* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Civil War (1861-1865)
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Frémont Emancipation wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Gettysburg Address wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Assassination of Abraham Lincoln wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
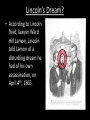
The Civil War (1861-1865) Part 3: Reconstruction Rebuilding the Union • From the beginning, Lincoln had wanted to make the South’s return to the Union as easy as possible. Rebuilding the Union • The process of bringing the South back into the Union was known as Reconstruction. Rebuilding the Union • Unfortunately, Lincoln would never get the opportunity to see Reconstruction through. • On the night of April 14, 1865, Lincoln attended a play at Ford’s Theater in Washington, DC. The Star of the Show • An actor named John Wilkes Booth had been planning to kidnap Lincoln for months. • He heard of the President’s plan to attend the play. • His plan moved from kidnapping to assassination. The Conspiracy • Booth had co-conspirators (accomplices) who were also supposed to assassinated the Secretary of State and Vice-President Johnson that night. All of them back out at the last minute John Surrat, Confederate Secret Service Samuel Arnold, friend Michael O’Laughlin, friend David Herold, a pharmacist Lincoln’s Dream? • According to Lincoln fried, lawyer Ward Hill Lamon, Lincoln told Lamon of a disturbing dream he had of his own assassination, on April 4th, 1865. The Assassination of Lincoln, 1865 • Dream or not, Lincoln attended the showing of Our American Cousin, a comedy, at Ford’s theater the night of April 14th, 1865. The Assassination of Lincoln, 1865 • Booth attended the play as well, bringing a single shot pistol and a hunting knife. The Assassination of Lincoln, 1865 • Booth, familiar with both the theater and the play, timed his moves perfectly. • He waited for a joke that would cause the theater to erupt in laughter, hoping the noise would muffle the sound of the shot. The Assassination of Lincoln, 1865 • Booth jumped from the balcony, breaking his leg, but escaped. • Lincoln died the following day. The Assassination of Lincoln, 1865 • Newspapers printed wanted posters announcing that Lincoln was assassinated by John Wilkes Booth at Ford’s Theater The Assassination of Lincoln, 1865 • A few days later, Booth was found in a nearby tobacco warehouse. • He didn’t leave the building alive The Assassination of Lincoln, 1865 • His accomplices were tried, convicted of treason, and hung. President Johnson • Vice-President Andrew Johnson was sworn in as president. • Without the strength of Lincoln, the Radical Republicans began to control Reconstruction Reconstruction • Presidential Reconstruction – bring the South back easily • Radical Reconstruction – punish the South before allowing them to enter the Union Reconstruction Amendments • One condition for the South to reenter the Union was to accept the 13th, 14th and 15th Amendments to the Constitution. 1. The 13th Amendment • Freed the slaves, ended slavery in the United States 2. The 14th Amendment • Former slaves became citizens of the United States 3. The 15th Amendment • Gave AfricanAmerican males the right to vote How you remember the amendments Conclusion • Reconstruction would not be complete in the South until 1877 (12 years after the Civil War ended.) • The issue of race in the South has never been resloved. • Even today, we are still a sectional society Conclusion • The issue of state’s rights and sectional differences between the North and the South are still very real issues in the United States • The issue of slavery has been replaced by Civil Rights, and more recently Gay Rights. • Even as recent as 2009, states have mentioned secession as an option.