* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Medication
Survey
Document related concepts
Pharmaceutical marketing wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Electronic prescribing wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
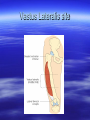
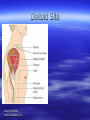
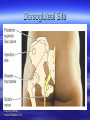
MEDICATION King Saud University College of Nursing NUR 122 Drug administration Medication: substance administered for the diagnosis, cure, treatment, or relief of a symptom or for prevention of a disease. Medication or drugs are given to exert specific physiologic effects on the body. They play an important role in preventing, treating, and curing illness, their administration has become one of the most important, complex and risk-laden aspects of nursing care. Routes of drug administration Oral: Per mouth Sublingual: under the tongue Buccal: against the cheek Pareneteral: IV, IM, SC, intradermal, intracardiac, intrathecal,intrapleural, intraosseous Topical: skin, eyes, ear, nose, rectum or vagina. Effects: local, systematic. Medication are prescribe by physician. Medication order includes the name of the drug, the dose, the route, frequency, date and time. Effects of Drugs Therapeutic effect = desired effect – Reason drug is prescribed Side effect = secondary effect – Unintended, usually predictable – May be harmless or harmful Drug toxicity – Result from overdose, ingestion of external use drug – Buildup of drug in blood Drug allergy – Immunologic reaction to drug – Mild to severe reactions (anaphylaxis) Drug tolerance – Need increasing doses to maintain therapeutic effect Drug interaction – One drug affecting effect of another Actions of Drug on the body Pharmacodynamics: – Process by which drug changes the body (mechanism of action). Pharmacokinetics: – Study of absorption, distribution, biotransformation, and excretion of drugs Pharmacokinetics Absorption: movement from the administration site into the bloodstream. Distribution: transportation of the drug from its site to the site of action. Metabolism: the drug is converted by enzymes into a less active form that can be excreted, (most drugs are metabolized in the liver). Excretion: elimination from the body. The kidneys are the most important route. Drug Nomenclature Chemical name — describes the chemical constituents of the drug Generic name — assigned by the manufacturer that first develops the drug Trade name — brand name given by the company that sells the drug Drug Preparations Oral: – Capsule, pill, tablet, suspension, syrup Topical: – lotion, ointment, suppository, transdermal patch Injectable: - Vial, Ampoule Mechanisms of Drug Actions Drug-receptor interaction — drug interacts with one of more cellular structures to alter cell function Drug-enzyme interaction — combines with enzymes to achieve desired effect Acting on cell membrane or altering the cellular environment Factors Affecting Drug Absorption Route of administration Drug solubility pH Local conditions at site of administration Drug dosage Serum drug levels Adverse Effect of Medications Iatrogenic disease: disease caused unintentionally by medical therapy. Allergic effects: immunologic reaction to the drug. Toxic effects Drug interactions Signs and Symptoms of Drug Allergy Rash Urticaria Fever Diarrhea Nausea Vomiting Anaphylactic reaction Factors affecting Medication action Developmental considerations Weight Gender Diet Genetic and cultural factors Psychological factors Illness & disease Environment, timing of administration Types of Medication Orders Standing order — carried out until cancelled by another order Prn order — as needed Stat order — carried out immediately & once Parts of the Medication Order Patient’s name Date and time order is written Name of drug to be administered Dosage of drug Route by which drug is to be administered Frequency of administration of the drug Signature of person writing the order Medication Prescription The 7 rights 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Right Medication Right Dose Right Rout Right Time (b.i.d, t.i.d, q.i.d. q8h) Right Client Right information Right Documentation Controlled Substances Required Information Name of patient receiving narcotic Amount of narcotic used The hour narcotic was given The name of physician prescribing narcotic Name of the nurse administering narcotic Oral Medications Solid form — tablets, capsules, pills Liquid form — suspensions, syrups – Oral Route — having patient swallow the drug. – Enteral route — administering drug through an enteral tube – Sublingual administration — placing drug under tongue – Buccal administration — placing drug between tongue and cheek Administration of Parenteral Medications Subcutaneous injection — subcutaneous tissue (0.5-1 ml) Intramuscular injection - muscle tissue (1-3ml) Intradermal injection — corium (under epidermis) (0.1 ml) Intravenous injection — into a vein Intracardial injection — heart tissue Intraperitoneal injection — peritoneal cavity Intraspinal injection — spinal canal Intraosseous injection — bone Sites for Intramuscular Injections Ventrogluteal site Vastus lateralis site Deltoid muscle site Dorsogluteal site Ventrogluteal site Vastus Lateralis site Deltoid Site Copyright 2008 by Pearson Education, Inc. Dorsogluteal Site Copyright 2008 by Pearson Education, Inc. Criteria for Choosing Equipment for Injections Route of administration Viscosity of the solution Quantity to be administered Body size Type of medication Topical Administration of Medications Eye: eye drops, ointments Ears: ear drops Nose: nasal drops Rectal: suppositories Skin applications: ointment, cream lotion Medical Record Documentation Document & sign each dose of medication, as soon as it is given, and the patient response. Intentional or inadvertent omitted drugs. Refused drugs. Medication errors. Type of Medication Errors Inappropriate prescribing of the drug Extra, omitted, or wrong doses Administration of drug to wrong patient Administration of drug by wrong route or rate Failure to give medication within prescribed time Incorrect preparation of a drug Improper technique when administering drug Giving a drug that has deteriorated Medication Errors Check patient’s condition immediately; observe for adverse effects. Notify nurse manager and physician. Write description of error on medical record and remedial steps taken. Complete special form for reporting errors. Patient Teaching 1. Review techniques of medication administration. 2. Remind patient to take the medication as prescribed for as long as prescribed. 3. Instruct patient not to alter dosages without consulting physician. 4. Caution patient not to share medications with others even if they have the same disease.