* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A Brief History of Planetary Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Higgs mechanism wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Electric dipole moment wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
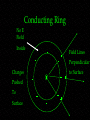
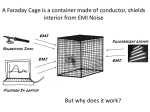
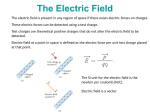
Electric Field Physics 102 Professor Lee Carkner Lecture 10 Force on Charges Fy = 8.99X109(4)(2)/(22) = 1.8X1010N Fx = 8.99X109(2)(5)/(32) = 1X1010 N F2 = Fx2 + Fy2 F = 2.1X1010 N tan q = (Fy/Fx) q = arctan (Fy/Fx) q = 61 degrees q3 = 4 C 2m q1 =-2 C q 3m q2 = 5 C Electric Field at Origin Ey = 8.99X109(4)/(22) = 9X109 N /C Ex = 8.99X109(5)/(32) = 5X109 N/C E2 = Ex2 + Ey2 E = 1X109 N/C Field indicates direction positive test charge will move tan q = (Ey/Ex) q = 61 degrees (below X axis) q3 = 4 C 2m q 3m q2 = 5 C Electric Field E = k q/r2 Where k = 8.99X109 (N m2/C2) Note that, F = Eq0 mC = millicoulombs = mC = microcoulombs = We can draw the field lines to get a map of the field Examples of Fields Field Lines and the Field What is the force on a small positive test charge? Direction: At any point, the F vector is tangential to the field lines Strength: Density of lines proportional to field strength Dipole Called a dipole Electric field is strongest in the space between them Magnetic fields are always dipolar How to Draw Field Lines Lines point from positive to negative More charge, more lines Lines must begin and end at a charge or infinity Conductors and Fields The charges in the conductor are free to move and so will react to the field Charge distributes itself uniformly over the surface of a conductor Inside the Conductor The positive will go to one surface and the negative will go to the other side The field inside the conductor is zero For any point inside, the forces from all the charges cancel out A conductor shields the region inside of it Faraday Cage Called a Faraday cage Your car is a Faraday cage and is thus a good place to be in a thunderstorm Conducting Ring No E Field Inside Field Lines Perpendicular Charges Pushed To Surface to Surface Charge Distribution How does charge distribute itself over a surface? A uniform surface will have a uniform distribution The charge arrangement will make the E field perpendicular to the surface Charge accumulates at points (for a nonuniform surface) Next Time Read 17.1-17.6 Homework: Ch. 16, P 28, 31, 32, Ch. 17, P 2, 14 To charged objects attract each other with force F. If the amount of charge on one object is doubled and the distance between the objects is also doubled, what is the new force in terms of the old? A) B) C) D) E) ¼F ½F 1F (force is unchanged) 2F 4F A charge +Q is placed in the center of a square. When a charge –Q is placed on one corner of the square the net force between them is 2 N. What is the net force on the center charge if a charge –Q is placed on all corners? A) B) C) D) E) 0N 2N 4N 8N You can’t tell from the information given A fixed negative charge sits on a table. Directly above the charge. A) The field points down and a negative charge would move up B) The field points down and a negative charge would move down C) The field points up and a negative charge would move up D) The field points up and a negative charge would move down E) The field would be zero and a negative charge would not move