* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Type three secretion system wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
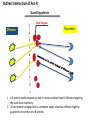
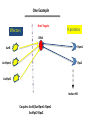
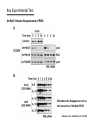
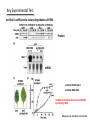
Plant response to bacterial TypeIII effectors Lihua 12.3.08 Plant responses to pathogens Susceptibility: host-pathogens Resistance: non-host pathogens •Basal defense: first line defense PAMP-triggered immunity(PTI): common pathogen-associated moleculars (lipopolysaccharides, flagellin, elongation factor and peptidoglycans) •Hypersensive response(HR): Avirulence protein-R protein interaction Effector-triggered immunity(ETI): Type III effetors (T3Es) Structural class of R proteins Kruijt M et al. Molecular plant pathology 2005,6( 1 ),85–97 Avirulence and Virulence activity of effectors Block A et al. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 2008, 11:396–403 Indirect interaction of Avr-R Guard Hypothesis Host Targets Effectors R proteins 1. A R protein could response to two or more unrelated type III effectors targeting the same host machinery. 2. A host protein complex that is a common target of various effctors might be guarded by more than one R protein. One Example Host Targets Effectors R proteins RIN4 Rpm1 AvrB AvrRpm1 Rps2 AvrRpt2 Induce HR Couples: AvrB/AvrRpm1-Rpm1 AvrRpt2-Rps2 Key Experimental Test Yeast two-hybrid and coimmunoprecipitation data shows that: RIN4 directly interacts with AvrB, AvrRpm1 and RPM1 RIN4 is required for the HR induced by RPM1 Col-0: as positive control Rpm1/rps2: double mutant of two R proteins as negative control rin4-as : homozygous rin4 with normal morphology Mackey D et al. Cell 2002. 108: 743–754 Key Experimental Test AvrRpm1 or AvrB Induces RPM1-indepentdent Phosphorylation of RIN4 Mackey D et al. Cell 2002. 108: 743–754 Key Experimental Test AvrRpt2 induces disappearance of RIN4 What does the disappearance do to the interaction of AvrRpt2-RPS2? Mackey D et al. Cell 2003. 112: 379–389 Key Experimental Test Elimination of RIN4 Activates RPS2: T-DNA insertion into the RIN4 gene is protein null and seedling lethal, while rin4/rps2 double mutants survive Overexpression of RIN4 suppresses RPS2-induced HR Mackey D et al. Cell 2003. 112: 379–389 Key Experimental Test AvrRpt2 is sufficient to induce degradation of RIN4 Protein mRNA avrRpm1-RIN4-Rpm1 avrRps2-RIN4-Rps2 AvrRpt2 could block the function of RPM1 By reducing RIN4 Mackey D et al. Cell 2003. 112: 379–389 Conclusion RIN4 is required for the HR induced by both RPM1 and RPS2 AvrRpm1 or AvrB Induces RPM1-indepentdent Phosphorylation of RIN4, and RPM1 recognizes the phosphorylation to induce HR AvrRpt2 induces disappearance of RIN4, and RPS2 induce HR by the recognization of disappearance Weak point: 1. Need more convincing evidence from mass spectrometer about the phsophorylation of RIN4 since some other modification may exist; 2. Also need RIN4 in Col-0 treated with CIP as a control in following figure a a b 3.Need pattern of the expression level of RIN4 at different hours without inoculation of effectors in figure b. T H A N K Y O U