* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download US Regents Power Point 4 (Civil War to Jim Crow
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Freedmen's Colony of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
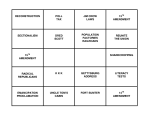
U.S HISTORY AND GOVERNMENT REGENTS REVIEW POWER POINT 4 Civil War to Jim Crow Laws Differences Between North and South • North – Economy based on production and trade – Large population – Center of abolitionist movement • South – Economy based on farming – Small population – Slavery was a widespread practice Long Term Causes of the Civil War • States’ Rights Debate: Southern states believed that they could nullify a federal law if they believed that it was unconstitutional – Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions – South Carolina Ordinance of Nullification • Extension of Slavery into the Territories – Missouri Compromise 1821: Maine enters as free state, Missouri enters as slave state; no slavery in LA territory – Compromise of 1850: California enters as free state, Texas enters as slave state; popular sovereignty used to decide status of slavery in Mexican Cession – Bleeding Kansas: Kansas Nebraska Act states that popular sovereignty will be used to decided status of slavery in LA territory; causes violence over the issue; overrules Missouri Compromise Immediate Causes of the Civil War • Republican Party: – Stop the spread of slavery into the territories • Dred Scott v. Sanford: – Pro-slavery ruling; Missouri Compromise is unconstitutional bc it denies a slaveholder his right to property • Raid at Harper’s Ferry – Failed slave uprising strikes fear in the south • Election of 1860 – Republican Abraham Lincoln elected as president despite the fact that no southern state voted for him • Southern Secession 1861 – Southern states secede from the Union creating their own country Lincoln’s Wartime Goals and Actions • Lincoln’s 1st Inaugural Address – Goal in declaring war on the south is to preserve the Union • Lincoln’s Wartime Actions – Made military decisions without the consent of Congress – Suspends habeas corpus in Union territories – Martial law: arrest anyone who is suspected of disloyalty – Overall effect: strengthens the federal gov’t Union Advantages • Population – Larger population means greater supply of soldiers • Production – Most factories were located in the North – Easier to ascertain supplies • Transportation – 90% of RR lines were located in the North – Easier to transport supplies and soldiers • Location – Most of the fighting happened in the South Major Events of the Civil War • Battle of Gettysburg 1863 – Considered the turning point of the Civil War – 3 day battle – Union emerges as the victor and continues to push confederate army back into the south • Sherman’s Total War – March from Atlanta to the Atlantic Ocean – Destroy everything: plantations, livestock, homes, etc. • Surrender at Appomattox Courthouse 1865 – Union army surrounded Lee and the confederate army – After one month of being surrounded with no supplies, Lee surrendered to Grant Reconstruction Plans • Lincoln’s Plan – Show leniency on the south – Heal the nation’s wounds quickly – South was never separated from the Union • Radical Reconstruction – Harsh on the south – Use of military to ensure south’s cooperation Help for Freedmen • Freedmen’s Bureau – Gov’t funded program – Builds schools and help freed slaves find jobs • 13th Amendment 1865 – Slavery is illegal • 14th Amendment – Citizenship and equal protection under the law for freed slaves – Legal protection cannot be denied based on race • 15th Amendment 1870 – The ability to vote cannot be denied based on race Freedmen Voting Restrictions • Poll Tax – Voters must pay a tax in order to vote • Literacy Test – Voters must pass a rigorous reading test in order to vote • Grandfather Clause – Anyone whose father/grandfather voted in the election of 1868 is exempt from poll taxes and literacy test – Automatically excluded freedmen bc they did not receive the right to vote until 1870 • Ku Klux Klan – Use of violence against freedmen and white republicans – Scare these groups from voting Andrew Johnson’s Impeachment • Andrew Johnson passed almost 30 vetoes • Against helping freedmen • Radical Republican Congress impeached Johnson • Johnson was acquitted by Senate (by one vote) • Impeachments of Johnson in 1868 and Clinton in 1998 are similar because both presidents were acquitted Segregation • Jim Crow Laws: establish segregation in the south – Blacks and whites were kept separate in all public facilities • Plessy v. Fergusson 1896: upholds the constitutionality of segregation – Segregation is acceptable if the facilities are separate but equal Cycle of Poverty • Plantation owners still need to operate large farms • Sharecropping: – Plantation owners become landlords – Former slaves become tenant farmers – Tenant farmers share their profits with landlord • Poor harvests make it difficult for landlords and tenant farmers to repay debts keeping them in a constant cycle of debt and poverty