* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 8 Circulatory PPT
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
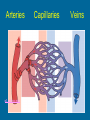
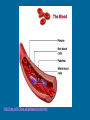
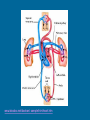
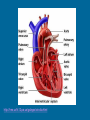
The Circulatory System Function of the Circulatory System • Use blood to move materials through the body – Oxygen to our cells – Glucose to our cells for energy – Hormones – Antibodies that fight germs – Wastes such as Carbon Dioxide Parts of the Circulatory System • Divided into three major parts: – The Blood Vessels – The Blood – The Heart Blood Vessels Hollow tubes that circulate your blood – Arteries- Carry blood with oxygen AWAY from the heart – Veins-Carry blood with carbon dioxide TO the heart – Capillaries-very thin so oxygen, glucose, and carbon dioxide can pass through Have strong, muscular walls The inner layer is very smooth so that the blood can flow easily http://hes.ucf.k12.pa.us/gclaypo/circdia.html Valves are located inside the veins. The valves only allow blood to move in one direction. http://hes.ucf.k12.pa.us/gclaypo/circdia.html Arteries w3.uokhsc.edu Capillaries Veins Blood 3 Types of Blood Cells: 1. Red blood cells carry nutrients, water, oxygen and waste products to and from your body cells. Most numerous of the blood cells. 2. White blood cells, or leukocytes, are the body's defense system. Largest in size but fewest in number. 3. Platelets: Prevents bleeding. Smallest of the blood cells. http://hes.ucf.k12.pa.us/gclaypo/circdia.html http://hes.ucf.k12.pa.us/gclaypo/circdia.html The Heart • • • • Size of your fist Thick muscular walls Divided into 4 chambers (rooms) Upper chambers – “Atriums” receive blood coming in from the veins • Lower chamber – “Ventricles” squeeze blood out into the arteries Circulation Right Atrium: Receives blood from body. Low in Oxygen, High in CO2. Right Ventricle: Pumps oxygen poor blood to the lungs Left Atrium: Receives blood from lungs. High in Oxygen Left Ventricle: Pumps oxygen rich blood to all parts of the body. www.biosbcc.net/doohan/ sample/htm/heart.htm http://sln.fi.edu/biosci2/systems/ http://hes.ucf.k12.pa.us/gclaypo/circdia.html The heart, the lungs, and the blood vessels work together to form the cycle part of the circulatory system. Pulmonary Circulation Movement of blood from the heart, to the lungs, and back to the heart again. Coronary Circulation Coronary circulation refers to the movement of blood through the tissues of the heart. What is “heart rate”? Heart rate is the number of heartbeats per unit of time. Also known as “pulse”. What is Blood Pressure? The force of blood against the walls of blood vessels. It is responsible for the movement of blood through the arteries. Good blood pressure is 120/80.