* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download document
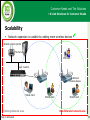
Survey
Document related concepts
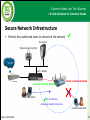
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Authentication Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
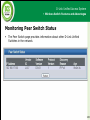
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.11 wikipedia , lookup
Wireless USB wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
[Wireless] Version 1.2 Course Outline Introduction to Wireless Customer Needs and The Solution Wireless Standards and Certifications D-Link Unified Access System • Unified Access System Overview • D-Link Unified Wireless Switch Wireless Access Point Operation Modes • D-Link Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Power Over Ethernet • D-Link Unified Access Point Wireless Antenna Wireless Security • Market Analysis for D-Link Wireless Switch D-Link Wireless Product Wireless Solution Wireless Application • Wireless Switch Deployment Application • Success Stories 2 DCS – Wireless Introduction to Wireless 3 Introduction to Wireless Introduction to Wireless After this session, you should be capable of express: 1. What is wireless LAN technology, its advantages and differences between the wired LAN 2. The evolution of wireless LAN 3. Basic knowledge of wireless technology: What is the minimum requirement to build a WLAN, types of wireless network and stepby-step needed in building WLAN 4 Introduction to Wireless WLAN Technology Wireless LAN Technology Overview Wireless LAN Definition • Advantages of implementing WLAN technology • • • Network infrastructure where all data are being transmitted and received use radio signals over the air instead of wires. Increase mobility Low implementation and network expansion Scalability Differences between wired LAN and wireless LAN Wired LAN • • • • Run network cable installation Limited by network media Depend on physical location Data are sent through network cable Wireless LAN • Not required to run network cable installation • Not limited by network media • Independent on physical location • Data are sent through the air 5 Introduction to Wireless WLAN Technology Comparison between Wired LAN & Wireless LAN Wired LAN Wireless LAN Installation Moderate level of difficulty Easier, but must be careful with the interference issue Cost Less More Reliability High Reasonably High Performance Very Good Good Security Reasonably Good Reasonably Good Mobility Limited Outstanding 6 Introduction to Wireless History of WLAN History of Wireless LAN Below are the evolution of Wireless LAN 1970 1985 1991 1997 • 1970 – ALOHAnet was developed at the University of Hawaii • 1985 – Federal Communication Commission (FCC) announced authorized license-free wireless bands • 1991 – First workshop held by IEEE. WLAN product had been launched, and IEEE had just started to develop wireless standard • 1997 – Federal Communication Commission (FCC) announced authorized wireless equipment which used the license-free bands Page is Animated 7 Introduction to Wireless Basic Knowledge on Wireless Network Basic Component for Wireless Network Basic component for wireless network • Wireless Client/STA – e.g. Wi-Fi Phone, PDA with Wi-Fi built-in, etc – Wireless adapter for client device (used only for client that does not support wireless – Wireless USB Adapter – PCMCIA – Express Card and PICe • Wireless device – Access Point – Wireless Router • Antenna D-Link Wireless USB Adapter D-Link PCMCIA wireless network adapter D-Link Access Point Outdoor Antenna 8 Introduction to Wireless Basic Knowledge on Wireless Network Wireless Network Types Ad-Hoc type (1) • • • Infrastructure type (2) • • Connect to other wireless client devices without the use of any wireless media Useful for establishing a network where wireless infrastructure does not exist or where services are not required Not suitable for large scale network Connect to other wireless client device with the use of any wireless media to act as a central point Suitable to be deployed for a large scale network Hybrid type (3) • • Combination between Ad-Hoc and Infrastructure Sometimes supported. Security problem might appear if clients additionally formed Ad-Hoc network with no or simple authentication 9 Introduction to Wireless Basic Knowledge on Wireless Network Building Wireless LAN Steps in building WLAN • • • • • • Evaluate and assess customer requirements Do site survey activity task Plan and design the solution Choose the right wireless equipment Implement the solution Enhance the network (security, etc) Consideration in building WLAN • Same wireless channel cannot overlap • Same frequency used by other devices may interfere the performance of wireless LAN 10 Introduction to Wireless Summary Summary Using wireless technology, all data are being transmitted and received over the air use radio signal instead of wires. WLAN technology provides more advantages compared to LAN technology, especially in flexibility and mobility. The idea of inventing wireless technology first came on 1970 when ALOHAnet was developed at University of Hawaii and it was continuously improved until now. To build a wireless network, the minimum devices required are Wireless compatible client (or wireless adapter needed for wireless incompatible client) and the wireless device such as access point. Actually, there are two wireless network types: Ad-Hoc type for small network and infrastructure type for bigger network. In building WLAN, there are things needed to be considered and it will be better if we follow the right steps. 11 Introduction to Wireless Questions and Answers Questions and Answers 1. Select options that are not advantages of using wireless technology. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. E. Increase mobility High implementation cost No standardization for wireless technology High scalability Easy network expansion 2. Select characteristics belonging to wireless technology. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. Data are sent through network media Depend on the physical location Not required to run network cable installation Data are sent using radio signal 3. Select year when FCC first announced authorized license-free wireless bands. A. B. C. D. 1970 1985 1991 1997 12 Introduction to Wireless Questions and Answers Questions and Answers 4. Select requirements that are needed when building a wireless network. (Choose two) A. B. C. D. E. Access Point Router Switch Wireless Adapter Bridge 5. Select the statement that best describes Ad-Hoc wireless network type. A. B. C. D. The wireless coverage area is known as Basic Service Set or Cell Require single device that control the communication in the network All clients within the network are equal Suitable to be deployed for a large scale network 13 DCS – Wireless Customer Needs and The Solutions 14 Customer Needs and The Solutions Customer Needs and The Solutions After this section, you should be capable of expressing: 1. Common customer needs when building network infrastructure 2. Solutions that D-Link provide to fulfill all customer needs 15 Customer Needs and The Solutions Common Customer Needs Common Customer Needs when Deploying Network Infrastructure Flexibility Scalability Ease of deployment Secure network infrastructure Simple network management 16 Customer Needs and The Solutions D-Link Solutions for Customer Needs Flexibility We can flexibly connect the WLAN with LAN Receive the packet, Print the documents Shared network printer File Server Get documents from file server Mobile client Layer 2 switch AP receive the packet Forwards the packet to switch Switch receive the packet and forward it to network printer Document to be printed Mobile client Send document to the network printer Page is Animated Mobile client 17 Customer Needs and The Solutions D-Link Solutions for Customer Needs Scalability Network expansion is scalable by adding more wireless devices Shared network printer File Server PDA User Layer 2 switch Additional wireless device Mobile client Existing Network area Page is Animated Mobile client Mobile client New Extended network area 18 Customer Needs and The Solutions D-Link Solutions for Customer Needs Ease of Deployment Customers are not limited to physical area when deploy a wireless network infrastructure, for example: different location in the same building or connect building-to-building wireless infrastructure Less effort in cable installation – Customers do not need to do so much cable installation Minimal Cable installation in the WLAN File Server Shared network printer PDA Layer 2 switch Mobile client Mobile client Mobile client 19 Customer Needs and The Solutions D-Link Solutions for Customer Needs Secure Network Infrastructure Permits only authorized users to connect to the network File Server Shared network printer Layer 2 switch Router Access to network Allowed Authorized Client Join to network, Accessing network resources Access to network denied ✕ Unauthorized client Page is Animated 20 Customer Needs and The Solutions D-Link Solutions for Customer Needs Simple Network Management Administrator or authorized user can simply managed the network infrastructure Easy when do some monitoring task and control network traffics Manage any wireless devices and control network traffics through client’s device AP_1 Page is Animated AP_2 21 Customer Needs and The Solutions Summary Summary When building a network infrastructure, some requirements from the customer that need to be fulfilled are quite common. Generally, the customer wants the network built were deployed easily, provides flexibility, scalability, secured, and easy to manage and monitor. D-Link provides solutions for these customer needs. One of the solutions is implementing wireless technology. D-Link wireless products provide many advantages for customers and is widely known as a powerful device. 22 Customer Needs and The Solutions Questions and Answers Questions and Answers 1. Select common customer needs when deploying network infrastructure. (Choose all that apply) A. Complicated network infrastructure to prevent users from attacking the internal network B. Customers are not limited to physical area when deploying a wireless network infrastructure C. Easy when doing some monitoring task and control network traffics D. High effort in cable installation 23 DCS – Wireless Wireless Standards and Certifications 24 Wireless Standards and Certifications Wireless Standards and Certifications Wireless Standards Wireless Certifications 25 Wireless Standards and Certifications Wireless Standards Wireless Standards After this section, you should be capable of expressing: 1. All wireless standards (802.11a/b/g/n) start from characteristics, differences between each standard 2. Advantages for the newest wireless standard (802.11n) 26 Wireless Standards and Certifications Wireless Standards Overview IEEE Wireless Standard Overview 802.11a – 5GHz, ratified in 1999 (shipping 2001) 802.11b – 11Mbps, 2.4GHz, ratified in 1999 802.11c – MAC-layer bridging (802.1d) 802.11d – Additional regulatory domains (world mode) 802.11e – Quality of Service 802.11f – Inter-Access Point Protocol (IAPP) 802.11g – Higher Data Rate (>20Mbps, actually 54Mbps), 2.4GHz 802.11h – 54Mbps at 5GHz using DFS and TPC (Europe) 802.11i – Authentication and security 802.11j – Japan regulatory conformance 802.11k – Radio Resource Management (Signal Quality, 2004) 802.11m – Various 802.11 improvements (bugfixes) 802.11n – Beyond 100Mbps, longer distances (2007) 802.11p – Wireless Access for the Vehicular Environment (WAVE) 802.11r – Fast roaming 802.11s – Mesh networks 802.11T – Wireless Performance Prediction (WPP), test methods and metrics 802.11u – Interoperability with non-802 networks (e.g. cellular) 802.11v – WLAN Management 27 Wireless Standards and Certifications Ratified Wireless Standards List of Ratified Wireless Standards Standards 802.11a 802.11b 802.11g October 1999 October 1999 June 2003 5 GHz 2.4 GHz 2.4 GHz Throughput (Typical) 23 Mbps 4.3 Mbps 19 Mbps Max. Data Rate 54 Mbps 11 Mbps 54 Mbps OFDM DSSS OFDM ~ 35 meters ~ 38 meters ~ 38 meters ~ 120 meters ~ 140 meters ~ 140 meters Release Date Frequency Modulation Technique Range (Indoor)* Range (Outdoor)** * Range depends on number of walls and the type. ** Range depends on total loss (include any obstacles) 28 Wireless Standards and Certifications Ratified Wireless Standards Comparison of 802.11a/b/g Wireless Standards 802.11a 802.11b 802.11g Speed Fast speed Slow speed Fast speed Compatibility with other 802.11 standards Not compatible with 802.11b/g standards Compatible with 802.11g standard Compatible with 802.11b standard Vulnerable to interference No No No Distance coverage Short distance Long distance Long distance Signal strength due to penetrating obstacles Poor Lower Lower Suitable application Nearby building-tobuilding connection (rarely implemented today) Hotspot area, office, hospital, etc 29 Wireless Standards and Certifications 802.11n Wireless Standard Characteristics of 802.11n on D-Link Products 802.11n ** Release Date Speed Frequency Range September 2009 300 Mbps 2.4GHz and 5.0GHz 250 meters ** 802.11n is still in draft (version 2) and has been not ratified yet, so maximum range value may change 30 Wireless Standards and Certifications 802.11n Wireless Standard Advantages of 802.11n 802.11n - Wide Wireless coverage area Multiple Antenna (MIMO) Optimize data speed and greater coverage area Message received by AP, AP forward the message to client B 802.11b/g 802.11a Client B received the message Start to send message to AP Faster data transfer Wireless client A Client A want to send message to client B Page is Animated Wireless client B 31 Wireless Standards and Certifications Summary: Wireless Standard Summary: Wireless Standard Currently, there are three wireless standards which already ratified by IEEE. Those standards are 802.11a, 802.11b, and 80211g. 802.11a runs on the frequency of 5GHz while 802.11b and 802.11g run on the frequency of 2.4GHz. 802.11a and 802.11g provide 54Mbps of speeds, while 802.11b provides only 11Mbps of speed. The newest wireless standards which has not been ratified yet is 802.11n. It runs on both frequency (2.4GHz and 5.0GHz). D-Link products do support 802.11n standard for both frequencies. The speed for this standard can be up to 300Mbps and provides the farthest signal strength. 32 Wireless Standards and Certifications Questions and Answers: Wireless Standards Questions and Answers: Wireless Standards 1. Select ratified wireless standards that run on 2.4GHz frequency. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. 802.11a 802.11b 802.11g 802.11n 2. Select ratified wireless standards that provide the fastest speed. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. 802.11a 802.11b 802.11g 802.11n 3. Select standard that is least prone to interference. A. B. C. D. 802.11a 802.11b 802.11g 802.11n 33 Wireless Standards and Certifications Questions and Answers: Wireless Standards Questions and Answers: Wireless Standards 4. Select advantages of 802.11n over other wireless standards. (Choose two) A. B. C. D. High level of security Support dual-band operation (2.4GHZ, and 5.0GHz) Least prone to interference The use of MIMO speeds up data transfer 34 Wireless Standards and Certifications Wireless Certifications Wireless Certifications After this section, you should be capable of expressing: 1. What is Wi-Fi Alliance and its purpose 2. Types of certifications defined by the Wi-Fi Alliance along with the general information for each certification 35 Wireless Standards and Certifications Wi-Fi Alliance Wi-Fi Alliance Overview Wi-Fi Alliance is a non-profit international association formed in 1999 to certify interoperability of wireless Local Area Network products based on IEEE 802.11 specification. • 210 member companies from around the world • 865 products have received Wi-Fi® certification • The goal of the Wi-Fi Alliance’s members is to enhance the use experience through product interoperability 36 Wireless Standards and Certifications Types of Certifications Certification defined by Wi-Fi Alliance Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi) Certification • Wi-Fi CERTIFIED logo is the only assurance that a product has met rigorous interoperability testing requirements to ensure that compatible products from different vendors will work together. Wireless Multimedia (WMM) Certification • Technology that maintains the priority of audio, video and voice applications in a Wi-Fi network so that other applications and traffic are less likely to slow them. Wireless Security Certification (WPA/WPA2) • Wi-Fi Alliance has to ensure that all Wi-Fi Certified wireless products must support WPA/WPA2 for the security features Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) Certification • To standardize an easy and secure setup solution for Wi-Fi network • User can configure the home network with WPA2-PSK easily 37 Wireless Standards and Certifications Summary: Wireless Certifications Summary: Wireless Certifications Wi-Fi Alliance is a non-profit international association formed to certify interoperability of wireless Local Area Network products based on IEEE 802.11 specification. Wi-Fi certification ensures that compatible products from different vendors will work together. Wireless Multimedia (WMM) certification is wireless QoS technology that maintains the priority of audio, video and voice applications in a Wi-Fi network so that other applications and traffic are less likely to slow them. Wireless security (WPA/WPA2) certification ensures that all Wi-Fi Certified wireless products must support WPA/WPA2 for security features. 38 Wireless Standards and Certifications Questions and Answers: Wireless Certification Questions and Answers: Wireless Certifications 1. Select certification defined by Wi-Fi Alliance that maintains the priority of audio, video and voice applications in a Wi-Fi network. A. B. C. D. Wi-Fi certification WMM certification Wireless security certification WPS certification 2. Select optional programs provide by Wi-Fi Alliance. (Choose two) A. B. C. D. WMM power save WPA/WPA2 certification Wi-Fi certification Wi-Fi Protected Setup 39 DCS – Wireless Wireless Access Point Operation Modes 40 Wireless Access Point Operation Modes Wireless Access Point Operation Modes After this section, you should be capable of expressing: 1. Types of AP operation modes 2. Characteristics of each AP mode 3. Benefits obtained for each AP mode 4. General illustration on how to deploy each AP mode 41 Wireless Access Point Operation Modes AP Operation Modes Types of AP Operation Modes There are different operation modes where wireless AP can run • • • • • • • Access Point WDS WDS with AP Universal Repeater Wireless Client WISP Repeater* WISP Client Router* * WISP Repeater and WISP Client Router Modes are supported by DAP-1160. 42 Wireless Access Point Operation Modes Access Point Operation Mode Access Point Mode Overview and Illustration Characteristics of AP mode • Device acts as a central connection point for any computer (client) Benefits of using AP mode • • Connect and share network resources from any mobile clients easily Mobile connectivity regardless of the location Hotspot area at a cafe ADSL Ethernet Modem Access Point Café guest Café guest 43 Wireless Access Point Operation Modes WDS Operation Mode Wireless Distribution System Mode Overview Characteristics of WDS mode • Wirelessly connect separate LAN that cannot be connected together with a cable Benefits of using WDS mode • Ease-of-deployment network extension – extend the network without any difficulties, easier than deployment of wired network infrastructure • Cost reduction – customers can connect to the remote network wirelessly at a minimal cost 44 Wireless Access Point Operation Modes WDS Operation Mode WDS Mode Application WDS mode application – Connect Head Office to Branch Office in different locations • Branch office of a training center is located in Street A wants to connect its network to the Head Office located in Street B with a minimal cost. Access point at both of the office must be WDS mode enabled for the two network can be connected A Branch Office Head Office B 45 Wireless Access Point Operation Modes WDS with AP Operation Mode WDS with AP Mode Overview Characteristics of WDS mode with AP • Has the same function with WDS mode, but it can also act as an access point • Client with wireless adapter can wirelessly connect to the AP and then connect to other LAN Benefits of using WDS mode with AP • Ease-of-deployment network extension • Cost reduction – customers can connect to the remote network wirelessly at a minimal cost • Flexibility – connect to any type of network (wired or wireless) 46 Wireless Access Point Operation Modes WDS with AP Operation Mode WDS with AP Mode Application Integrate separate wireless network across the campus buildings in a school • A university needs to interconnect the entire campus which includes main building and remote business-administration faculty campus building where no wired infrastructure existed and it is just 160 meters away from the main building. WDS mode enabled Main campus Area Running AP mode Outdoor AP Indoor AP Mobile users associated to the indoor AP Connected via Ethernet 160m WDS with AP mode enabled BusinessAdministration Faculty Campus Indoor AP Mobile users associated to the AP 47 Wireless Access Point Operation Modes Universal Repeater Operation Mode Universal Repeater Mode Overview Characteristics of universal repeater mode • Increase the range of the wireless network by extending the wireless coverage of another AP or wireless router without the need to cable installation • The use of universal repeater mode in an access point will gain an extra 50% coverage area • Universal repeater mode means that this mode can be used in any types of access point regardless their brand Benefits of universal repeater mode • Expand wireless coverage area • Increase users mobility 48 Wireless Access Point Operation Modes Universal Repeater Operation Mode Universal Repeater Mode Application Office area expansion due to new formed department • When a new department is formed, it means more space from the office will be needed. Universal repeater mode can be used to expand the coverage area, so new department can be easily connected to the existing wireless infrastructure. NO cable installation needed Office area expanded Wired network Access Point running repeater mode Two APs connect wirelessly PDA user Access Point Mobile user Mobile user 49 Wireless Access Point Operation Modes Wireless Client Operation Mode Wireless Client Mode Overview and Application Characteristics of wireless client mode • • The AP running wireless client mode enabled a wired device to act wirelessly as if it is a wireless device AP with wireless client mode enabled will not be visible as an access point. Hence, it will not accept any wireless connections from client devices. Benefits of using wireless client mode • Alternation solution to make a wired device to become a wireless device Wireless client mode enabled Access point mode Wired IP Camera Ethernet switch Access Point Enabled the wired device (i.e. IP camera) to act as a wireless device Mobile user Ethernet client 50 Wireless Access Point Operation Modes WISP Operation Mode WISP Repeater Mode Overview and Application Wireless Internet Service Provider (WISP) Repeater mode / Client Router mode • Characteristics of WISP Repeater mode – The device wirelessly connects to a WISP AP – It also acts as a router and share Internet connection for both wired and wireless clients on the network • Benefits of using WISP Repeater mode – Share Internet access to all clients without the need of extra device Antenna directed Signal directed to the WISP Running WISP to WISP Repeater mode Access Point WISP Client www.google.com Share WISP connection to both wired and wireless client The AP repeats the signal received from the WISP www.yahoo.com Subscribe internet connection from WISP Mobile users can surf to the internet 51 Wireless Access Point Operation Modes WISP Operation Mode WISP Client Router Mode Overview and Application Wireless Internet Service Provider (WISP) Client Router Mode • Characteristics of WISP client router mode – The device wirelessly connect to a WISP AP – It also acts as a router for wired clients and provides Network Address Translation (NAT) and DHCP server (generate IP addresses for wired clients) • Benefits of using WISP client router mode – The WISP subscriber can share the WISP connection without the need for extra router. Signal directed to the WISP Antenna directed to WISP Access Point www.google.com WISP Client Running WISP Client router mode Share Internet connection to the wired clients www.yahoo.com Subscribe internet connection from WISP Users from the wired LAN can surf to the internet 52 Wireless Access Point Operation Modes Summary Summary D-Link wireless access points provide six operation modes which are AP mode, WDS mode, WDS with AP mode, universal repeater mode, wireless client mode and WISP repeater modes. AP mode functions as a central connection point for any computers (clients) WDS mode allows to connect multiple wireless LANs together (connect separate network wirelessly). WDS with AP mode connect separate networks wirelessly while also functions as a central connection point for any clients. Universal repeater mode allows to repeat the wireless signal of the root access point. Wireless client mode allows any device with an Ethernet connect to connect to the wireless network. WISP repeater mode enabled AP function to share Internet connection to all the clients without the need of extra device. 53 Wireless Access Point Operation Modes Questions and Answers Questions and Answers 1. Select operation modes that can be used to connect separate remote networks. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. E. Access Point mode WDS mode WDS with AP mode Universal Repeater mode WISP Repeater mode 2. Select operation modes that do not allow clients to associate to the AP. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. E. WDS mode WDS with AP mode Universal Repeater mode Wireless Client mode WISP Repeater 54 DCS – Wireless Power over Ethernet 55 Power over Ethernet Power over Ethernet After this section, you should be capable of expressing: 1. What is Power over Ethernet technology (characteristics and benefits) 2. When is the most suitable time to implement PoE 3. How to implement PoE technology 56 Power over Ethernet Overview Power over Ethernet (PoE) Overview Characteristics of PoE device • • • Based on IEEE 802.3af standardization It delivers electrical power (DC voltage) to a device over the same network cable which is used to send data Used when the AC power supply is not available at the location where the wireless LAN infrastructure devices are installed Benefits of PoE devices • • Increase flexibility – clients can locate the access point anywhere without having to consider the existence of power outlet Managed fewer cable to the power outlet. This will make the wireless infrastructure deployment easier. PoE Switch Distribute electrical power Power Access Point Power Power Send and receive data traffic Access Point Send and receive data traffic Access Point 57 Power over Ethernet Application of PoE Power over Ethernet Application Setting an access point at the roof top of a building • • An outdoor access point must be placed at the roof top of a building. This seems to be an easy task, but what makes it difficult is to think how to plug the AP to the power outlet (there is no power outlet at the roof top). The easiest solution is using PoE switch which can delivers power to the AP. Just connect the AP to any of the switch port and connect the PoE switch to power outlet. The problem is now solved. Connected using network cable Impossible to plug the AP directly to power outlet for this condition Outdoor Access Point Ethernet Switch Located somewhere at the building within 100metres from the AP 58 Power over Ethernet Summary Summary Device provides PoE feature can deliver electrical power (DC voltage) to a device over the same network cable which is used to send data. It is based on IEEE 802.3af standardization. PoE can be used when the AC power supply is not available at the location where the wireless LAN infrastructure devices are installed. 59 Power over Ethernet Questions and Answers Questions and Answers 1. Select statement that is not characteristics of PoE devices A. B. C. D. Based on IEEE 802.3ad standardization Deliver electrical power (DC voltage) Use the same network cable to send data None of the above 2. Select the most common implementation of PoE A. B. C. D. Deliver electrical power to all network devices in the server room Place an access point at the roof top of a building Network deployment in the Campus environment All of the above 60 DCS – Wireless Wireless Antenna 61 Wireless Antenna Wireless Antenna After this section, you should be capable of expressing: 1. Types of wireless antenna and the characteristics 2. Differences between each antenna 3. Suitable condition to use each antenna 4. Models of wireless antennas 62 Wireless Antenna Overview Wireless Antenna Characteristics and Types Characteristics of wireless antenna • Used on wireless devices (APs, wireless bridges, wireless routers) • Increase the output signal strength from a wireless device • Receives wireless signals from other devices such as wireless client Types of wireless antenna • Omni-directional antenna / Dipole antenna – Antenna which radiates the signal to all directions • Semi-directional antenna – Antenna which radiates the signal to certain direction in a shorter but wider coverage area • Highly-directional antenna – Antenna which radiates the signal to certain direction in a longer but narrower distance coverage area 63 Wireless Antenna Types of Wireless Antennas Omni-Directional / Dipole Antenna Characteristics of omni-directional antenna • • • The most common wireless LAN antenna The signal radiates equally in all directions Suitable to be deployed in office area or in a building which connect multiple networks from any directions As long as users are inside the coverage area, they still can receive the signal Mobile user Signal Received ✕ Outside the coverage area, user can not receive the signal Mobile user 360° signal radiation Signal Received Page is Animated PDA user All wireless device around the antenna can receive the signal 64 Wireless Antenna Types of Wireless Antennas Semi-Directional Antenna Characteristics of semi-directional antenna • • • Radiate the signal in a certain direction Suitable for short coverage area Commonly deployed in an office or an area where the coverage area is limited or to prevent the wireless coverage goes throughout the area which allows the stranger to access the wireless resources Office area Can not access to network Wireless coverage area Shorter but wider Mobile user Outside the coverage area Semidirectional antenna 65 Wireless Antenna Types of Wireless Antennas Highly-Directional Antenna Characteristics of highly-directional antenna • • Similar to semi-directional antenna which radiates the signal only to certain direction but with longer distance of the signal radiation Commonly deployed to connect building-to-building or area-to-area where the distance is quite far but the signal only needs to radiate to the remote building/area (certain direction) Signal radiation is longer but narrower Office A Separated to different location Office B 66 Wireless Antenna Models of D-Link Wireless Antennas Indoor Antenna Directional Antenna DWL-R60AT ANT24-0600 Omni-Directional Antenna ANT24-0501 ANT24-0700 DWL-50AT ANT24-0502 ANT24-0501c ANT24-0700c 67 Wireless Antenna Models of D-Link Wireless Antennas Outdoor Antenna Directional Antenna for Point-to-Point transmission ANT24-0801 ANT24-1400 ANT24-1201 ANT70-1000 ANT24-1800 ANT24-1801 ANT24-1200 ANT70-1800 68 Wireless Antenna Models of D-Link Wireless Antennas Outdoor Antenna Omni-Directional Antenna for Point-to-Multi-Point transmission ANT24-0800 ANT24-0500 ANT70-0800 ANT70-0801 New Product Sector Antenna Locate Omni-Directional Antenna here 69 Wireless Antenna Maximum Distance of D-Link Wireless Antennas Maximum Distance of D-Link Wireless Antennas PtMP(Omni) Outdoor 2km~5km 5dBi 8dBi Outdoor 500m~2km 14dBi ANT24-0500 18dBi PtMP(Dir.) Omni 8dBi ANT24-0800 ANT70-0800 ANT70-0801 PtP(Dir.) Patch ANT24-1800 ANT24-1801 ANT70-1800 (5GHz) 8.5dBi 12dBi ANT24-0801 ANT24-1200 ANT70-1000 ANT24-CB03N ANT24-CB06N ANT24-CB09N ANT24-1201 6dBi Patch ANT24-1400 ANT70-1800 (2.4GHz) ANT24-CB03N ANT24-CB06N ANT24-CB09N 0.5km 1.0km 1.5km 2.0km 2.5km 3.0km (5.5km) 70 Wireless Antenna Summary Summary There are three types of wireless antennas: Omni-directional / dipole antenna, semi-directional antenna, and highly directional antenna. Omni-directional antenna is used to radiates the signal to all directions. Semi-directional antenna is used to radiates the signal to certain direction in a shorter but wider coverage area. Highly-directional antenna is used to radiates the signal to certain direction in a narrower but longer distance of the signal radiation. There are both indoor antenna and outdoor antenna. 71 Wireless Antenna Questions and Answers Questions and Answers 1. Select wireless antennas that radiate signal only to certain direction. (Choose two) A. B. C. D. Omni-directional antenna Dipole antenna Semi-directional antenna Highly-directional antenna 2. Select wireless antenna that is most suitable to connect two buildings. A. B. C. D. Omni-directional antenna Dipole antenna Semi-directional antenna Highly-directional antenna 3. Select the advantages of using wireless antenna. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. Increase the output of signal strength receives from wireless device\ Receive wireless signal from wireless clients Prevent unauthorized user from receiving the signal from the AP Classified into the way it radiates the signal 72 DCS – Wireless Wireless Security 73 Wireless Security Wireless Security After this section, you should be capable of expressing: 1. Risks of deploying WLAN 2. How to overcome security issues (the risk of deploying WLAN) 3. Characteristics of WEP, WPA/WPA2 and the differences between each other 4. What is RADIUS and the way it authenticates users 5. What is MAC filtering 74 Wireless Security Risk of WLAN Risk of Deploying Wireless LAN (1) Unauthorized users may access the network facilities such as Internet connection freely Wireless coverage area excess the office This may allow unauthorized users to access network resources from the office Unauthorized user Page is Animated DANGER!!! Wireless network detected!!! Try to connect to the network… Wireless network connected successfully!!! 75 Wireless Security Risk of WLAN Risk of Deploying Wireless LAN (2) Some people try to get some important / confidential data sent through the air by using wireless Hotspot area Access Point DANGER!!! RECEIVE ALL the data (Password, Credit card number, etc) User A is browsing the Internet and send confidential data User A The hacker comes in and try to sniff the data Confidential data is send to the AP Hacker Data SNIFFED!!! Risk of WLAN in public area Page is Animated 76 Wireless Security Solutions for Security Issues Solutions for Security Issues Overview Configure wireless security on your WLAN with one or more of the methods below • Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) – Weak authentication method using static key • Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA/WPA2) – Strong authentication method using dynamic key • Remote Access Dial-Up Service (RADIUS) – Centralized authentication user’s protocol • MAC Filtering / IP Filtering – Allow clients to join the network based on client’s MAC address / IP address • WLAN Partition – Isolate the wireless network, so mobile clients are not allowed to exchange data through the access point 77 Wireless Security Solutions for Security Issues Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) Overview Characteristics of WEP • Most basic security for wireless LAN • Commonly used for home users, but is not suitable to be implemented for enterprise environment • All the clients must share the same key with the one configured in the access point in order to communicate with each other Weaknesses of WEP • Password hold by all clients is never changed unless the administrator change it (static key) • Most vulnerable security type which can be easily cracked by using hacking tools 78 Wireless Security Solutions for Security Issues Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) Illustration Illustration on how WEP works I want to join the network User A and user B want to connect to the network Shared Key = abc Shared Key = abc User A Send request for association Access point configured with WEP ➀ Receive the request I also want to join the network Shared Key = xyz ➀ User B Send request for association I’ve received the requests, ➁ Challenge What is the shared key? Challenge ➂ Respond the challenge ➂ Respond the challenge Key = xyz Key = abc User A welcome to the network!!! ➃ User A, Password matched. User authenticated Password matched User B, Password unmatched. ➄ Request rejected Password unmatched Page is Animated ➁ Request rejected Association failed 79 Wireless Security Solutions for Security Issues Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) Overview Characteristics of WPA • Improved version of WEP • This infrastructure includes clients, access points and authentication servers (typically RADIUS servers) • Key always changes automatically (dynamic key) Benefits of using WPA instead of WEP • Provide a stronger method of authentication compared to WEP 80 Wireless Security Solutions for Security Issues WPA2 Overview Characteristics of WPA2 • • • • Personal mode – protects unauthorized network access by utilizing a set-up password Enterprise mode – Authenticate network clients through a server, usually is RADIUS server Compatible (can communicate) with device secured using WPA authentication method Similar to WPA authentication method, the main difference is that WPA2 uses more advanced encryption technique WPA WPA2 Enterprise Mode (Business, Government, Education) Authentication: IEEE 802.1X/EAP Encryption: TKIP/MIC Authentication: IEEE 802.1X/EAP Encryption: AES-CCMP Personal Mode (SOHO, Home/Personal) Authentication: PSK Encryption: TKIP/MIC Authentication: PSK Encryption: AES-CCMP Different authentication methods for different environment 81 Wireless Security Solutions for Security Issues WPA / WPA2 Illustration WPA / WPA2 provide stronger authentication method with dynamic encrypted key per user, per session, and per packet data User want to send data Access Point configured with WPA/WPA2 Mobile user Encrypted key Request for association Key matched! Allow the user to join the network Compare the encrypted key Client join the network successfully Data + key1 Compare the encrypted key Key matched! Data received Every time user send data to the AP, the data will sent along with dynamic key Page is Animated 82 Wireless Security Solutions for Security Issues Differences between WEP, WPA and WPA2 Differences between WEP – WPA – WPA2 are shown in the table below Encryption method Security level Main characteristic WEP WPA WPA2 WEP/RC4 TKIP/RC4 CCMP/AES Weak Strong Strongest Use static key Use dynamic key Use dynamic key 83 Wireless Security Solutions for Security Issues Remote Access Dial-Up Service Overview Characteristics of RADIUS • A protocol for centralized remote user authentication and accounting • RADIUS stores the authentication data either locally at the RADIUS server or in an external database • RADIUS accounting can be used independently to log certain events Benefits RADIUS • RADIUS enables centralized management of authentication data, such as usernames and passwords • Significantly increase security by enabling the centralization of password management 84 Wireless Security Solutions for Security Issues Step-by-Step RADIUS Operation Steps which are done by RADIUS to authenticate the client 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Client attempts to connect to the access point Access point prompts for username and password or challenge User replies RADIUS client sends username and encrypted password to the RADIUS server RADIUS server responds with Accept, Reject When access-accept message received and RADIUS accounting is enabled, access point sends a RADIUS Accounting-Request (Start) message to the RADIUS Server RADIUS Server RADIUS Client Mobile user 1 Access Point 2 Authentication process 3 4 Authorization process 5 6 Accounting process Server adds an accounting record to its log and acknowledges the request 85 Wireless Security Solutions for Security Issues MAC Filtering Overview Characteristics of MAC Filtering • • Easily control which computers can gain access to the network based on specific MAC address Rarely used as a single method because it can be hacked easily by anyone using tools that can alter the MAC address on the wireless adapter Advantages of MAC Filtering • It does not affect the network performance User A attempt to join the network User A MAC: AA User E attempt to join the network Allow User A to join the network User E cannot join the network List of allowed MAC address AA BB CC AP check client’s MAC address from the database MAC address is in the list MAC address is not in the list User E MAC: EE Page is Animated 86 Wireless Security Summary Summary When deploying wireless technology in a network, security becomes the main issue. Some risks such as unauthorized users trying to access internal network or get some important/confidential data sent through the air by using wireless have to be considered. To prevent these unwanted conditions, security enhancement is needed. This can be achieved by configuring security method to the network. Methods provided are by applying authentication to all users with one of the following: WEP, WPA, WPA2 or using RADIUS authentication. Other methods that can be additional security enhancement is implementing MAC filtering. 87 Wireless Security Questions and Answers Questions and Answers 1. Select security method that provides the weakest authentication method using static key. A. B. C. D. WEP WPA WPA2 MAC Filtering 2. Select the reason why WPA2 is more superior than WPA. A. B. C. D. It protects unauthorized network access by utilized a dynamic key The encryption of data is upgraded with Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) It can filter users based on specific physical address It enables centralized management of authentication data 3. Select the statement that does not describe RADIUS. A. Protocol for centralized user authentication and accounting B. Provide three steps of operation which include authentication, authorization and accounting C. The accounting features of the RADIUS protocol cannot be used independently of RADIUS authentication or authorization D. Centralized password management 88 Wireless Security Questions and Answers Questions and Answers 4. Select statements that describe MAC filtering. (Choose all that apply) A. Often used as single security method B. Strongest authentication method because MAC address cannot be modified C. Control access to the network based on specific logical address D. Control access to the network based on specific physical address 89 DCS – Wireless D-Link Wireless Product 90 D-Link Wireless Product D-Link Wireless Product After this section, you should be capable of expressing: 1. Features for each D-Link Access Point 2. Feature differences between D-Link Access Points 91 D-Link Wireless Product D-Link Indoor Access Points DWL-2100AP Features Overview Configurable Operation Modes • • • • • Access Point WDS with AP WDS AP Repeater AP Client Connectivity Performance • 802.11g wireless standard • Up to 108Mbps (Turbo Mode) Wireless Speed • Wireless connection to Ethernet network / servers through 10/100BASE-TX port • AP grouping for Load Balancing Security / QoS • • • • Setup / Management • • • • • • 64/128/152-bit WEP data encryption WPA/WPA2 Personal and Enterprise security with TKIP and AES support User access control MAC address filtering Wireless Station Partition (STA), 802.1Q VLAN tagging and Multiple SSID (Up to 8) for network segmentation • WMM (Wi-Fi) Multimedia Certified Windows-based AP manager utility Web-based management with SSL Remote management using Telnet or SSH Built-in MIB for SNMP management (SNMPv3) IP address limit for management access System log 92 D-Link Wireless Product D-Link Indoor Access Points DWL-2200AP Features Overview Configurable Operation Modes • Access Point • WDS with AP • WDS Connectivity Performance • • • • • Security / QoS • • • • Setup / Management • • • • • 802.11g wireless standard 802.3af Power over Ethernet Up to 108Mbps (Turbo Mode) Wireless Speed Wireless connection to Ethernet network / servers through 10/100BASE-TX port AP grouping for Load Balancing 64/128/152-bit WEP data encryption WPA/WPA2 Personal and Enterprise security with TKIP and AES support User access control MAC address filtering Wireless Station Partition (STA), 802.1Q VLAN tagging and Multiple SSID (Up to 4) for network segmentation • WMM (Wi-Fi) Multimedia Certified Windows-based AP manager utility Web-based management (HTTP) Remote management using Telnet Built-in MIB for SNMP management (SNMPv3) System log 93 D-Link Wireless Product D-Link Indoor Access Points DWL-3200AP Features Overview Configurable Operation Modes • Access Point • WDS with AP • WDS Connectivity Performance • 802.11g wireless standard • 802.3af Power over Ethernet • Up to 108Mbps (Turbo Mode) Wireless Speed Security / QoS • • • • Setup / Management • • • • • 64/128/152-bit WEP data encryption WPA/WPA2 Personal and Enterprise security with TKIP and AES support User access control MAC address filtering Wireless Station Partition (STA), 802.1Q VLAN tagging and Multiple SSID (Up to 8) for network segmentation • WMM (Wi-Fi) Multimedia Certified • Rogue AP detection Windows-based AP manager utility Web-based management (HTTP and HTTPS) Remote management using Telnet and SSH Built-in MIB for SNMP management (SNMPv3) System log 94 D-Link Wireless Product D-Link Indoor Access Points DWL-7100AP Features Overview Configurable Operation Modes • • • • Access Point WDS (PtP, PtMP) Repeater Wireless Client Connectivity Performance • 802.11a/b/g wireless standards • 802.3af Power over Ethernet • Up to 108Mbps (Turbo Mode) Wireless Speed Security / QoS • • • • 64/128/152-bit WEP data encryption WPA Personal and Enterprise security with TKIP and AES support User access control MAC address filtering Wireless Station Partition (STA) Setup / Management • • • • • Windows-based AP manager utility Web-based management (HTTP) Remote management using Telnet Built-in MIB for SNMP management (SNMPv3) System log 95 D-Link Wireless Product D-Link Indoor Access Points DWL-82000AP Features Overview Configurable Operation Modes • Access Point • WDS with AP • WDS/Bridge (No AP Broadcasting) Connectivity Performance • • • • Security / QoS • • • • • Setup / Management • • • • • 802.11a/g wireless standard Dual-band operation (2.4GHz and 5GHz) Up to 108Mbps (Turbo Mode) Wireless Speed Dual Ethernet ports with 802.3x flow control 64/128/152-bit WEP data encryption WPA/WPA2 Personal and Enterprise security with EAP and PSK support WPA PSK/AES over WDS User access control MAC address filtering Wireless Station Partition (STA), 802.1Q VLAN tagging and Multiple SSID (Up to 16) for network segmentation • WMM (Wi-Fi) Multimedia Certified • Rogue AP detection Windows-based AP manager utility Web-based management (HTTP and HTTPS) Remote management using Telnet and SSH Built-in MIB for SNMP management (SNMPv3) System log 96 D-Link Wireless Product D-Link Outdoor Access Points DWL-2700AP Features Overview Configurable Operation Modes • Access Point • WDS with AP • WDS Connectivity Performance • • • • • • Security / QoS • • • • • Setup / Management • • • • • 802.11g wireless standard 802.3af Power over Ethernet Up to 108Mbps (Turbo Mode) Wireless Speed Dual Ethernet ports with 802.3x flow control Load Balancing Wireless connection to Ethernet network/servers through 10/100BASE-TX port 64/128/152-bit WEP data encryption WPA/WPA2 Personal and Enterprise security with EAP and PSK support WPA PSK/AES over WDS User access control MAC address filtering Wireless Station Partition (STA), 802.1Q VLAN tagging and Multiple SSID (Up to 8) Multiple SSID for network segmentation • WMM (Wi-Fi) Multimedia Certified • Rogue AP detection Windows-based AP manager utility Web-based management (HTTP and HTTPS) Remote management using Telnet and SSH Built-in MIB for SNMP management (SNMPv3) System log 97 D-Link Wireless Product D-Link Outdoor Access Points DWL-7700AP Features Overview Configurable Operation Modes • Access Point • WDS with AP • WDS Connectivity Performance • • • • 802.11a/g wireless standards 802.3af Power over Ethernet Load Balancing Wireless connection to Ethernet network / servers through 10/100BASETX port Security / QoS • • • • 64/128/152-bit WEP data encryption WPA/WPA2 Personal and Enterprise security with EAP and PSK support User access control MAC address filtering Wireless Station Partition (STA), 802.1Q VLAN tagging and Multiple SSID (UP to 4) for network segmentation Setup / Management • • • • • Windows-based AP manager utility Web-based management Remote management using Telnet Built-in MIB for SNMP management (SNMPv3) System log 98 D-Link Wireless Product D-Link Outdoor Access Points DAP-3220 Features Overview Characteristics • • • • Water / dustproof IP65 standard Internal thermostat and heater Steal-proof design Convenient outdoor installation with locking brackets included Configurable Operation Modes • • • • Access Point WDS with AP WDS Wireless Client Connectivity Performance • 802.11g wireless standard • Up to 108Mbps Wireless Speed (when operating with other D-Link 108G devices) • 802.3af Power over Ethernet Security / QoS • • • • • • • Multiple SSID and 802.1Q VLAN tagging MAC address filtering Rogue AP detection WPA/WPA2 Personal / Enterprise WPA PSK/AES over WDS 64/128/152-bit WEP Encryption WMM (QoS) Setup / Management • • • • Web browser (HTTP / HTTPS) CLI using Telnet / SSH SNMPv3 (D-View module / private MIB) AP Manager II Software included 99 D-Link Wireless Product Summary Summary D-Link provides several access points with various features where users can choose it flexibly depends on their requirements. D-Link provides two types of access points: indoor access points and outdoor access points. For indoor access points, the models are DWL-2100AP, DWL2200AP, DWL-3200AP, DWL-3260AP, DWL-7100AP, DWL-8200AP. For outdoor access points, the models are DWL-2700AP, DWL7700AP, DAP-3220. DAP-3220 is D-Link new model for outdoor AP. 100 D-Link Wireless Product Questions and Answers Questions and Answers 1. Select D-Link outdoor access point models. (Choose two) A. B. C. D. DWL-2200AP DWL-2700AP DWL-7100AP DWL-7700AP 2. Select D-Link indoor access point models. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. E. DWL-2100AP DWL-2200AP DWL-2700AP DWL-7100AP DWL-7700AP 3. Select model that can run on either 2.4GHz or 5GHz frequency. A. B. C. D. DWL-2100AP DWL-2200AP DWL-2700AP DWL-8200AP 101 DCS – Wireless Wireless Solution 102 Wireless Solution Wireless Solution After this section, you should be capable of expressing: 1. What is Multiple SSID 2. Characteristics and benefits of deploying wireless WLAN 3. When to deploy wireless VLAN 4. Characteristics and advantages of wireless roaming 5. Characteristics and benefits of 802.1p priority queue 6. What is rogue AP detection and the benefits of this feature 7. What is SNMP 8. What is D-View SNMP Network Management System and its benefits 9. Characteristics and benefits of QoS WMM 103 Wireless Solution Wireless VLAN Multiple SSID By assigning multiple SSIDs to the access point, it logically divides the access point into several virtual access point within a single hardware device. Each Virtual AP appears to stations (STAs) to be an independent physical AP. Virtually divided into several APs Virtual AP Virtual AP SSID_1 Virtual AP SSID_2 SSID_3 Wireless network detected!!! SSID_1, SSID_2, SSID_3 Multiple SSID Mobile user 104 Wireless Solution Wireless VLAN Wireless VLAN Overview Characteristics of wireless VLAN • Wireless VLANs define the area where clients are logically grouped into one segment • In the wireless VLANs, multiple SSIDs are applied (each VLAN hold different SSIDs) • Each SSID is mapped to a VLAN-ID Benefits of deploying wireless VLAN • Segment users into different department without additional device • Enable the separation of wireless applications based on security and performance requirements 105 Wireless Solution Wireless VLAN Common Wireless VLAN Infrastructure Wireless VLAN applied in the office which consist of two departments (Operational and Marketing). There are three VLANs configured for each department and for guests to separate the company’s policies between each VLAN. SSID=Operational AP_1 802.1q trunk SSID=Marketing Layer 3 Switch AP_2 SSID VLAN ID Security Policy Marketing 20 WPA/WPA2 Operational 30 WPA/WPA2 Guest 40 Open 802.1q trunk SSID=Operational SSID=Guest SSID=Marketing 106 Wireless Solution Roaming Wireless Roaming Overview Characteristics of wireless roaming • Enables personalized, seamless and secure connectivity for mobile customers when moving across different WLANs. • Wireless Roaming maintains client’s connectivity so that clients do not need to re-authenticate and re-login every time they move to different WLANs. Advantages of wireless roaming • Increased effectiveness • Increased flexibility 107 Wireless Solution Roaming Common Application of Wireless Roaming User attempt to connect to AP User connected to network A The user is moving User disconnected from the network PDA User Page is Animated The user is moving again User attempt to connect to AP User connected to network B Network A Network B Access Point Access Point PDA User PDA User 108 Wireless Solution Priority Queue Priority Queue (802.1p) Overview Characteristics of 802.1p Priority Queue • A specification to give Layer 2 switches the ability to prioritize traffic (and perform dynamic multicast filtering) • Eight classes of traffic types are defined by 802.1p Benefits of 802.1p Priority Queue • Critical data traffic can be prioritized 109 Wireless Solution Rogue AP Detection Rogue AP Detection Overview Typically, rogue APs are connected to a network by well-intentioned employees unaware of the security risks they cause Advantages of rogue AP protection • • • Automatically detect rogue AP based on criteria specified by the administrator Administrator can add rogue APs to the AP list Better control of the network’s environment which will help to avoid RF interference and minimize bandwidth utilization 110 Wireless Solution Single Network Management Protocol SNMP Overview Definition of SNMP • • Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a set of protocols for managing complex networks used in network management systems to monitor networkattached devices for conditions that warrant administrative attention. SNMP enables network administrators to manage network performance, find and solve network problems, and plan for network growth Implementation of SNMP • An SNMP-managed network consists of three key components: managed devices, agents and network-management systems (NMSs) 111 Wireless Solution Single Network Management Protocol D-View SNMP Network Management System D-View Overview • D-Link SNMP Network Management System is a comprehensive standard-based management tool designed to centrally manage critical network characteristics such as availability, responsiveness, resilience and security in a consistent way. • D-View provides useful tools to allow the user to effectively manage device configurations, fault tolerance, performance, security and accounting services Features and benefits • • • • • Modular architecture Managing third-party devices Microsoft Access format database Versatile features User Account Management & Billing System Outfitted in Professional Version 112 Wireless Solution Quality of Service Quality of Service - WMM Characteristics of QoS (Wi-Fi Multimedia) • Provides basic QoS features to IEEE 802.11 networks • WMM prioritizes traffic according to the four ACs (Access Categories) – voice, video, best effort, and background • Suitable for simple applications that require QoS, such as VoIP on Wi-Fi phones Advantages of WMM • • • • • • • Interoperability Availability Wide appeal User confidence Coexists with devices that do not support WMM Adapts well to dynamic data rates Compatible with Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) QoS 113 Wireless Solution Summary Summary Multiple SSID is used to logically devices the access point into several virtual access point within a single hardware device. Multiple SSID is usually applied when implement wireless VLAN. Wireless VLAN enables the separation of wireless applications based on security and performance requirements. Wireless Roaming maintains client’s connectivity so clients do not need to re-authenticate and re-login every time they move to different WLAN. 802.1p is a specification to give Layer 2 switches the ability to prioritize traffic (and perform dynamic multicast filtering). Rogue AP detection is used to detect rogue AP based on criteria specified by the administrator. Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) enables network administrators to manage network performance, find and solve network problems, and plan for network growth. WMM prioritizes traffic to 802.11 networks according to the four ACs (Access Categories) – voice, video, best effort and background. 114 Wireless Solution Questions and Answers Questions and Answers 1. Select two options that are required to deploy wireless VLAN. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. Multiple SSID is applied To deploy VLAN, users from different group must be associated to different AP One SSID is used to all VLANs in the network Each SSID is mapped to a VLAN ID 2. Select feature that enable consistent connectivity for mobile customers when moving across different WLAN. A. B. C. D. Wireless VLAN Wireless roaming Quality of Service Priority Queue 3. Select advantages of Rogue AP Protection feature. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. Remove rogue AP found from the network Blacklist all rogue AP found in the network automatically Avoid RF interference Minimize bandwidth utilization 115 Wireless Solution Questions and Answers Questions and Answers 4. Select categories uses to prioritize data traffic in the network using WMM. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. Voice Video Foreground Data size 5. Select traffic type that are defined by 802.1p. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. Data-critical traffics Delay-sensitive applications Control-Load applications Background applications 116 DCS – Wireless Wireless Application 117 Wireless Application Wireless Application After this section, you should be capable of expressing: 1. Where wireless technology is usually applied 118 Wireless Application Application Illustration Example Small Office Home Office (SOHO) Wireless application are now commonly used in the SOHO or small business environment, where there is one (or more) access point connect to the LAN and WLAN. Sometimes, it also connects to the Internet for the client to gain access to it. Small office layout Ethernet client Network printer Access Point Connect WLAN and LAN Meeting Area Etherne t client Wireless router For Internet sharing Mobile users 119 Wireless Application Application Illustration Example Extending Existing Network Infrastructure Wireless network can serves as a network extension which connect to the wired network or connect to another wireless network in different location. For example, there are another network in different floor or even in different building. Different networks can be connected Wired network Warehouse areal Server Farm Mobile client PDA client Antenna PDA client Mobile client Mobile client Office Area Page is Animated 120 Wireless Application Application Illustration Example Network Infrastructure in Public Area for Mobile Computing Wireless network mainly supports mobility and flexibility where mobile users can gain network access easily. Nowadays, there are many public area facilitate wireless hotspot area, for example: Malls, Cafes, Hospitals, etc. Hotspot area at a restaurant Wireless coverage area Mobile user Access point Mobile user PDA user 121 Wireless Application Application Illustration Example Connecting Network Between Two Buildings Wireless network can implemented to connect two buildings at different areas. One real case that had been implemented recently in Singapore was deployment of wireless network infrastructure as a backup connection to provide redundancy from Mount Faber cable car station to Harbourfront Tower 2 cable car station to cable station at Sentosa Island. Deploy wireless network infrastructure to Sentosa Island Located at two different location Office A Office B 122 Wireless Application Site Survey Consideration Site Survey Consideration Main Point • • Decide type and model of antenna that will be used Decide the quality of the antenna Second Point • • • Consider the interference issue (building, tower, trees, etc) Consider the throughput require and distance between building (Point-to-Point or Point-to-Multi-Port) Consider the number of base stations Max. distance supported Total bandwidth given. (E.g. 11Mbps) 123 Wireless Application Deploy a Wireless Application Wireless ISP Application Equipment Required: • • • • • 1, 2 Omni-directional antenna Directional antenna Outdoor access point Wireless router Wireless LAN card 3 Deployment Steps: 1. Select a center location 2. Setup AP and outdoor omnidirectional antenna 3. Setup modem to connect to the Internet 4. Setup directional antenna to receive the signal from the center 5. Use wireless LAN card to receive the signal from the outside 4 5 124 Wireless Application Deploy a Wireless Application School Roaming Application Equipment Required: • • • Omni-directional antenna Directional antenna Outdoor access point Deployment Steps: 1. Use wireless technology using 5.0 GHz of frequency (low noise) as a backbone 2. Setup directional antenna to receive the signal from the backbone 3. Setup Omni antenna to transmit signal for students using roaming by 2.4GHz) 125 Wireless Application Summary Summary There is no (or few) restrictions when deploying wireless network. Its flexibility makes wireless technology to be widely applied for most conditions and requirements. Wireless technology can be applied in SOHO, to extend existing network infrastructure, to provide Internet connectivity in public area, to connect remote networks and many more. 126 Wireless Application Questions and Answers Questions and Answers 1. Select common purposes when implement wireless technology. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. Connect networks between buildings Shrink existing network infrastructure Increase mobility and flexibility All of the above 127 DCS – Wireless D-Link Unified Access System 128 D-Link Unified Access System D-Link Unified Access System Unified Access System Overview D-Link Unified Wireless Switch D-Link Wireless Switch Features and Advantages D-Link Unified Access Point Market Analysis for D-Link Wireless Switch Wireless Switch Deployment Application Success Stories 129 D-Link Unified Access System Unified Access System Overview Unified Access System Overview After this section, you should be capable of expressing: 1. Characteristics of legacy WLAN deployment 2. What are common customer needs to improve legacy WLAN deployment 3. Solutions provided by D-Link for these customer needs 4. What is Unified Access System Solution 5. How to deploy unified access system using overlay solution or unified solution 130 D-Link Unified Access System Legacy WLAN Deployment Characteristics of Legacy WLAN Deployment Server Farm Layer 3 Switch Layer 2 switch Decentralized AP configuration, security and management Layer 2 switch Difficult to maintain wireless area coverage Complex network management causes inefficiency in time Channel overlapping causes network performance degradation Page is Animated 131 D-Link Unified Access System Legacy WLAN Deployment Illustration of Legacy WLAN Layer 3 Switch Access Point Channel overlap causes network performance down to 50% Server Farm Layer 2 switch Channel 6 Access Point Server Room Coverage hole Access Point Power level is too weak Rogue AP Access Point RF Interference Security breach 132 D-Link Unified Access System Customer Needs and D-Link Solution Customer Needs Unified wired and wireless access system United management and security • Centralized AP and client management • Rogue AP detection / mitigation Better performance • Guarantee on no-overlapping wireless coverage area Seamless roaming 133 D-Link Unified Access System Customer Needs and D-Link Solution D-Link Unified Access System Solution D-Link Unified Access System Solution can provide: • • • • • • • Unified Switching (=Wireless Controller + L2+ Switch) Centralized Policy Management Automatic Power/Channel Adjustment AP Load Balancing Fast L2/L3 Roaming Rogue AP Management Log for Dynamic RF Status All D-LINK features above give what customer needs for unified network infrastructure and for better performance 134 D-Link Unified Access System Introduction to Wireless Switch Introduction to Unified Access System Solution What is Unified Access System Solution • D-Link solution that enables WLAN deployment while providing state-ofthe-art wireless networking features. • It provides secure wireless connectivity and seamless layer 2 and layer 3 roaming for end users. D-Link Unified Access System Component • D-Link Unified Switch (DWS-3024 and DWS-3026) • D-Link Unified Access Point (DWL-3500AP and DWL-8500AP) 135 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Deployment Solution Overlay Solution In overlay solution deployment, Wireless switch is introduced into existing network infrastructure to protect current investment in network infrastructure with all the benefits of WLAN switching. Wireless Switch Layer 2 switch Page is Animated Server Farm Layer 3 Switch Layer 2 switch 136 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Deployment Solution Unified Solution Unified Solution / Converged Edge Deployment • • • Deploy at the network edge for greatest scalability Peer-to-peer WLAN Switches facilitate “Converged” WLAN Edge by distributing WLAN Switching capability Full Gigabit Ethernet speed ready for next generation 802.11n Layer 3 Switch Server Farm All layer 2 switches are replaced with wireless switch Wireless Switch Page is Animated Layer 2 switch Layer 2 switchWireless Switch 137 D-Link Unified Access System Summary: D-Link Unified Access System Overview Summary: D-Link Unified Access System Overview On larger networks the legacy wireless deployment may cause several difficulties such as time consuming network management which then make customer needs a new solution that provides centralized network management. D-Link provides solution to cover those problems faces by the customer with D-Link Unified Access System Solution. D-Link Unified Access System is a wireless local area network (WLAN) solution that enables WLAN deployment while providing state-of-the-art wireless networking features. To implement D-Link unified access system solution, it requires DLink wireless switch and D-Link unified access point. Customers can deploy the unified access system solution using either overlay solution or unified solution. 138 D-Link Unified Access System Questions and Answers: D-Link Unified Access System Overview Questions and Answers: D-Link Unified Access System Overview 1. Select devices that are component of D-Link Unified Access System. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. E. DWS-3024 and DWS-3026 DWL-3260AP DWL-3500AP DWL-8200AP DWL-8500AP 2. Select characteristics of overlay solution deployment for D-Link unified access system. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. With this solution, the wireless APs are not connected to the wireless switch directly With this solution, the deployment of wireless switches is at the network edge Peer-to-peer WLAN switches facilitate “converged” WLAN Edge by distributing WLAN Switching capability Alls customers to keep their existing network hardware/switches 3. Select characteristics of unified solution deployment for D-Link unified access system. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. With this solution, the wireless AP’s are not connected to the wireless switch directly With this solution, the deployment of wireless switches is at the network edge Peer-to-peer WLAN switches facilitate “converged” WLAN Edge by distributing WLAN Switching capability Allows customers to keep their existing network hardware/switches 139 D-Link Unified Access System D-Link Unified Wireless Switch D-Link Unified Wireless Switch After this section, you should be capable of expressing: 1. Functions of Unified Wireless Switch 2. Models for D-Link Unified Wireless Switch 3. Advantages of Unified Wireless Switch 4. Features of Unified Wireless Switch 140 D-Link Unified Access System D-Link Unified Wireless Switch Unified Wireless Switch Overview Unified Wireless Switch allows to control the discovery, validation, authentication, and monitoring of peer unified switches, D-Link Access Points, and clients on the WLAN, including discovery and status of rogue APs and clients. The D-Link Unified Access System works with the following D-Link switches: • DWS-3024 (24 GE ports) • DWS-3026 (24 GE ports + 2 10GE ports) 141 D-Link Unified Access System D-Link Unified Wireless Switch Unified Wireless Switch Advantages Core units controlling entire wireless network High performance, easy deployment 24 Gigabit ports, no restriction on port usage Scalable expansion & unified wired/wireless deployment Authentication, security & power management Simplified configuration & deployment Maximum performance Maximum network performance Maximum investment protection 142 D-Link Unified Access System D-Link Unified Wireless Switch Unified Wireless Switch Features List (1) Centralized management of wireless network • Track and maintain user authentication as users roam throughout the network • Intelligently designates users to virtual groups based on user’s authenticated identity • Provide scaled, resilient, integrated management infrastructure • Centrally manage user authentication/security policies • Provide key management for each security protocol • Configure and control all connected access points Scalable unified wired/wireless network infrastructure • • • • • Simplified and resilient network deployment • 802.3af Power over Ethernet simplify AP installation • Gigabit connection ready for future wireless speed upgrade • Redundant power supply support maximizes network uptime 24 10/100/1000BASE-T Gigabit ports Up to 48 wireless APs direct/indirect connections Mixed wired/wireless connection from any port Four combo SFP for flexible fiber connection Two open slots for optional 10-Gigabit attachment to fiber backbone* • Expandable to four peer switches * Available on DWS-3026 only 143 D-Link Unified Access System D-Link Unified Wireless Switch Unified Wireless Switch Features List (2) Security management • • • • • 64/128/152-bit WEP data encryption WPA/WPA2 personal WPA/WPA2 enterprise MAC address filtering Rouge AP classification and detection Bandwidth and power management • • • • • Auto-adjust RF channels for AP Provide fast intra-switch or inter-switch roaming Advanced inter-subnet roaming Auto-adjust transmit output for AP Allow remote boot of AP LAN management • L2+ features: spanning tree, 802.3ad link aggregation, port mirroring, jumbo frames • IPv4 packet routing • QoS with 802.1p priority queues, granular bandwidth control • LAN security with ACL, RADIUS, TACACS+ authentication, DoS prevention, broadcast storm control Secure and versatile management • • • • • • Web access using HTTP Telnet server/client SSH v2, SSLv3 SNMP v1, v2c, v3, RMON SYSLOG, Dual image CLI 144 D-Link Unified Access System Summary: D-Link Unified Wireless Switch Summary: D-Link Unified Wireless Switch Wireless Switch allows to control the discovery, validation, authentication, and monitoring of peer unified switches, D-Link access points, and clients on the WLAN, including discover and status of rogue APs and clients. D-Link provides DWS-3024 and DWS-3026 for Unified Wireless Switch. D-Link Unified Wireless Switch offers several advanced features to manage the entire network. 145 D-Link Unified Access System Questions and Answers: D-Link Unified Wireless Switch Questions and Answers: D-Link Unified Wireless Switch 1. Select statement that shows the difference between DWS-3024 and DWS-3026. A. B. C. D. Control entire wireless network Only DWS-3026 supports WPA2 authentication method Only DWS-3024 provides four combo SFP for flexible fiber connection DWS-3026 provides two open slots for optional 10-Gigabit attachment to fiber or copper backbone 2. Select advantages of unified wireless switch. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. Control the entire wireless network Unified wired/wireless network High level of security by applying restrictions on port usage Support IPv6 packet routing 146 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages D-Link Wireless Switch’s Features and Advantages Overview After this section, you should be capable of expressing: 1. What is pre-set configuration and centralized management and its benefits 2. What is automatic channel adjustment and the benefits 3. What is automatic power adjustment and the benefits 4. Characteristics of load balancing and the way it works 5. What is rogue AP management and the benefits 6. Characteristics and benefits of fast roaming 7. Network monitoring in D-Link wireless switch and WLAN visualization 8. Capabilities of D-Link wireless switch that support large scale WLAN deployment 147 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages D-Link Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Pre-set configuration and centralized AP management RF management • Automatic channel adjustment • Automatic power adjustment D-Link wireless switch + unified access point Self-healing wireless network • Load balancing Enhanced security enforcement Fast wireless roaming Simple network monitoring Suitable for medium to large scale network deployment 148 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Pre-set Configuration and Centralized Management Security can be pre-set and management of AP can be centralized • • • The Profile configuration is applied to a managed AP on the event such as when an AP initially transitions to managed mode, or when AP is reset. Wireless switch will automatically detect all APs attached to the switch. When an AP is removed or added, the switch automatically configures new AP with same configuration of replaced unit. APs detected on the network AP-1 2> New AP detected!!! Wireless switch 1> AP-3 appear and attached to a AP-3 wireless switch port AP-1 AP-2 Page is Animated AP-2 AP-3 3> Configured AP with the pre-set profile configuration 149 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Pre-set Configuration and Centralized Management Central Policy Control • Security setting/configuration can be saved even when the AP is powered off. Wireless Switch L3-switch Content of pre-set profile configuration packet: Pre-set profile configuration L2-switch •RADIUS server settings •Security settings •Radio configuration •SSIDs, VLAN & Tunnel setting •QoS configuration Access points attached to the network Pre-set profile configuration Page is Animated Pre-set profile configuration Pre-set profile configuration 150 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages RF Management Automatic channel adjustment • • Wireless Switch automatically adjusts channels in the controlled access points in an event such as a new AP being added or being removed Wireless Switch can be programmed to automatically readjust channels periodically at certain time or upon a certain interval. Wireless Switch Channel 36 Channel 44 Experience signal interference, Change channel Channel 44 Appear rogue AP which using channel 44 Channel 52 Channel 40 Page is Animated Channel 48 New AP attached to the network Scan RF area for occupied channel… Select non-interfering channel 151 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages RF Management Automatic power adjustment • • Automatically adjust the RF signal to broadcast far enough to reach wireless clients, but not so far that it interferes with RF signals broadcast by other APs. When a managed AP is powered down, the power of its neighboring AP(s) managed by the same switch is immediately increased by 20% (Fail-safe feature). Power adjusted to prevent interference Power increased Wireless coverage area Another AP appear on the network Wireless coverage area The AP is powered down Page is Animated 152 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Self-Healing Wireless Network (Load Utilization) Wireless switch performs load utilization across the switch-managed access points on per radio basis based on AP’s utilization rate. The APs report bandwidth utilization to the wireless switch regularly. If the bandwidth utilization reaches a configured threshold then the new client associations are rejected. The new client will be forced to connect to an overlapped neighbor AP with lower utilization. Default bandwidth utilization: 60% Utilization rate increased Wireless Switch Reach utilization threshold!!! User4 rejected Force to connect AP-1 to AP-2 user4 Page is Animated Utilization rate for AP-2 AP-2: 10% User4 connect to AP-2 Attempt to connect AP-1 user4 153 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Enhanced Security Enforcement Rogue AP Management • An AP is considered to be a rogue if the following conditions are met: – Switch learns about an AP that is not in the database, and the AP has not tried to discover the switch. – AP is not managed by a peer switch. – The MAC address of the AP is in the local or RADIUS MAC address database with the mode set to “WS Managed”, but the AP is not actively managed by the wireless switch or a peer switch. • • Using rogue AP management, rogue AP can be acknowledged as a valid AP Administrator can get better control of the environment through knowing rogue APs’ information (MAC, SSID, Channel, etc) Complete Security Features Wireless • • • • • Managed AP MAC list Wireless Client MAC list WEP (Static/Dynamic) WPA Enterprise/Personal WPA2 Enterprise/Personal Wired • • • • • • ACL 802.1X DoS Control Broadcast Storm Control Port Security RADIUS/TACACS+ 154 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Fast Roaming Roaming allows wireless clients to move from one location to another, seamlessly switching from one Access Point to another and maintaining access to the network. This feature can be supported within a subnet (Layer 2) or across subnet boundaries. When a wireless client (fast) roams among different APs on the same SSID, the same security setting and IP address “follows” the client. That means there is no need for IP re-allocation and re-authentication in order to keep the connection alive. Hence, it is seamless. Wireless switch Mobile user With Fast Roaming feature, mobile users can move to any place where covered by an overlapped neighbor without the need to re-authenticate No re-authenticate when user moves Mobile user want to move HERE Page is Animated 155 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Wireless Switch Operation Steps of wireless switch from attach an AP to user authentication process. 1. AP-1 is attached to a switch port and switch will discover AP-1 automatically. 2. Network admin can determine whether AP-1 is a rogue or a legal AP. 3. Network admin can perform central management of AP, including configuration, firmware upload, security and RF control. 4. All clients are authenticated by the Central Policy Control on the switch. 5. Roaming from AP-1 to AP-2 without re-allocating IP and re-authentication to keep the connection alive. Wireless switch AP-1 AP-1 is legal AP-2 PDA User Page is Animated 156 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Comprehensive Network Management D-Link Unified Access System includes a set of comprehensive management functions for managing and monitoring the WLAN by using one of the three methods provided • Web-based Management Interface • Command-Line Interface(CLI) – The CLI is a text-based way to manage and monitor the system. CLI can be accessed by using a direct serial connection or by using a remote logical connection with Telnet or SSH. • Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) – D-Link Unified Switch uses both standard public MIBs for standard functionality as well as a number of additional private MIBs for additional functionality supported by the switch. 157 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Comprehensive Network Management D-Link Unified Switch can discover, validate, authenticate, or monitor the following system devices: • • • • • Peer unified switches D-Link access points Wireless clients Rogue APs Rogue wireless clients The following monitoring task that can be done by the unified switch: • • • • • • • • • Monitoring wireless global information Monitoring peer switch status Monitoring all access points Monitoring managed access point status Viewing access point authentication failure status Monitoring rogue and RF scan access points Monitoring associated client information Viewing client authentication failure status Monitoring and managing ad hoc clients 158 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Monitoring Wireless Global Information Show status and statistics collected periodically about the peer switches and all of the objects associated with it. 159 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Monitoring Peer Switch Status The Peer Switch page provides information about other D-Link Unified Switches in the network. 160 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Monitoring All Access Points Show summary information about managed, failed and rogue access points the switch has discovered or detected. The font color for the AP listing indicates that the AP is one of the following types: • • • Green – Managed AP Red – Failed AP Gray – Rogue AP 161 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Monitoring Managed Access Points Status Provide a variety of information about each AP that the switch manages. • • Status tab provides configuration and association information about managed APs and their neighbors. Statistics tab displays information about the number of packets and bytes transmitted and received on different interfaces. 162 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Viewing Access Point Authentication Failure Status Show information about APs that failed to establish communication with the D-Link Unified Switch. The AP can fail due to one of the following reasons: • • No Database Entry – The MAC address of the AP is not in the local valid AP database or the external RADIUS server database, so the AP has not been validated. Authentication – The authentication password configured in the AP did not match the password configured in the local database or RADIUS database. 163 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Monitoring Rogue and RF Scan Access Points Show information about all APs detected via RF scan, including those reported as Rogues. 164 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Monitoring Associated Client Information Show a variety of information about the wireless clients that are associated with the APs the switches manages. 165 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Viewing Client Authentication Failure Status Shows a list of clients that fail to associate or authenticate with the D-Link Access Point. 166 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Monitoring and Managing Ad-Hoc Clients View and manage wireless clients that are connected to the WLAN through an ad hoc network. 167 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Simple Network Monitoring Capture screen of associated client status. 168 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Network Monitoring – WLAN Visualization WLAN visualization Overview • An optional feature that graphically shows information about the wireless network. • Display D-Link WLAN Controller Switches, D-Link Access Points, other access points and associated wireless clients. Benefits of WLAN visualization • Track how and how many managed APs are deployed graphically. • Monitor the wireless network stats via the dynamic updated diagram. • Access visual information, such as how APs are placed, how many clients are associated to a certain AP, and where rogue APs are located graphically. 169 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Network Monitoring – WLAN Visualization The diagram below shows an example of a floor plan and network with a DLink Unified Switch that manages two APs. The graph also shows a peer switch and a rogue AP in the network. 170 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Medium to Large Scale WLAN Deployment Visual Access Points forms Roaming group • Geographical overlapped wireless network is made possible with minimum number of physical APs. Medium to Large Scale of AP Deployment • Four Peer Switches in the same Roaming Group – Not only can D-Link’s DWS-3000 series supports fast roaming between APs being managed by a particular switch, but can support up to four peer Unified Switches in a roaming group. – Support up to 192 APs. – Since each switch can support up to 48 APs, this means up to 192 APs can be supported in a mobility group or domain. Note: The maximum number of managed AP – 192 only applies on APs in the same roaming group. There is no constraint for the number of managed APs at a site if not for roaming. But still, each switch can manage up to 48 APs. 171 D-Link Unified Access System Summary: Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Summary: Wireless Switch Features & Advantages Using D-Link wireless switch, security can be pre-set and management of certain model of APs can be centralized. Wireless switch provides automatic channel adjustment and automatic power adjustment feature. Wireless switch automatically adjust channel in the controlled Access Points in an event such as a new AP being removed. It will also adjust RF signal to broadcast far enough to reach wireless clients, but not so far that it interferes with RF signals broadcast by other APs. Wireless switch performs load balancing across the switch-managed access points on per radio basis based on AP’s utilization rate. Using rogue AP management feature, the administrator can get better control of the environment through knowing rogue AP’s information (MAC, SSID, Channel, etc). 172 D-Link Unified Access System Summary: Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Summary: Wireless Switch Features & Advantages Fast Roaming allows wireless clients to move from one location to another, seamlessly switching from one Access Point to another and maintaining access to the network. Wireless switch provides simple network monitoring and WLAN visualization feature that graphically shows information about the wireless network. Wireless switch can be used to deploy large scale WLAN infrastructure. 173 D-Link Unified Access System Questions and Answers: Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Questions and Answers: Wireless Switch Features and Advantages 1. Select features that can be used to avoid network interference. (Choose two) A. B. C. D. Self-healing wireless network Automatic channel adjustment Fast roaming Automatic power adjustment 2. Select contents of pre-set profile configuration packet. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. E. TCP/IP settings Security settings QoS configuration Firmware upgrade VLAN ID 3. Select characteristics of load balancing in wireless switch. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. E. Load balancing is performed across the managed APs on per radio basis. Default value for the wireless bandwidth utilization threshold is 70%. If the bandwidth utilization reaches a configured threshold, the new client cannot connect to the network until the bandwidth utilization is lower than the predefined value. Load balancing sets thresholds for client associations and AP utilization. If the bandwidth utilization reaches a configured threshold, then new client associations are rejected and enforced to connect to an overlapped neighbor AP with lower utilization. 174 D-Link Unified Access System Questions and Answers: Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Questions and Answers: Wireless Switch Features and Advantages 4. Select the characteristics of rogue AP. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. AP is not managed by the wireless switch. AP which failed to connect to wireless switch. AP what is not in the local or RADIUS MAC address database but is actively managed by the wireless switch. Switch learns about an AP that is not in the database, and the AP has not tried to discover the switch. 5. Select the advantage of fast roaming. A. B. C. D. Wireless clients can move to the external network that is out of control from the switch Fast roaming can be applied up to 200 APs Allow wireless clients to move from one location to another, seamlessly switching from one Access Point to another and maintaining access to the network All the APs can be in different Roaming Groups 6. Select devices that can be monitored by D-Link wireless switch. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. E. Peer unified switches D-Link access points Ethernet switches Bridges Wireless clients 175 D-Link Unified Access System Questions and Answers: Wireless Switch Features and Advantages Questions and Answers: Wireless Switch Features and Advantages 7. Select monitoring task that can be done by D-Link wireless switch. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. Monitoring offline wireless devices Monitoring managed access point status Viewing access point authentication success status Monitoring associated client information 176 D-Link Unified Access System Unified Access Point Unified Access Point After this section, you should be capable of expressing: 1. Models of D-Link Unified Access Point and the features for all models 2. Operation mode supported by the unified access point and the differences between each mode 177 D-Link Unified Access System Unified Access Point Unified Access Point Overview Can work in both standalone mode and managed mode Provide migration ability and deployment flexibility DWL-3500AP • • • • • • Wireless G access point Up to 108Mbps wireless speed PoE support Two high gain antennas WMM for QoS Connect directly to wireless switch or indirectly through LAN switch DWL-8500AP • • • • • • Wireless AG access point Up to 108Mbps wireless speed PoE support Two high gain antennas WMM for QoS Connect directly to wireless switch or indirect through LAN switch 178 D-Link Unified Access System Unified Access Point Modes in Unified Access Point Standalone Mode • • • Independent access point (Decentralized management) Suitable for small scope network Manually set up the configuration, such as: – – – – – SSID User authentication Power level QoS etc Ethernet LAN Layer 2 switch Standalone mode UAP Manual set up configuration Standalone mode UAP Manual set up configuration Standalone mode UAP Manual set up configuration 179 D-Link Unified Access System Unified Access Point Modes in Unified Access Point Managed Mode • Managed / controlled by the wireless switch – Centralized management with all extra benefits from wireless switch • • Automatically received the configuration from wireless switch Suitable for large scope network Ethernet LAN Wireless switch Layer 2 switch No Manual Configuration for each AP Standalone mode UAP Managed mode UAP Managed mode UAP Managed mode UAP Instead Centralized AP profile dispatch Centralized security policy enforcement Large network deployment using managed mode UAP Centralized wired/wireless VLAN/QoS/ACL control Auto Power/Channel adjustment AP Self healing & Fail-over Fast Roaming Page is Animated 180 D-Link Unified Access System Summary: Unified Access Point Summary: Unified Access Point There are two models of unified access point provided by D-Link, which are DWL-3500AP and DWL-8500AP. These unified access point can be used along with the D-Link wireless switch. Two operation modes supported for both models of unified access point: standalone mode and managed mode. 181 D-Link Unified Access System Questions and Answers: Unified Access Point Questions and Answers: Unified Access Point 1. Select the main difference between DWL-3500AP and DWL-8500AP. (Choose two) A. DWL-8500AP supports WMM for QoS while DWL-3500AP does not B. DWL-3500AP supports PoE while DWL-8500AP does not C. DWL-3500AP supports 802.11a standard while DWL-8500AP support 802.11a and 802.11g standard D. DWL-3500AP provides only one antenna while DWL-8500AP provides two antennas 2. Select characteristics that describe managed mode unified access point. (Choose all that apply) A. B. C. D. “Fat” access point with centralized management from the wireless switch. “Thin” access point with centralized management from the wireless switch. All AP configurations are automatically received from the wireless switch. AP configuration configured all the wireless switch must be applied manually to the AP. 182 D-Link Unified Access System Market Analysis for D-Link Wireless Switch Market Analysis for D-Link Wireless Switch After this section, you should be capable of expressing: 1. D-Link wireless switch target market 2. Product comparison between each model of D-Link wireless switch 3. Prospect for D-Link wireless switch product in the market 4. Product comparison between D-Link wireless switch and competitor’s products 183 D-Link Unified Access System Market Analysis for D-Link Wireless Switch Highlight of WLAN Market Revenue from sales of WLAN switches and controllers increased 92% year on year, totally $572 million (equivalent to 43% of the WLAN market revenue). The business market will continue the gradual shift from the traditional stand-alone WLAN architecture to the newer, centralized one (WLAN switches and controllers managing coordinated access points) in 2007. Source: Gartner, 2007 184 D-Link Unified Access System Market Analysis for D-Link Wireless Switch D-Link Wireless Switch Market Target customer – Medium to enterprise business solution • • • • Entertainment Education Manufacture All business category 185 D-Link Unified Access System Market Analysis for D-Link Wireless Switch D-Link Product Comparison Category DWS-3024 DWS-3026 24GE + 4 Combo SFP for fiber uplink to LAN 24GE + 2 10GE Redundant Power Supply Yes Yes L2 Switching Full 4K VLAN Support Yes Yes L3 Routing Static Routing, VRRP Yes Yes Wireless Deployment Overlay Deployment Yes Yes Unified Edge Deployment Yes Yes # APs supported per Switch Yes Yes Fast Layer 3 Roaming Yes Yes Inter-Switch Layer 3 Roaming Yes Yes Dynamic Channel and Power Yes Yes Self healing around failed APs Yes Yes Monitoring Topology Visualization Yes Yes Wireless Security Rogue AP and Client Detection Yes Yes HW Interface Wireless Switching RF Management Product Gigabit and 10G Uplink 186 D-Link Unified Access System Market Analysis for D-Link Wireless Switch Prospect for D-Link Wireless Switch Product Competitor Analysis – Gigabit wireless controller / switch • Ring Master Management Tool • Third Party AP Support • RF Attack Mitigation • Individual User Groups Performance DES-1228P + WLAN Manager Is the match <-> • No embedded Network Visualization (RFMaps) • Lower Switching Capacity Aruba 2400 Cisco 4400 • Third party AP support • RF Attack Mitigation • No L3 roaming • Weak L2/L3 feature • No Peer Switching • No embedded • No Network Visualization • Lower Switching Capacity 3Com WX4400 • Weak L2/L3 feature • No Peer Switching • Less no. of VLANs • Lower Switching Capacity • More Advanced Security VPN/Firewall • Proprietary features • RF Attack Mitigation • Location tracking • Thin APs only • Weak L2/L3 feature • Less no. of VLANs • Lower Switching Capacity D-Link DWS-3000 Current Wireless Controller don’t have Unified Switching capability Strength 3Com Unified Gigabit Switch Weakness Page is Animated P r i c e 187 D-Link Unified Access System Market Analysis for D-Link Wireless Switch Product Comparison Between Competitor Category DWS-3026 3Com Unified Switch Aruba 2400 Cisco 4402 24GE+2 10GE 24GE 24 10/100 (2 GBIC Slots) 2GE Redundant Power Supply Yes No No Yes L2 Switching Full 4K VLAN Support Yes No No No L3 Routing Static Routing VRRP Yes No Yes No Wireless Deployment Overlay Deployment Yes No Yes Yes Unified Edge Deployment Yes Yes No No #APs supported per switch 48 24 48 12/25/50/100 Wireless Switching Fast Layer 3 Roaming Yes No Yes Yes Inter-Switch Layer 3 Roaming Yes No Yes Yes RF Management Dynamic Channel and Power Yes Yes Yes Yes Self-Healing around failed APs Yes Yes Yes Yes Monitoring Topology Visualization Yes No Yes Yes Wireless Security Rogue AP and Client Detection Yes Yes Yes Yes HW Interface Feature Gigabit and 10G Uplink * Different number of APs supported based on buying upgrade licenses Wireless Controllers 188 D-Link Unified Access System Summary: Market Analysis for D-Link Wireless Switch Summary: Market Analysis for D-Link Wireless Switch The business market will continue the gradual shift from the traditional stand-alone WLAN architecture to the one (WLAN switches and controllers managing coordinated access points) in 2007. D-Link target market for its wireless switch products is mainly for medium to enterprise business solution for any fields. D-Link wireless switch provides many advantages and features that are not supported in competitor’s products. 189 D-Link Unified Access System Questions and Answers: Market Analysis for D-Link Wireless Switch Questions and Answers: Market Analysis for D-Link Wireless Switch 1. Select target markets for D-Link Unified Access System. (Choose two) A. B. C. D. SOHO ISP/WISP University Internet Cafe 2. Select the advantages of D-Link wireless switch over the other competitors. (Choose two) A. D-Link wireless switch provides 24 Gigabit Ethernet ports and two 10GE uplink ports which other competitors provide only 24 Gigabit Ethernet without uplink ports. B. D-Link wireless switch is so much cheaper than other competitors’ products. C. D-Link wireless switch provides lifetime warranty while other competitors’ products must pay extra fee to get lifetime warranty. D. D-Link wireless switch provides full 4K VLAN support while other competitors do not. 190 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Deployment Application Wireless Switch Deployment Application After this section, you should be capable of expressing: 1. Suitable implementation for different scenarios and requirement 2. Basic topology for deploying network infrastructure using wireless switch product series 191 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Deployment Application Wireless Switch Deployment in a School In this project, three wireless switches were used to connect the entire campus (Class rooms, labs, teacher room, library). All APs distributed to all campus are managed centrally at the wireless switch. Thus, it makes network management and monitoring easier. Toilet Classroom-5 Server Room Library Classroom-4 Labs Classroom-6 Classroom-7 Classroom-9 Teacher’s room Classroom-3 Main Hall Classroom-2 Classroom-8 Classroom-1 Administrator Office Classroom-10 Classroom-11 Toilet 192 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Deployment Application Wireless Switch Deployment in a Hotel A hotel wants to build wireless hotspot area to enhance customer satisfaction. The network must run reliably with high speed Internet connection. It has to be easier to maintain as no staff knows about wireless technology. D-Link wireless switch provides the solution. It provides control, security and management features that are key requirements to allow the hotel staff to manage AP better and easier. 19th floor ………. 12th floor 11th floor ………. 1st floor 2 Wireless switch are each placed at 11th floor and 12th floor. furthermore, 95 wireless AP managed by the wireless switch are distributed to all floors over the hotel. 5 AP for each floor, placed at common area. 193 D-Link Unified Access System Wireless Switch Deployment Application Summary: Wireless Switch Deployment Application D-Link wireless switch can be implemented widely depending on the condition and requirement from the customer, mainly on medium to large business environment. For example, implementation in a hotel, university, bank, etc. 194 D-Link Unified Access System Success Stories Success Stories Lankwitzer Premium Coating, Germany American School of Dubai, Middle East Concorde Hotel, Malaysia 195 D-Link Unified Access System Success Stories Lankwitzer Counts on Innovative Wireless Switching Solution Lankwitzer wants to connect its new building wirelessly for the transmission of data and voice, especially wireless telecommunication through an internal Voice over IP-telephone system. D-Link Germany in cooperation with the Multicomp Systemhaus helped to implement a wireless network infrastructure, which offers a maximum of flexibility and bandwidth as well as superior security and management functions using wireless switch solution. List of devices used: • • • D-Link wireless switch, DWS-3024 24 D-Link unified access point, DWL-8500AP xStack switch, unmanaged switch, firewall 196 D-Link Unified Access System Success Stories Wireless Switch Solution for Mobile Learning Space in ASD American School of Dubai (ASD) wants to create a continuous (mobile) learning space in the campus to enable the students access the network resources wirelessly. D-Link Middle East successfully implement the project which provide secured network infrastructure with seamless wireless coverage area and centralized network management. List of devices used: • • • • Two D-Link wireless switch, DWS-3026 Two unified AP, DWL-8500AP 61 unified AP, DWL-3500AP Layer 3 switch, DES-3828P 197 D-Link Unified Access System Success Stories Concorde Hotel Provides Wireless Hotspot Using Unified Solution Management of Concorde Hotel in Kuala Lumpur wants to provide wireless hotspot area within the hotel to enhance customer satisfaction. They want to manage the entire network through an easy, unified solution. D-Link Malaysia provides wireless access through minor customizations at a reasonable cost. List of devices used: • • Two units of D-Link wireless switch, DWS-3024 95 units of unified access points, DWL-3500AP (five units for common area in each floor) 198