* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Multicast Over Wireless Networks
Survey
Document related concepts
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.11 wikipedia , lookup
Wireless USB wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Reliable Multicast in MultiAccess Wireless LANs
Speaker : Chi-Wen Yang
Advisor : Kai-Wei Ke
Date : 2007/05/07
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
1
Reference
UPKAR VARSHNEY, Multicast Over Wireless
Networks. Communications of the ACM, Vol.
45, No. 12(Dec. 2002), 31–37.
JOY KURI and SNEHA KUMAR KASERA,
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless
LANs, Kluwer Academic Publishers. , 2001,
359–369.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
2
Outline
Multicast Overview
Multicast Over Wireless Network
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access
Wireless LANs
Summary
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
3
Outline
Multicast overview
Multicast Over Wireless Network
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access
Wireless LANs
Summary
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
4
Multicast overview
Multicast is the delivery of information to a
group of destinations simultaneously using
the most efficient strategy to deliver the
messages over each link of the network only
once, creating copies only when the links to
the destinations split.
Multicast is defined
in RFCs 966, 988, 1054,
and 1112.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
5
Multicast overview
A multicast application can be
characterized as one of three types:
One-to-Many
Many-to-Many
Many-to-One.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
6
Multicast overview
One-to-Many multicast transmission from a single host to all intended recipient
hosts. The sender dispatches a multicast packet addressed to the multicast
group of receivers.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
7
Multicast overview
Many-to-Many multicast transmission from two senders to all intended recipient
hosts. The senders dispatch multicast packets addressed to the multicast group
of receivers.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
8
Multicast overview
Many-to-one multicast transmission from two senders to a single receiver. The
senders dispatch multicast packets addressed to the multicast group of
receivers. In the illustrated example above, the group consists of a single host.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
9
Multicast overview
Multicast protocols :
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM)
Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol
(DVMRP)
Multicast BGP (MBGP)
Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP)
Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD)
GARP Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP)
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
10
Multicast overview
Multicasting has been implemented using
Mbone.
Mbone (short for "multicast backbone") is an
experimental backbone for IP Multicast traffic
across the Internet.
IGMP 、 Multicast Router and IP tunnel
DVMRP、PIM-DM、PIM-SM and MOSPF in
MBone
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
11
Multicast overview
IP multicast support in the MBone using tunneling.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
12
Multicast overview
A multicast can be divided into two
mode:
Sparse
Mode
(PIM-SM)
Dense Mode
(DVMRP)
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
13
Multicast overview
Example for Multicast working.
Multicast source, routers, and receiver group, showing the network segments
that form the multicast path between them as red arrows.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
14
Outline
Multicast overview
Multicast Over Wireless Network
A New Multicast Routing Protocol
Based on Autonomous Clustering in Ad
Hoc Networks
Summary
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
15
Multicast Over Wireless Network
Problem of mobility in wireless :
Loss of packets
Incorrect routing
Discard multicast packets
Transmission range limited
Dynamic connectivity
Group membership management
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
16
Multicast Over Wireless Network
Qualitative comparison of wired and wireless multicast.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
17
Multicast Over Wireless Network
Multicast Routing for Infrastructure-based Wireless
Networks:
DVMRP
MOSPF
PIM
PIM-SM
Multicast Routing for Ad Hoc Wireless Networks:
MAODV (tree-based)
ODMRP (meshed-based)
CAMP (meshed-based)
AMRoute (hybrid)
AMRIS (tree-based)
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
18
Multicast Over Wireless Network
Multicast routing protocols is classified
into three categories:
Multicast
routing using a tree (tree-based)
Multicast routing using mesh (mesh-based)
Multicast routing using other structures
(stateless and hybrid)
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
19
Multicast Over Wireless Network
Multicast routing using a tree
Use source based route between souces and
receivers, there is only one route path for any pair
source
Route update in one of three ways:
• Store and update
• Delete all and refresh
• Unicast protocol support
A multicast tree is subject to disruption due to
link/node failure and node mobility.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
20
Multicast Over Wireless Network
Multicast routing using mesh:
Use multiple redundant routes for rubost handling
of link failure and node mobility during a multicast
session.
It may have looping problem.
Multicast routing using other structures:
Multicast routing provides stateless topologyindependent routing.
Forwarding packets in many directions and
functioning independent of topology.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
21
Multicast Over Wireless Network
Multicast routing in ad hoc wireless networks.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
22
Multicast Over Wireless Network
Reliable in Wireless Multicast:
Packet loss can be detected through one
of two approaches:
• Sender-initiated
– Receivers return ACK for correctly received packets.
• Receiver-initiated
– NAK are used by receivers to inform the sender
about packet loss.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
23
Outline
Multicast overview
Multicast Over Wireless Network
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access
Wireless LANs
Summary
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
24
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
•
2007/05/07
Top view of the system, showing
bases, terminals, the shared
wireless channel in each cell and
the wired interconnection
between bases.
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
25
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
Two important issues:
The problem of the sender acquiring the
multi-access channel for multicast
transmission.
For reliable multicast in each cell of the
wireless LAN, we examine ARQ-based
approaches.
• The second issue is important because the wireless link
error can be very high.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
26
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
There are significant differences
between the wired and wireless LAN
transmission media.
CSMA/CD
in wired LAN.
RTS/CTS in wireless LAN.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
27
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
Hidden Terminal.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
28
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
RTS/CTS/data/ACK and NAV setting
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
29
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
Three generic protocols:
Leader-based protocol (LBP)
Delayed feedback-based protocol (DBP)
Probabilistic feedback-based protocol
(PBP)
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
30
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
Leader-based protocol:
Base→Receivers (Slot 1).
• Send multicast-RTS.
Receivers→Base (Slot 2).
• Leader: If ready to receive data, send CTS.
If not ready to receive data (e.g., due to
insufficient buffers), do nothing.
• Others: If ready to receive data, do nothing.
If not ready to receive data, send NCTS (Not
Clear to Send)1.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
31
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
Base→Receivers (Slot 3).
• If a CTS was heard in slot 2, start multicast transmission.
• If no CTS was heard in slot 2, back off and go to step A.
• The next step is executed only when multicast
transmission occurs in step C.
Receivers→Base (Slot (l + 3)).
• Leader: If packet received without error, send ACK.
If in error, send NAK.
• Others: If packet received without error, do nothing.
If in error, send NAK.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
32
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
Delayed feedback-based protocol:
Base→Receivers.
• 1. Send multicast-RTS.
• 2. Start a timer (timeout period T ), expecting to hear a
CTS before the timer expires.
Receivers→Base.
• 1. On hearing RTS, start timer with an initial value
chosen randomly from {1, 2, . . . ,L}.
• 2. Decrement timer by 1 in each slot.
• 3. If a CTS is heard before timer expires, freeze timer
(CTS suppression).
If no CTS is heard before timer expires, send CTS.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
33
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
Base→Receivers.
• If no CTS is heard within T , back off and go to step A.
• If a CTS is heard within T (at a random time), start data
transmission.
• After finishing transmission, prepare to transmit next
packet and go to step A (no waiting for feedback).
• The next step is executed only when multicast
transmission occurs in step C.
Receivers→Base.
• If packet received without error, do nothing.
• If in error, contend for the channel to send NAK.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
34
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
Probabilistic feedback-based protocol:
• PBP is similar to DBP with one difference.
• The receivers in PBP could send NCTS if they
are not ready.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
35
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
Comparison of the three protocols:
A successful RTS-CTS exchange, DBP
and PBP would take longer than LBP.
The buffer requirements in DBP is higher
both at the base-station and receivers.
A problem with DBP and PBP is the choice
of right parameters for waiting times and
probability of sending feedback.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
36
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
There are two ways in which hidden terminal
can affect the operation of LBP:
The first occurs then there is a collision during the
control packet exchange.
The second way in which multicast transmission
can be affected occurs when there is a collision
affecting the multicast data.
• The second is the same holds true for the other protocols
DBP and PBP.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
37
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
Compare the performance of LBP, DBP
and PBP:
It’s
evidently in favor of DBP and PBP
since no retransmissions are necessary.
DBP have a shorter mean access period
than PBP.
The performance of LBP is better than the
best performance achievable with DBP.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
38
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
Variation of ph with L, keeping N and T fixed.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
39
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
Performance of DBP:
The probability that the base hears a CTS within time T:
The time that the base spend in the access period:
The mean time spent in the access period:
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
40
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
Performance of PBP:
The probability that the access period lasts 2 slots:
The mean time spent in the access period:
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
41
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
Comparison of the expected time spent in the access period under DBP and
PBP.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
42
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
Cost under DBP versus cost under LBP:
The cost of a packet under DBP:
The cost of a packet transmission under LBP:
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
43
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
Events on the error-free channel; DBP.
Events on the error-free channel; protocol LBP.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
44
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access Wireless LANs
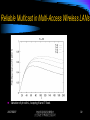
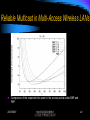
Comparison of packet transmission costs under DBP and LBP; C = 20.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
45
Outline
Multicast overview
Multicast Over Wireless Network
Reliable Multicast in Multi-Access
Wireless LANs
Summary
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
46
Summary
The leader-based protocol provides
very efficient solutions to the CTS and
ACK/NAK collision problems.
It is very simple to implement.
It can be potentially integrated with the
current wireless LAN.
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
47
THE END
Q and A
2007/05/07
無線與寬頻網路實驗室
台北科技大學資訊工程系所
48