* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 16.1
Battle of Fort Donelson wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Fort Stanton (Washington, D.C.) wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Gettysburg Address wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hampton Roads wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Fort Monroe wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Fort Pulaski wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Missouri secession wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Henry wikipedia , lookup
Galvanized Yankees wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hatteras Inlet Batteries wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
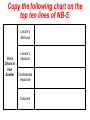
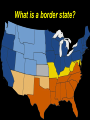
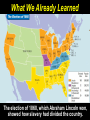
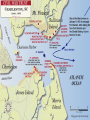
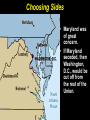
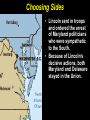
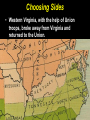
Copy the following chart on the top ten lines of NB-5. Lincoln’s dilemma First Shots at Fort Sumter Lincoln’s decision Confederate response Outcome Copy the following chart on the middle ten lines of NB-5. Northern states’ response Lincoln Calls Out the Militia Southern states’ response Virginia’s importance Lee’s decision Copy the following chart on the bottom ten lines of NB-5. Importance of the border states Maryland Choosing Sides Kentucky Virginia Missouri Lesson 16.1a: War Erupts Today we will examine the decisions made by Lincoln in the first few weeks of the Civil War. Vocabulary • examine – look at closely • dilemma – a difficult problem with two equally undesirable solutions • militia – group of volunteers who serve in their state’s military during emergencies • border states – slave states that hadn’t seceded yet • secession – withdrawal from the Union Check for Understanding • What are we going to do today? • What is a dilemma? What is a militia? What is a border state? What We Already Learned The election of 1860, which Abraham Lincoln won, showed how slavery had divided the country. What We Already Learned In 1858, Lincoln himself had warned that slavery might fatally divided the Union. • “A house divided against itself cannot stand. I believe this government cannot endure, permanently half slave and half free. • I do not expect the Union to be dissolved — I do not expect the house to fall — but I do expect it will cease to be divided. • It will become all one thing, or all the other.” What We Already Learned After Lincoln’s election, seven Southern states seceded and by February 1861 had formed the Confederate States of America. Read aloud with me! What We Already Learned In his inaugural address, Lincoln reassured the South that he had no intention of interfering with slavery, but also spoke forcefully against secession. What We Already Learned • Lincoln wanted no invasion, but he would not abandon the government’s forts in the South. • Most of these, including Fort Sumter in South Carolina, were still manned by Union troops. • These forts would soon need to be resupplied. Get your whiteboards and markers ready! 1. How did the secession of the Southern states confirm the fears Lincoln had expressed in his “House Divided” speech? A. The powers of the House of Representatives would have to be increased. B. It demonstrated that Congress was too weak to deal with the nation's problems. C. It showed how the issue of slavery was threatening the Union. D. It meant slavery would have to be outlawed in the United States. First Shots at Fort Sumter • Fort Sumter was running out of supplies. Read aloud with me! First Shots at Fort Sumter • Fort Sumter was running out of supplies. • Lincoln decided to send supply ships to Fort Sumter. First Shots at Fort Sumter • Fort Sumter was running out of supplies. • Lincoln decided to send supply ships to Fort Sumter. • Confederate commander P.G.T. Beauregard’s shore guns fired on the fort for 34 hours. First Shots at Fort Sumter • Fort Sumter was running out of supplies. • Lincoln decided to send supply ships to Fort Sumter. • Confederate commander P.G.T. Beauregard's shore guns fired on the fort for 34 hours. • The fort commander Major Robert Anderson was forced to surrender. Get your whiteboards and markers ready! 2. Where were the first shots of the Civil War fired? • Fort Sumter was where the first shots of the Civil War were fired. Lincoln Calls Out the Militia Two days after the surrender of Fort Sumter, President Lincoln asked the Union states to provide 75,000 militiamen for 90 days to put down the uprising in the South. Lincoln Calls Out the Militia Lincoln’s call for 75,000 state militia troops for 90 days led to enthusiasm in the North. Lincoln Calls Out the Militia Many responded with excitement, relief, or eagerness. Some feared the war would be over before they got a chance to fight. Get your whiteboards and markers ready! 3. Which seven states were the first to secede to form the Confederacy? Which one is NOT included? 3. Which seven states were the first to secede to form the Confederacy? A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. South Carolina Mississippi Kentucky Florida Alabama Georgia Louisiana Texas Which one is NOT included? Lincoln Calls Out the Militia • Southern states that had not yet seceded reacted with shock and anger to this decision. • They thought Lincoln’s call for troops was evil and aggressive. Lincoln Calls Out the Militia Virginia, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Arkansas voted to join the Confederacy. Lincoln Calls Out the Militia As in the North, Southern volunteers also rushed to enlist, with many fearing the war would be over before they could join the fight. Virginia’s Secession • With Virginia on its side, the Confederacy had a much better chance for victory. • The Confederacy was strengthened by Virginia’s wealth, population, and prestige. Virginia’s Secession In recognition of Virginia’s importance, the Confederacy moved its capital to Richmond. Lee’s Decision • Lincoln prepared for the war by offering command of all Union forces to the talented general, Robert E. Lee. • Unwilling to fight against his home state, Lee resigned from the U.S. Army and offered his services to the Confederacy. Get your whiteboards and markers ready! 4. Why was Virginia important to the Confederacy? A. It was home to many important factories. B. It was a large and wealthy state. C. It was the home of the talented general, Robert E. Lee. D. Its mountains and valleys served as a protective barrier for the Confederate capital in Charleston. Choose all that are true! 5. Why did Robert E. Lee decide to fight for the Confederacy ? A. He did not support the idea of the Union. B. He hoped to serve in the Confederate government some day. C. He refused to fight against his home state. D. He wanted to keep using slaves on his plantation. Choosing Sides • It was important to Lincoln that the border states did not secede. • Border states were slave states that bordered the North and had not yet seceded. Choosing Sides The location and resources of the border states made them pivotal in tipping the scales to one side or the other. Choosing Sides • Maryland was of great concern. • If Maryland seceded, then Washington, D.C., would be cut off from the rest of the Union. Choosing Sides • Lincoln sent in troops and ordered the arrest of Maryland politicians who were sympathetic to the South. Choosing Sides • Lincoln sent in troops and ordered the arrest of Maryland politicians who were sympathetic to the South. • Because of Lincoln’s decisive actions, both Maryland and Delaware stayed in the Union. Choosing Sides • Kentucky was deeply divided over secession. • Its rivers could provide an invasion route into the South, or provide a barrier for the South. • An 1861 invasion by Confederate troops convinced the state to stay in the Union. Choosing Sides • Western Virginia, with the help of Union troops, broke away from Virginia and returned to the Union. Choosing Sides • In Missouri, Union troops and local unionists fought against secessionists. • In the end, Missouri also stayed in the Union. Get your whiteboards and markers ready! 6. Why were the border states important to both sides? A. Their location and resources made them pivotal in tipping the scales to one side or the other. B. They contained most of the people and wealth of the country. C. They believed in secession, but did not recognize slavery. D. Many European immigrants lived there, and could influence the support of European nations. 7. Which border state was formed when it seceded from a Confederate state? A. B. C. D. E. North Carolina North Dakota West Virginia New Jersey Arkansas 7. Which border state was formed when it seceded from a Confederate state? A. B. C. D. E. North Carolina North Dakota West Virginia New Jersey Arkansas