* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Ultrastructure
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
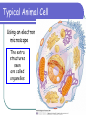
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
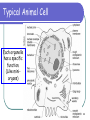
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
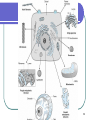
Confocal microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Higher Biology Cell Ultrastructure By the end of this lesson: You should be able to: Know what an organelle is Recognise the following: ribosomes; nucleus; rough endoplasmic reticulum; chloroplasts; mitochondrian; Golgi Body Label named organelles on diagrams Know the functions of named organelles 2 Electron Microscope The light microscope has limited magnification. The electron microscope uses a beam of highly energetic electrons to examine objects on a very fine scale. This examination can yield the following information: Topography The surface features of an object or "how it looks", its texture; direct relation between these features and materials properties (hardness, reflectivity...etc.) 3 Electron Microscope Morphology The shape and size of the particles making up the object; direct relation between these structures and materials properties (ductility, strength, reactivity...etc.) Composition The elements and compounds that the object is composed of and the relative quantities of them; direct relationship between composition and materials properties (melting point, reactivity, hardness...etc.) 4 Typical Animal Cell Using a light microscope 5 Typical Animal Cell Using an electron microscope Much more detail is revealed 6 Typical Animal Cell Using an electron microscope The extra structures seen are called organelles 7 Typical Animal Cell Each organelle has a specific function. (Like miniorgans) 8 9 Typical Plant Cell Using a light microscope 10 Typical Plant Cell Using an electron microscope 11 Ultrastructure Insert and complete the “Cell Ultrastructure” sheet from your pack into your notes. 2. Draw a table to show the functions of the following 7 cell structures: 1. Mitochondria Ribosome Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Chloroplasts Nucleus Golgi body Cell membrane Use Pages 317-318 of Torrance 12 By the end of this lesson: Can you do it? Know what an organelle is Recognise the following: ribosomes; nucleus; rough endoplasmic reticulum; chloroplasts; mitochondrian; Golgi Body Label named organelles on diagrams Know the functions of named organelles 13