* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell transport
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
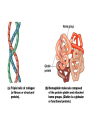
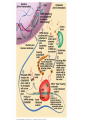
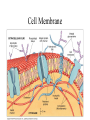
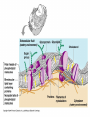
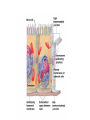
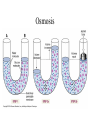
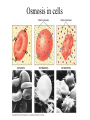
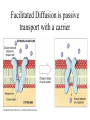
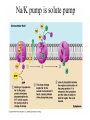
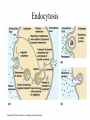
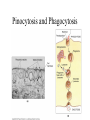
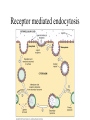
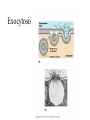
• Inorganic compounds: • water • salts • acids and bases • Organic compounds: • carbohydrates: sugars – Mono, di, and polysaccharides • lipids: fats – Triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids • Proteins! • Nucleic Acids! Proteins • 50% organic matter • C, H, O also N, S • amino acids in large chains...like letters form words • 2 kinds – fibrous – bind structures, provide strength – globular – antibodies, hormones, enzymes. Globular proteins DO things! • enzymes-catalyst for EVERY chemical reaction in the body, remains unchanged Nucleic Acids • DNA & RNA: make up genes, dictate protein structure • C, O, H, also N, P • Nucleotides – Adenosine – Guanine – Cytosine – Thymine – Uracil • DNA – replicates before cell division – blueprints for every protein • RNA – Carry out DNA instructions to build proteins Protein Synthesis • DNA codes for amino acid sequence of proteins – Ex. AAA = phenylalanine • Ribosomes use DNA code to synthesize proteins… • Problem: DNA in nucleus, ribosomes in cytoplasm RNA to the rescue! • 3 kinds of RNA – messenger • transcription of DNA to RNA in nucleus • brings DNA message to ribosome – transfer • transfers amino acids to ribosome • amino acids make up proteins – ribosomal • forms part of ribosome ATP • adenosine triphosphate • energy used by all • high energy phosphate bonds • ATP ADP + P + ENERGY! hydrolysis Cell Membrane (plasma membrane) • General functions – Physical isolation – Regulation of exchange in the environment – Structural support Structure of the cell membrane • 6-10 nm thick • Contains lipids, proteins and carbohydrates – Lipids • Phospholipids • Cholesterol – Proteins • Integral • Peripheral – Carbohydrates Cell Membrane Specializations of cell membrane • Microvilli-increase surface area • Membrane junctions – tight junctions - impermeable sheet of cells • intestine – desmosomes – anchor cells together • skin – gap junctions –communication between cells • heart A closer look at membrane transport • Remember that cells are living in a fluid environment (solution) • solute • solvent – Intracellular fluid - cytosol – Interstitial fluid - surrounds cell Cell membranes are selectively permeable. • What does this mean? • How are compounds transported across the cell membrane? – Passive transport – Active transport Passive transport: Diffusion • Random motion and collision of molecules • Movement down their concentration gradient What conditions influence the diffusion of a compound? Diffusion through the cell membrane Diffusion of water is called osmosis • Water is a polar molecule……which means what?? • How does water pass through the cell membrane? Osmosis Osmosis in cells Osmosis • Aquaporins-proteins in membrane • isotonic – equal tension • hypotonic – deficient tension – Ex. saltwater fish in freshwater – given to dehydrated patients • hypertonic – excessive tension – Ex. pouring salt on slug – given to patients with edema Facilitated Diffusion is passive transport with a carrier Active Transport • Requires ATP • Movement of a substance is against the concentration gradient Two examples of active transport – solute pump – bulk transport Na/K pump is solute pump Bulk Transport • Moves large volumes of material in/out of the cell – Endocytosis – Exocytosis Endocytosis Pinocytosis and Phagocytosis Receptor mediated endocytosis Exocytosis