* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13 Life in the State of Texas
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Union blockade wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Arkansas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Jubal Early wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
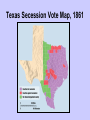
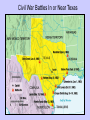
Chapter 14 The Civil War 1860-1865 Essential Questions What conditions in the US led to the Civil War? Why did Texas choose to join the Confederate States of America? How did the Civil War and Reconstruction effect Texas? A Nation Divided • By 1860, nation was divided and many southern states were threatening to secede from Union • Both sides were willing to fight for what they believed in…war was looming • Republican Party: formed in 1854 – goal to stop western spread of slavery – Rep party members thought slavery counter to democracy and American ideals – Also wanted to end slavery in states where slavery already existed – Supported economic change and a higher tariff – Tariff: tax placed on imported or exported goods • Tariff would help American industry in North by raising prices on competing imports A Nation Divided, cont • Most Texans were Democrats and were opposed to new Republican Party • Thought that Republican tariff would destroy southern economy because it depended on foreign trade and slave labor • Democrats wanted to prevent Republicans from gaining control of US government • Debate between Dem/Rep lead to arguments over state’s rights – Many in south didn’t think federal govt should have power to decide whether a state could have slavery or not – Also, they thought each state should have right to withdraw from Union if citizens voted to – Northern states disagreed and said that federal laws applied to all states and states could not legally separate from Union – These topics were strongly debated in Presidential Election of 1860 Presidential Election of 1860 • Democratic Party held convention on Charleston, SC to select Dem candidate…even within the party, they couldn’t agree on issue of slavery • As a result, most southern delegates (including Texas) left convention on protest • Remaining Democrats met in Baltimore, MD and selected Stephen A. Douglas (IL) as candidate for President • Democratic delegates who left Charleston, selected current VP John Breckinridge as candidate • Republican Party met in Chicago, IL and nominated Abraham Lincoln as their candidate Presidential Election, cont • Split in Democratic Party, gave Republican Party better chance to win • Southern states threatened to secede from the union if Republican candidate won • To prevent this, a new party was formed – Constitutional Union Party • selected John Bell of Tennessee as their candidate. – Goal was to keep any of the 4 candidates from getting enough votes to win. Then, House of Representatives would have to choose new president • Texas Governor Sam Houston wanted to keep Union together – He wanted to be the Constitutional Union Party Candidate… – He didn’t get nomination but he fought hard to keep Texas in Union…didn’t want war at all Presidential Election, cont • Texans voted for Breckinridge, then Bell, then Douglas (only 410 votes) • Lincoln didn’t receive any votes in Texas. His name wasn’t even on ballot • But, Lincoln received most Northern votes and won the election – He became the 16th president of the US Reaction to Lincoln’s Election • Soon after Lincoln was elected, SC seceded from Union – Then, Georgia, Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, and Louisiana seceded from Union – They joined together as the Confederate States of America • Many Texans wanted to secede, too – They wanted a convention to vote on issue but Gov Sam Houston ignored request – Other leaders formed the convention anyway and the delegates who would vote were elected The Secession Convention in Texas • Jan. 28, 1861: delegates met in Austin • Elected Judge Oran M. Roberts of Texas Supreme Court as leader • Meeting was very tense but outcome was clear…they met to vote to secede • They voted 166-8 to adopt an Ordinance of Secession Ordinance: an official order Secession Convention, cont • Feb. 23, 1861: Texas citizens voted to approve the ordinance • Some counties voted against the ordinance – mostly where the German immigrants lived, some counties along Red River and in Angelina County (East Texas) • The Texas Constitution of 1845 was changed to reflect Texas’ vote – Revised constitution changed United States of America to Confederate States of America – New constitution defended state’s rights and slavery • Stated that freeing slaves was illegal • On March 2, 1861: Texas became 7th state to secede from Union Texas Secession Vote Map, 1861 Governor Houston’s Response • Sam Houston couldn’t prevent secession • He wanted Texas to remain independent and not join Confederacy but that didn’t happen • Texas was immediately accepted into the Confederacy • During process of secession, Lincoln offered Houston federal troops to forcefully keep Texas in the Union – Houston refused use of the troops – He had fought for Texas and refused to fight against it – The troops remained in Texas even though Houston refused to use them – Dealing with the troops became first goal of new Confederate State of Texas Governor Houston’s Response, cont • All Texas government officials had to take oath of office to the Confederacy but Sam Houston refused to take the oath – When his name was called 3 times to take the oath, he sat silently and office of Governor of Texas was declared vacant – Lieutenant Gov Edward Clark became the first ad interim governor of Confederate Texas • After he was removed from office, he left Austin and went to Galveston for awhile. • Then he went to Huntsville to his “steamboat house” (see p. 307) He died there on July 3, 1863 (70 yrs old) http://www.tspb.state.tx.us/spb/gallery/govs/images/1989_38_Edward_Clark_LG.jpg John Breckinridge Edward Clark John Bell http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_C._Breckinridge http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Bell_(Tennessee_politician) http://0.tqn.com/d/history1800s/1/0/v/3/-/-/Abraham-Lincoln-1865-400.jpg http://www.abrahamlincolns.com/images/categories/presidential/abraham-lincoln-speech.jpg Abraham Lincoln Sam Houston http://www.tshaonline.org/handbook/online/arti cles/ccs06 http://www.shsu.edu/~smm_www/Tour/grounds /sh1.shtml http://samhoustonmovie.com/index.php/samh/ places/ http://www.roadsideamerica.com/story/7247 http://texashistory.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metapth6587/small/ Organizing the Confederacy • Francis R. Lubbock: Texas’ first Confederate governor • Confederate President: Jefferson Davis • 2700 Federal troops still stationed in Texas…were asked to leave • Confederate Brigadier General Ben McCulloch had to force federal soldiers out of Texas…done peacefully Organizing the Confederacy, con’t • All 11 Confederate States demanded that Union surrender all federal property in their states • Many forts taken peacefully…good for Confederate states because they got the supplies that were in forts • Union troops refused to leave Fort Sumter, in Charleston, SC. – Fighting broke out • Civil War began in Fort Sumter on April 12, 1861 Military Strength of Texas • About 60,000-70,000 Texas volunteers fought in Civil War • Hood’s Texas Brigade: sent to Virginia to fight; named after their commander, John Bell Hood – Confederate General Robert E. Lee respected their courage and military ability; called them “my Texans” • Terry’s Texas Rangers: commanded by General Benjamin “Frank” Terry • Ross’s Brigade: commanded by General Lawrence “Sul” Ross • Texans fought in the Army of Northern Virginia, the Army of Tennessee, and the Army of the Trans-Mississippi Sending More Troops to Fight • Texas had no more men who volunteered to fight so Texas started a draft: – Draft: the enlisting of persons for required service in the armed forces • The draft made people mad – Didn’t want to fight in war – Exceptions: if owned more than 20 slaves didn’t fight – Draft threatened cotton production • John Bankhead Magruder: commanded Texas troops during Civil War Military Affairs in Texas • During the Civil War, Texans expected Confederate soldiers to guard frontier – But they couldn’t…too busy fighting – Texans had to defend against Native Americans • No major battles were fought in Texas • During Civil War, most fighting in Texas was centered on keeping Gulf Coast ports open • Texas called “Storehouse of the Confederacy”: supplied food, weapons, and supplies for Confederacy Military Affairs, cont • John R. Baylor: led troops into NM to claim as part of Confederacy • General H. H. Sibley: led more Confederate troops into NM. Defeated Union at Valverde but lost at Battle of Glorieta. So, NM became Union again • Battle of Galveston Island: Pres Lincoln ordered a blockade: – Blockade: action to stop transportation of goods or people into or out of an area Civil War Battles In or Near Texas Battle of Galveston Island • Supplies were shipped in and out of Galveston Bay • Because of the blockade, Union troops captured the island…wanted to use it as a base to guard Gulf of Mexico • Texas General John B. Magruder launched attack to retake island on Jan 1, 1863 – One group of Confederate soldiers sailed into Galveston Harbor on Cottonclads: flat bottom boats lined with bales of cotton to protect soldiers from bullets – Another group of Confederate soldiers crossed railroad bridge from mainland – Confederate forces took over Galveston Island and remained in control till end of Civil War Other Military Campaigns • Battle of Sabine Pass: Sept 8, 1863 – Sabine Pass is narrow channel along border of Louisiana – Union General Banks planned to move Union troops by ship up channel and then march north to cut of TX railroad connection to Louisiana – But, Confederate Lieutenant Dick Dowling stationed his soldiers along channel – When Banks’ ships entered channel, Confederate troops fired on them and sank 2 ships. No other Union ships tried to get through – Confederacy won that battle Other Military Campaigns, cont • Union Gen Banks tried to get into Texas again by sending troops up Mississippi River and then up Red River…he wanted to take over North Texas • But, many Confederate soldiers met Union forces in Mansfield, LA (25 miles east of TX border) • Smaller Confederate forces (led by General Richard Taylor) defeated Union forces and forced them to retreat • Texas was safe from invasion Other Military Campaigns, con’t • Battle of Sabine Pass, con’t – Confederate forces under command of John “Rip” Ford and Santos Benavides took over area on July 30, 1864 – On May 13, 1865, Union forces fought Confederate troops in a land battle at Palmito Ranch. Confederates won battle but war was actually already over – General Robert E. Lee had already surrendered by the time the Battle at Palmito Ranch was fought Other Military Campaigns, con’t • Battle of Dove Creek: – Jan 8, 1865 – 600 Kickapoos were migrating from Kansas to Mexico – 160 Confederate soldiers thought they were Comanches and Kiowas – 22 Confederate soldiers killed 14 Indians Other Military Campaigns, cont • Battle at Palmito Ranch: – last land battle of Civil War – fought at Palmito Ranch in South Texas near Brownsville…on May 12, 1865 • Union blockade of southern ports forced Confederate troops to find another way to get cotton out and supplies in • Cotton transported through Brownsville to Mexican port of Matamoros. Then it was loaded on ships for Europe…not affected by blockade • But, in Nov, 1863, Union forces took over Brownsville to try to enforce the blockade Facts • Civil War started: April 12, 1861 • Confederate (South) – President: Jefferson Davis – General in Charge: Robert E. Lee • Union (North/US) – President: Abraham Lincoln – General in Charge: Ulysses S. Grant • Civil War ended: April 9, 1865 • Pres Lincoln Assassinated : April 14, 1865 • 11 Confederate States: Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia Terry’s Texas Rangers http://www.terrystexasrangers.org/pictures/portraits/scouts.jpg Benjamin Frank Terry Terry’s Brigade http://www.lsjunction.com/people/ross.htm Sul Ross http://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Benjamin_Franklin_Terry The Effects of War • Read: A Real Life Story p. 315 • Read: Women in Combat p. 315 • Because no major battles were fought in Texas, land didn’t suffer as much damage as other southern states • But, many Texans fought in the war…left behind families, homes, job…more work left to do for those left behind The Effects of War, cont • Problems after the war: – Tensions between those who supported Confederacy and those who supported Union – Union blockades reduced sale of farm products (cotton) and the economy suffered – Supplies in Texas were scarce Union Supporters in Texas • Most supported Confederacy but about ¼ were against secession…remained loyal to Union during Civil War • North Texas: in 1862, Texans who opposed Confederate draft formed a secret society called the Peace Party – Confederate supporters thought Peace Party would help Union defeat Confederacy – Some vigilantes took matters into their own hands by hanging 40 members of the Peace Party at Gainesville to stop support of Union – Vigilantes: people who punished criminals or took control without authority to do so Union Supporters, cont • German Texans: some supported Union/opposed slavery and some supported slavery…depended on where they lived…some fought for Confederacy • Opposition to Confederate Draft caused some German Texans to organize a Union Loyal League to serve in Union army – Led by Major Fritz Tegner, left Texas to join Union army – But, some Confederate soldiers led by Lieutenant CD McRae followed them Union Supporters, con’t – McRae’s men caught up with German Texans at Nueces River…they fought in the Battle of the Nueces – Many Union German Texans died or were executed – Some survivors reached Union troops in New Orleans – A monument was built in Comfort, TX to honor the Germans & one Mexican American who died fighting for Union http://www.texasescapes.com/TexasHillCountryTowns/ComfortTexas/ComfortTexas.htm Wartime Economy • During War, Texans still grew cotton and raised cattle but the agriculture was greatly affected – By blockades…ports for shipping closed – Union victories along Mississippi River closed land routes – Texans couldn’t sell cotton – Farmers started growing more wheat and corn instead of cotton Wartime Economy, cont • Women took over men’s jobs – Stores, post offices, farms, plantations, ranches, teachers, doctors, factories • Weapons factory in Austin and Tyler…made 800 weapons/month • Iron furnaces opened in East Texas • Prisoners in Huntsville made clothes – Women made bandages and clothes for soldiers – Sent boxes filled with food and supplies to troops Wartime Economy, cont • Because Union blockades kept goods from entering or leaving Confederate states, people couldn’t sell as much so weren’t making as much money • But, expenses were going up…taxes went up to support war • Confederate money lost value • See Linking History to Economics about prices: p. 318 Home Front Hardships • Because of blockades, many items were in short supply – Clothes, shoes – Medicines and hospital supplies…they were sent to battlefield instead of towns – Paper…some newspapers stopped publishing – People got creative: brewed acorns or corn to drink instead of coffee; used honey instead of sugar, herbs instead of medicine Refugees • During war, thousands of slaves were sent to Texas from other states – Slave owners hoped that would prevent them from running away or being taken away – Many slave owners came to Texas with their slaves…not happy to be there – Read Texas voices p. 318 about Kate Stone The War’s End • April 9, 1865: Confederate General Robert E. Lee surrendered to Union General Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox Courthouse, Virginia. This ended war the Civil War • Some fighting still continued, though, as it took time for word to spread that war was over • June 2, 1865: Confederate General Edmund Kirby Smith signed official surrender of Trans-Mississippi area which included Texas…2 months after Lee surrendered • Soldiers went home to families • Much of the old Southern Way of life had ended • Much uncertainty…nobody knew what to expect next