* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Internet Traffic Patterns
Survey
Document related concepts
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Passive optical network wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
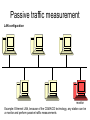
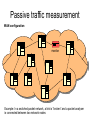
Passive traffic measurement • Capturing actual Internet packets in order to measure: – – – – – – Packet sizes Traffic volumes Application utilisation Resource utilisation Network monitoring Traffic characterisation • Commercial products and freeware software – HP openview, NetPredict, tcpdump Passive traffic measurement LAN configuration monitor Example: Ethernet LAN, because of the CSMA/CD technology, any station can be a monitor and perform passive traffic measurements Passive Traffic Measurement LAN configuration: – All the traffic of the LAN can potentially be captured – The network card of the monitor node runs in promiscuous mode – The monitor node is responsible for capturing and analysing all the data – Can be used at home in a wireless LAN or even with only a dial-up modem Passive traffic measurement WAN configuration monitor Example: In a switched packet network, a link is “broken” and a packet analyser is connected between two network nodes Passive Traffic Measurement • WAN configuration: • Because connections in WANs are usually point to point links, the measurement needs to be done at specific points • Only a network administrator has access to the specific link • There are special packet analysers connected as monitors (data processing only node) • Routers with packet collectors act as measurement points (regular network node) Passive Traffic Measurement • The following information can be collected: IP header IP packet content UDP/TCP header User data User data Passive Traffic Measurements Information that can be collected: • Through IP header: – Source IP address – Destination IP address – Packet size • Through TCP/UDP header: – Source port – Destination port • General utilisation of the LAN or WAN link Passive Traffic Measurement Disadvantages • Compromises security • Large storage space for headers and/or packets • If using WAN configuration only gives a localized view of the network • If using LAN configuration only gives a view of the LAN Passive Traffic Measurement Overcoming disadvantages • Do not capture user data • WAN configuration: set up several packet collection points (data processing becomes difficult) • Planning collection times so that file sizes can be minimised and the probability of probing different paths is minimised Passive Traffic Measurement Advantages • Detailed information about traffic • Effective technique to identify application performance and bandwidth requirements • Effective technique to identify possible offending hosts in the network Passive Traffic Measurement Examples of uses: • Volume of traffic • Packet inter-arrival times • Identify hosts responsible for congestion • Identifying most popular applications • Identifying flow behaviours • Packet sizes • Typical transfer sizes • Flow measurement Passive Traffic Measurement Passive Traffic Measurement Active traffic measurement Resources • Well known port numbers: http://www.iana.org/assignments/port-numbers • Trends in Wide Area IP Traffic Patterns http://www.caida.org/outreach/papers/200 0/AIX0005/AIX0005.html • CAIDA Internet Data -- Passive Data Sources http://www.caida.org/data/passive/ Summary • Passive traffic measurement – Able to measure specific protocol related data – Used to monitor, plan and estimate current and future use of networks – It does not provide with a global view of the network Traffic characterisation is important because it helps us to understand exactly how human activities affect networks in particular and the Internet in general.