* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Methods of Sexual Reproduction
Survey
Document related concepts
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Spawn (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Parental investment wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Reproductive suppression wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila melanogaster wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Animal sexual behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
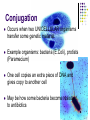
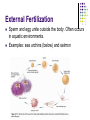
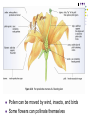
Mating Process by which gametes arrive in the same place at the same time. Mating seasons (environmental conditions) Mammals mate on land or in water Methods of Sexual Reproduction Conjugation Occurs when two UNICELLULAR organisms transfer some genetic material. Example organisms: bacteria (E.Coli), protists (Paramecium) One cell copies an extra piece of DNA and gives copy to another cell May be how some bacteria become resistant to antibiotics Hermaphrodites Have both male and female reproductive cells in one individual. Useful if immobile or rarely meet other individuals Examples: Earthworms, Sponges, Barnacles and flowers External Fertilization Sperm and egg unite outside the body. Often occurs in aquatic environments. Examples: sea urchins (below) and salmon Advantages very little energy required to find a mate Large amounts of offspring produced at one time Disadvantages Even though millions of gametes released, many will not survive outside parents Unprotected, sometimes preyed upon. Not cared for by parents, many do not survive to adulthood. Internal Fertilization The union of sperm and egg occurs inside the female. Examples organisms: some aquatic animals such as sharks and most land animals. Humans reproduce this way!! Advantage more offspring survive because as embryo they are protected, and parental care Disadvantage More energy to find a mate Results in fewer zygotes, compared with external fertilization. Pollination (in plants) Internal fertilization, called Pollination Transfer of male gametes (from male part of plant) called pollen to ovules (female reproductive part of plant) Pollen grains carry the sperm cells. The ovules contain the egg cells. Pollen can be moved by wind, insects, and birds Some flowers can pollinate themselves 1. What are types of asexual reproduction we went over? 2. What are methods of fertilization we went over for sexual reproduction? 3. Write out the definitions of the following Sexual reproduction: Asexual reproduction: 4. What are the advantages and disadvantages of sexual and asexual reproduction? Consider for individual plants and animals as well as entire populations. (make a chart to answer)