* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download modul 3 LOCAL AREA NETWORK
Survey
Document related concepts
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Low Pin Count wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.11 wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
MIL-STD-1553 wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
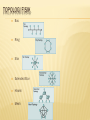
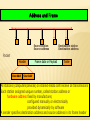
Jaringan Telekomunikasi Institut Teknologi Telkom LOCAL AREA NETWORK LOCAL AREA NETWORKS (LAN) Classifications of Computer Networks: LAN, MAN, WAN Point-To-Point Connection and Shared Medium LAN Topology: Star, Ring, Bus Typical LANs - Ethernet (CSMA/CD) - LocalTalk (CSMA/CA) - Wireless LAN - Token Ring - FDDI Unicast, Broadcast, Multicast DEFINISI LAN IEEE mendefinisikan jaringan wilayah lokal (LAN) sebagai “sebuah jaringan komunikasi untuk menghubungkan berbagai perangkat (contohnya personal computer, workstation, printer, perangkat penyimpanan file) yang dapat mengirimkan data pada daerah terbatas, biasanya dalam suatu fasilitas perkantoran/organisasi” Laju data LAN, jumlah divais maksimum yang terhubung ke LAN, jarak antar divais, dan pengembangan jaringan bergantung pada: Media transmisi yang digunakan Teknik transmisi (baseband atau broadband) Protokol pengaksesan jaringan Konfigurasi perangkat seperti repeater, bridge, router, hub, switch Classifications of Computer Networks LAN – Local Area Network: A network that spans a small geographic area, such as a single building or buildings close to each other. Examples: Ethernet, LocalTalk, Token Ring, FDDI, ATM PAN – Personal Area Network MAN – Metropolitan Area Network: A network that can span a geographic area the size of a city. Example: DQDB WAN – Wide Area Network: A network that can span a large geographic area, e.g., multiple cities, countries or continents. Examples: ARPANET, X.25, Frame Relay, SMDS, ATM Point-To-Point Connection Network point-to-point network provides a dedicated link between any two computers/devices - dedicated link: used by only two computers and not shared with others - high security and privacy - (N2-N)/2 links are needed for N computers/devices 45 links (N=10), 4950 links (N=100), 499500 links (N=1000) - Such network is not used in practical because of its cost and inflexibility Shared Communication Channel/Medium in LAN Shared Medium - wire, cable, fiber - radio, infrared, … Key natures of LAN: - Media type: wired/wireless, twisted pair/cable/fiber, radio/infrared - Topology: network shape/connection method - Protocol: how to use shared medium, media access control technique a) TDM: only one computer can send data in a time b) Frame: transfer element, each LAN has its own frame format - Bit rate: usually from 1Mbps~1Gbps TOPOLOGI FISIK Bus Ring Star Extended Star Hirarki Mesh Lecture 4 LAN Topologies Star Topology Ring Topology Bus Topology BUS Topologi yang menggunakan single backbone segment yang terhubung secara langsung ke semua host. Setiap komputer disambung dengan T Bus (Bus berbentuk T) dan kedua ujung sambungan diberi resistor 50 ohm. Semua perangkat jaringan yang terhubung dalam topology bus dapat melihat semua sinyal yang melintas dalam single backbone tersebut. Keuntungan: Murah, karena tidak memakai banyak media dan media yang dipakai sudah umum (banyak dalam pasaran) Setiap komputer dapat saling berhubungan langsung. Kerugian: Sering terjadi hang / crash, yaitu bila lebih dari satu pasang memakai bus yang sama. Tidak dapat dipakai secara bersamaan dalam satu waktu, harus bergantian atau ditambah relay. Jika single backbone terputus maka jaringan rusak. Trafik yang padat dan sering terjadinya collision paket data. Lecture 4 Ethernet - Bus Topology Media: Coax cable, twisted pair, fiber Topology: Logic bus (physically may be bus or star) Transmit: Only one can transmit at any time, all others receive transmission Speed: 10Mbps, 100Mbps (fast Ethernet) and 1000Mbps (gigabit Ethernet) Status: Most popular LAN and widely used History: Invented at Xerox (Palo Alto Research Center) in 1970s Defined a DIX standard by Digital Equipment, Intel and Xerox IEEE currently controls Ethernet standards Project 802.3 – Ethernet Define media, voltages, encoding, data rates, frames, wiring, … Lecture 4 When to start transmit - CSMA All computers connect a bus and only one can transmit at a time Who can? No central control when computers transmit on the bus. Ethernet employs CSMA to coordinate transmission among multiple computers CSMA (Carrier Sense with Multiple Access) - MA (Multiple Access): multiple computers are attached, any can access bus - CS (Carrier Sense): computer wanting to transmit listen carrier before send wait if medium is busy (another computer is transmitting) transmit if medium is idle (no one transmits) Lecture 4 When to start transmit – CSMA/CD Collision Animation Animation Even with CSMA, two computers may transmit simultaneously - Both find it idle and begin transmitting in almost a same time - Two signals exist in medium, interfere each other, call collision CD (Carrier Detection) - Monitor outgoing signal - Stop transmissions after collision is detected - Each waits random time in [0, S] - listen the bus and transmit again if it is idle - Wait random time in [0, 2S] if collisions is detected again - Double waiting time range [0, 2kS] when k+1 collisions detected called exponential backoff, very effective in practical Lecture 4 LocalTalk - Bus Topology reserve transmit Media: Coax cable, twisted pair Topology: Logic bus (physically may be bus or star) Transmit: Only one can transmit at any time, all others receive transmission Speed: 230Kbps ~ Status: IEEE Project 802.4, Apple’s Macintosh computers, low cost & easy install CSMA/CA: Using CSMA to listen and transmit Using CA (collision avoidance) rather than CD (collision detection) - send a short message to reserve the bus if it is idle - transmit a frame if reservation is successful (no collision) - listen and reserve again RING Menghubungakan suatu host dengan host berikutnya dan antar host yang terakhir dengan host yang awal sehingga terbentuk seperti cincin dari kabel. Tiap node hanya terkoneksi secara fisik dengan node yang ada di sebelahnya (kanan dan kirinya). Media transmisi yang dipakai dapat berupa twisted pair, kabel coaxial dan serat optik . Keuntungan: Seperti Topologi Bus Penggunaan sambungan point to point membuat transmission error dapat diperkecil Kerugian: Data yang dikirim bila melalui banyak komputer, transfer data menjadi lambat. Lecture 4 Token Ring - Ring Topology Token frame (3 bytes) SD AC ED Data frame token SD AC FC DAdd SAdd SD: Start Delimiter AC: Access Control ED: End Delimiter FC: Frame Control FS: Frame Status Payload CRC ED FS Up to 4550 bytes Animation Animation Media: Twisted pair (TW), fiber Topology: Logic ring (physically may be ring or star) Transmit: Bits flow in single direction from sender, next, destination to send Speed: 4, 16 or 100Mbps Status: IEEE Project 802.5, first developed by IBM Token: A permission to send data across the ring Only one token in a ring and the token rotates one by one If no data to be sent, computer passes received token to the next When a computer obtains the token, it can send a single packet A packet travels around entire ring and finally arrives source STAR Mengkoneksikan semua kabel dari tiap host ke central point sebagai konsentrator. Konsentrator ini biasanya berupa hub atau switch. Keuntungan: Akses ke server cepat Dapat menampung banyak user yang melakukan banyak proses ke server User dapat lebih banyak dibanding Bus Kerugian: Bila ada dua user yang ingin berhubungan (berkomunikasi) harus melalui server dulu sehingga ada kemungkinan terdapat error bila sambungan masing-masing user ke server kurang baik. Apabila konsentrator rusak maka jaringan rusak. Bentuk Konfigurasi Jaringan 2. Jaringan Bintang Pada sistem yang menggunakan jaringan bintang akan terdapaat satu sentral utama/host/tandem berfungsi sebagai sentral transit yang menghubungkan semua sentral yang terhubung kepadanya. Sentral A Sentral B Sentral Transit T Sentral D Sentral C Sifat-sifat jaringan Bintang 1. Cocok untuk jaringan dengan volume trafik yang rendah 2. Trafik ke sentral lain (antar sentral) dari suatu sentral dikonsentrasikan melalui sentral transit, sehingga sentral transit biasanya mempunyai derajat yang lebih tinggi. 3. Jumlah berkas saluran S linear terhadap jumlah sentral N atau S = N-1 Contoh : N = 5 sentral maka S = 5 – 1 = 4 saluran 4. Konsentrasi saluran besar 5. Efisiensi saluran tinggi Kelemahan jaringan bintang Bila sentral transit mengalami gangguan (break down) maka semua sentral di bawahnya akan terisolir (tidak dapat saling berhubungan) HIRARKI Mirip dengan extended star tetapi ia tidak punya konsentrator. Sistemnya terhubung ke komputer yang mengontrol traffic dalam topology. Mesh Tiap host punya koneksi sendiri ke semua host yang ada dalam jaringan. Karena tiap node terkoneksi ke semua node, maka data dapat dikirimkan melalui beberapa jalur yang ada. Bentuk Konfigurasi Jaringan Jumlah sentral 5 N 1. Jaringan Mata Jala S S 1 2 55 1 2 5.4 2 20 10 saluran 2 Jaringan mata jala adalah jaringan yang Keuntungan dari jaringan mata jala menghubungkan antara satu titik dengan 1. Tiap sentral mempunyai titik lain tanpa melalui satu titik pusat derajat yang sama. Sentral B Sentral A Sentral C Sentral E Sentral D Bila jumlah sentral sama dengan S dan jumlah saluran yang dibutuhkan adalah N maka dapat dirumuskan: N SS 1 2 2. Tiap sentral mempunyai hubungan langsung 3. Peralatan switching dapat lebih sederhana 4. Syarat saluran lebih murah 5. Bila salah satu saluran penghubung terganggu, maka hubungan antar sentral masih tetap dapat dilakukan melalui saluran yang lain. Kerugian jaringan mata jala 1. Efisiensi saluran rendah karena memerlukan banyak berkas 2. Konsentrasi saluran agak rendah 3. Jaringan mata jala yang satu dengan yang lain sulit dihubungkan ETHERNET Jaringan komputer umumnya menggunakan tipe jaringan ethernet, di mana topologi bisa berupa bus, dan star. Mode pengiriman digunakan CSMA merupakan salah satu skema dalam proses pengiriman paket, di mana pemakainya mendeteksi kanal lebih dahulu apakah kanal sibuk atukah sedang bebas, sebelum proses pengiriman paket. Bila pemakai mendeteksi kanal dalam keadaan bebas (idle), maka paket akan dikirimkan. Sedangkan bila kanal terdeteksi dalam keadaan sibuk (busy), maka pengiriman paket ditunda untuk beberapa saat. Collision antar paket masih mungkin terjadi. Untuk itu dibuat suatu perbaikan metode CSMA dengan nama CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection), yang sering disebut juga dengan metode Listen While Talk (LWT). TOKEN RING Token Ring merupakan salah satu protokol untuk LAN yang menggunakan kendali transmisi terdistribusi dan telah distandarisasi oleh IEEE nomor 802.5. Kendali transmisi pada Token Ring dilakukan oleh bit-bit token yang beredar sekeliling jaringan ring dari stasiun ke stasiun berikutnya. Bit-bit tersebut ditransmisikan secara serial melalui media transmisi fisik dan akan mengalami delay tiap melalui stasiun di dalam jaringan ring. Setiap stasiun akan membangkitkan kembali dan akan meneruskan setiap bit ke stasiun berikutnya. Jadi stasiun-stasiun dalam Ring juga berfungsi sebagai regenerator dan repeater. Suatu stasiun tujuan yang telah diberi alamat akan menyalin informasi yang dikirim stasiun awal bila informasi tersebut lewat, dan stasiun awal akan menghapusnya bila informasi tersebut telah membentuk satu loop penuh mengelilingi ring. FIBER DISTRIBUTED DATA INTERFACE FDDI (Fiber Distributed Data Intrface) digunakan dengan kabel fiber optic FDDI menggunakan arsitektur dual-ring dengan arah penjalaran data yang saling berlawanan, yaitu primary dan secondary ring Selama keadaan jaringan yang normal, maka ring primer yang digunakan untuk pentransmisian data, dan ring sekunder dalam posisi idle. FDDI biasanya digunakan sebagai backbone berkecepatan tinggi sebab mendukung bandwidth yang besar dan lebih jauh jangkauannya dibandingkan kabel tembaga. Lecture 4 FDDI - Ring Topology SD FC ED Token frame (3 bytes) Data frame SD FC DAdd SAdd Payload CRC ED FS Up to 4550 bytes Features: multiple frames for MM data or RT trans. Media: Fiber (Fiber Distributed Data Interconnect) or cable (CDDI) Topology: Two rings Transmit: Bits can flow in 2 directions for improving reliability Speed: 100 Mbps Status: ANSI standard, expensive than Ethernet and Token Ring Token: A permission to send data across the ring Only one token in a ring and the token rotates one by one If no data to be sent, computer passes received token to the next When a computer obtains the token, it can send a single packet A packet travels around entire ring and finally arrives source Lecture 4 Wireless LAN - Bus Topology Media: Air (infrared, spread spectrum, narrowband microwave) Topology: Logic bus Transmit: Only one can transmit, not all others can receive transmission depended upon transmitting energy and distance Speed: 1~10Mbps (infrared), 1~20Mbps (spread), 10~100Mbps (MW) Status: IEEE Project 802.11, many products from different companies CSMA/CA: Using CSMA to listen and transmit Using CA (collision avoidance) rather than CD (collision detection) - send a short message to reserve the medium if it is idle - transmit a frame if reservation is successful (no collision) - listen and reserve again WIRELESS LAN Wireless LAN: small range (< 100m) IEEE 802.11 (similar to Ethernet) - Defined by IEEE (Institute for Electrical and Electronic Engineers) - Access control: CSMA/CD (only one can send each time similar to TDMA, listen and transmit if no other transmission, otherwise wait) - Speed: 2Mbps (infrared), >10Mbps (Microwave, 2.4/5.2GHz) HIPERLAN - Defined by ETSI (European Telecommunication Standard Institute) - Access control: dynamic TDMA - Speed: 25Mbps (5GHz) and 155Mbps (17GHz) HomeRF - Defined by Home Radio Frequency Working Group (Industry, 1998) - Access control: similar IEEE 802.11 with priority and reservation control - Speed: 10Mbps (2.4GHz), support both data, voice and streaming Bluetooth - Defined by Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG, industry) - Access control: TDD (Time Division Duplex) with circuit and packet switch - Speed: 1M~10bps APLIKASI WIRELESS Address and Frame Source station Source address Destination station Destination address Packet Header Dest Addr Frame data or Payload Trailer Sour Addr All stations (computers/devices) on shared-media LAN receive all transmissions Each station assigned unique number, called station address or hardware address fixed by manufacturer, configured manually or electronically provided dynamically by software A sender specifies destination address and source address in its frame header Destination Address and Transmission Mode unicast broadcast multicast Packet can be sent to: - Single destination (station address) called unicast (1-to-1) - All stations (a special address), called broadcast (1-to-all) - Subset of stations (special addresses), called multicast (1-to-m) Ethernet - Each station has 48bits (6 bytes) unique address assigned by manufacturer - Broadcast address: all 1s address (1111…11) - Multicast address: [1xx…x], half of addresses reserved for multicast Ethernet Frame Format Preamble: 64bits (8 bytes) for receiver synchronization with incoming signal Destination address and source address Frame type (2 bytes): - 0000~05DC Reserved for use with IEEE LLC/SNAP - 0800 Internet IP Version 4 - 8008 AT&T Corporation - 8014 Silicon Graphics Corporation network games - 8137-8138 Novell Corporation IPX -… Data or Payload: Minimum 46 bytes and maximum 1500 bytes CRC (4 bytes): Cyclic redundancy check Exercise 1. Prove that the total number of links in a point-to-point network with N computers is (N2-N)/2 2. For each of bus, star and ring topologies, discuss the consequences if a station has broken. 3. In most technologies, a sending station can choose the amount of data in a frame, but the frame header is a fixed size. Calculate the percentage of bits in a frame devoted to the header, trailer and preamble for the largest and smallest Ethernet frame. 4. Assume a one megabyte file must be send from one computer to another (both are connected to a same 10BaseT Ethernet). What is the minimum time to send the file across the network? What is the minimum time across a Fast Ethernet? Across a gigabit Ethernet? 5. Give the definitions and examples of unicast, broadcast and multicast, respectively.