* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download preserving the Union
Battle of Hatteras Inlet Batteries wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fort Monroe wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Galvanized Yankees wikipedia , lookup
Gettysburg Address wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Henry wikipedia , lookup
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Jubal Early wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
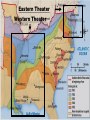
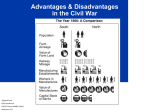
1860 Election (stance on slavery) • Democratic Party *split in two – Northern democrats nominated Stephen Douglas; South regarded him as a traitor because of his position on Lecompton and Freeport Doctrine (popular sovereignty) – Southern democrats nominated John Breckinridge • Kentucky moderate who favored preservation of Union • Platform was extension of slavery into territories and annexation of Cuba (slave as well) 1860 Election (stance on slavery) • Constitutional Union Party – John Bell of Tennessee was the nominee • Compromise candidate from border state – Party made up of former Whigs from border states and members of the Know-Nothing party – Main goal/platform was to elect a compromise candidate to preserve the union 1860 Election (stance on slavery) • Republican Party – Nominate Abraham Lincoln • William Seward was first choice but party decided he was too radical so Lincoln was seen as a moderate – Platform (know this!): • Non-extension of slavery (for Freesoilers) • Protective tariff (for industrialists) • No loss of rights for immigrants (against Know Nothings) • Transcontinental Railroad (for West) • Internal improvements at Federal expense (for West) • Free homesteads from public domain (for West) Lincoln won with less than 40% Lincoln not allowed on the ballot in 10 Southern states Once Lincoln is elected, South Carolina secedes from the United States (Secession: 12/30; election had been 11/6) •303 total electoral votes and 152 to win. Election of 1860 Secession!: SC Dec. 20, 1860 Created by Marjorie Pojer Edited by Raul Lopez Video Analysis 1. Why did Southerners dislike Abraham Lincoln? 2. Who were the first 7 states to secede from the Union? Why did Pres. Buchanan remain indifferent? 3. Who was nominated President of the Confederacy and how organized was their new government? 4. How did Lincoln address Secessionist states in his inauguration? What was his intention? 5. What effect did the attack on Fort Sumter have on the Confederacy? Inaugural Address • Lincoln vowed to preserve the Union – “hold, occupy, and possess” all Federal property in the South – “physically speaking, we cannot separate” – Careful not to offend border slave states with “hawkish” rhetoric – Republicans and Democratic Unionists supported the speech – Lower South saw it as a war message Fort Sumter • Located at the mouth of Charleston Harbor, Fort Sumter was one of the last remaining Federal forts in the South • Major Robert Anderson Notified Lincoln that the fort would soon be out of supplies and without them, he would have to surrender to confederate forces which now surrounded him Fort Sumter • Lincoln was in a no-win situation – Not sending supplies would ruin his credibility to uphold the Union – Sending supplies would be perceived as an act of war by Confederacy • Lincoln notified South Carolina that he was sending only supplies and no additional soldiers to the fort – If war breaks out, Lincoln wanted the South to fire first WHY? Fort Sumter • April 12, 1861- 70 confederate cannons begin bombardment of Fort Sumter – Anderson’s garrison held for 34 hours before they were forced to surrender the fort – Anderson’s men allowed to return North – No loss of life on either side in the first official skirmish of the Civil War Picture: Fort Sumter 1 Fort Sumter 2 WAR IS ON • April 15, 1861- Lincoln calls for 75,000 volunteers for a 90 day military service • Before Sumter many Americans thought South had the right to secede but with attack, many northerners to fight for honor of the North and to preserve the Union – Lincoln’s plan had worked- South was seen as the aggressors and the North as the victim WAR PLANS • April 19, 1861- Lincoln proclaims a blockade of Southern ports – Ineffective at first but eventually strangled the South • May 3, 1861- Lincoln calls for 3 year volunteers – 90 day militia not sufficient • 4 more states (VA, AK, TN, and NC) secede – Viewed Lincoln as waging war – Richmond replaces Montgomery as capital of Confederacy Border States • Kentucky, Missouri, Maryland, and (later) West Virginia – Remained in the Union since North didn’t start the war – Contained over 50% of white population in the South – Crucial to Union cause- sent 300,000 soldiers into Union army – Lincoln said he was “hoping to have God on his side, but he would rather have Kentucky” – West Virginia broke away from Virginia in 1861 to join Union – Strongest case against slavery being the cause • Slavery existed in border states but they still fought with Union – Family members often joined opposite sides of conflict Border States • Politically, Lincoln had to keep border states in mind when making decisionsthere was always the threat of them switching sides – ****Declared war was being fought to preserve union- not about freeing the slaves – Heavily criticized by abolitionists who saw him as a sell-out VA. 8 West Virginia secedes from Virginia in 1863 and sides with USA. Border states/slaves states remain loyal to the Union Secession •Born in Kentucky •Born in Kentucky •Self-educated •Served as Secretary of War •Congressmen from Illinois •Senator from Mississippi •Abolitionist •Slaveowner •First Presidential candidate for the Republican Party •Served as Secretary of State •Minority president •First and only President of the CSA BLUE/USA GRAY/CSA •United States of America or Union •President Abraham Lincoln •Capital: Washington, D.C. •Feds-----Federal •Yanks-----Yankees •Bluebellies •Blue coats •Confederate States of America •President Jefferson Davis •Capital: Richmond, VA •Rebs------Rebels---”Johnny Rebs” •Secessh-------Seccession •Graycoats •Yellow bellies 22 states 22,000,000 population Strong Industrial economy Majority of transportation Lincoln, a military novice. – Learns to be an exceptional commander in chief Believe war is about ending slavery and preserving the Union. 11 states 9,000,000 – includes 3.5 million slaves Agricultural economy – Exports, not food Limited manufacturing and railroad lines. Davis, military experience. – Fought in Mexican war Believe war is about states rights, independence and preserving their way of life. “The North’s major advantage would be its economy and the South’s main disadvantage was its economy” Confederate Differences • Defensive War – Only needed a stalemate- not an outright victory • North had to invade, conquer, occupy, and reintegrate the South • South felt they had the superior moral cause – Fought for self determination, its culture, its homeland, and freedoms (for whites) Confederate Differences • Better military officers – Robert E. Lee- one of the greatest military leaders in U.S. History. Offered command of US forces by Lincoln, but elected to join confederacy to remain loyal to his home state (VA) – Thomas J. “Stonewall” Jackson • Lee’s “right-hand” man • Southern soldiers more adept to outdoor life (outdoorsmen, hunters, knew the land, etc) • Shorter supply and communication lines • More unified in their cause Northern Advantages • Population of 22,000,000 to South’s 9,000,000 (which includes 3.5 million slaves) • ¾ of the nation’s wealth – Overwhelming advantage in manufacturing, shipping, and banking • • • • ¾ of the railroads in the U.S. Control of the seas: (Stronger Navy) Stronger leadership at the Federal level Ideal of preserving the union and, later, emancipation gave them the moral high ground Population Based on % North South Factories Wealth Cotton Strategy evolved over 4 years of fighting Initially plan was to win the war in Virginia by capturing Richmond- failed badly (Bull Run, Peninsula campaign, Chancellorsville) Gen Winfield Scott’s Anaconda Plan – Control river systems: cut confederacy in 2 by taking Mississippi River – Blockade and seizure of ports Later turned to a war of attrition under Grant and Sherman Don’t allow Confederacy to rest. Devastate the South by cutting a swath through GA. And then sending troops through the Carolinas Always tried to keep Confederate forces out of Defend and delay until Union gives up (war of attrition). Quick victories to demoralize Union Alliance with Great Britain Capture Washington, D.C. Defend Richmond Control border states Later Sought decisive battle that would convince the Union it wasn’t worth it Use better military leadership to your advantage and outsmart Union generals. Telegraph – Davis uses to gather forces for Shiloh. – Fredericksburg sees first extensive use on the battlefield. Railway – Greatly changes logistics and strategic maneuver. – North had good system; South had acceptable quantity, but no standardized track width. Outdated muskets replaced with rifle – greatly changes tactics. – more accurate, faster loading, fire more rounds than muskets – Minié ball (more destructive bullet) Artillery – invention of shells, devices that exploded in the air. – fired canisters, special shells filled with bullets. – Grenades – land mines are used Ironclads – replaces wooden ships Trench warfare replaces Napoleonic tactics Eastern Theater Western Theater