/ml 800 600 400 200 0 550 575 600 625 1000 800 600 400 200 0 650 0 10^1 10^2 Wavelength (nm) 10^3 10^4 10^5 10^6 ifu/ml 3. Performance of MAMEF in GenProbe Media and using dry swabs MAMEF MAMEF Figure 1. Probe-based detection using rapid MicrowaveAccelerated Metal-Enhanced Fluorescence (MAMEF) + - 21 4 + - + 19 13 - 7 11 NAAT NAAT • Vaginal swabs rehydrated in 2 mL of distilled water + 5 15 Dry swabs Sensitivity = 84% GenProbe media Sensitivity = 58% Testing of two individual sample sets from 95 individuals. Dry swabs – 45 samples and GenProbe media – 50 samples. Conclusions • Lysing chambers used for cell lysing and DNA fragmentation Cell lysis and DNA fragmentation is achieved in 30 seconds, and gold and aluminum lysing triangles are equally effective. • 5 minute centrifugation step Dry vaginal swabs are an effective collection method and sensitivity of the MAMEF assay is very high using dry swabs rehydrated in water. Rapid lysis of bacterial cells, fragmentation and detection of genomic DNA can be carried out in less than 10 minutes. Reference and acknowledgements Fire-in-the-hole plate used for DNA detection. Detection in the wells is mediated by probes as shown in figure 1. Figure 2. Workflow for the ultra-rapid and sensitive detection of CT DNA RESEARCH POSTER PRESENTATION DESIGN © 2012 www.PosterPresentations.com Zang Y, Agreda P, Kelly S, Gaydos C, Geddes CD. Development of a microwave-accelerated metal – enhanced fluorescence 40 second, 100 cfu/mL point of care assay for the detection of Chlamydia trachomatis. IEEE Trans BioMed Eng 58:781-784, 2011. The authors would like to thank The Meyerhoff Graduate Fellowship Program, The Institute of Fluorescence and the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Maryland Baltimore County for support. Financial support from the NIH / NIAID MARCE - Midatlantic Regional Center of Excellence for Biodefense and Emerging Infectious Diseases (NIAID/NIH) 2 U54 AI057168-06 and NIH/NIBIB 1U54 EB007958-4 are also gratefully acknowledged.