* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics_A2_41_BackEMF
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
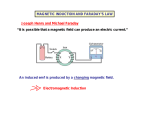
Book Reference : Pages 129 1. To understand that a spinning motor is also a generator 2. To understand how electric motors behave when lightly or heavily loaded Previously we have seen the following 1. Current carrying conductors in magnetic fields experience a force. The ultimate embodiment of this is an electric motor (a spinning coil in a magnetic field or similar) 2. Conductors in a changing magnetic field (due to movement or electromagnetic variation) will have an EMF induced in them. A generator is the ultimate embodiment of this (a spinning coil in a magnetic field or similar) Does an electric motor fit the second point & have an induced EMF? Discuss! A spinning coil in an electric motor will have an EMF induced in it because it sees changing flux linkage This EMF is called “Back EMF” because it follows Lenz’s law and opposes the potential difference (V) supplied to the motor At any moment : V - = IR Where V is the supplied PD, is the back EMF, I is the current through the coil and R is the resistance of the coil Like any generator, the induced back EMF will be proportional to the spin speed. 1. At low speed the current is high since the induced back EMF is small 2. At high speed the current is low since the induced EMF is high Focussing on current in our earlier equation..... If we take our earlier equation: V - = IR and multiply throughout by current : VI - I = I2R Which equates to : Electrical power supplied (IV) = Electrical power transferred to mechanical power (I) + Electrical power wasted due to circuit resistance (I2R) An unloaded motor will spin with a high speed, the induced back EMF will be high and the resulting current is low. The speed is limited by resistive forces (bearing friction and air resistance). Little power used In contrast a loaded motor will spin with a low speed, the induced back EMF will be low and the resulting current is high. Power is transferred from the voltage source to mechanical power in the load and wasted heat due to resistance An electric motor is connected to a battery and an ammeter. It is connected to a variable load Explain why the motor current is low when the load is zero Explain why the motor current increases when the load is increased