* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Survey
Document related concepts
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Glycemic index wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
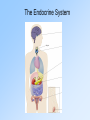
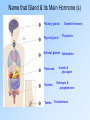
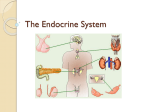
The Endocrine System Main Function and Vocabulary 1.The main function of the endocrine system is to release hormones into the bloodstream which deliver messages throughout the body. Basically it does what the Nervous system cannot. 2. Endocrine Gland- release the hormones into the blood stream. 3. Hormone- chemicals that travel through the bloodstream and affect bodily activities. Pituitary & Pineal Glands 1. Posterior lobe: stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus a. Antidiuretic hormone: stimulates kidneys to reabsorb water 2. Anterior lobe a. Growth hormone: promotes growth and development of the body 3. Disorder: Giantism & dwarfism 4. Pineal Gland: a. Releases melatonin which affects reproductive development & sleep cycle Thyroid Gland 1. Thyroid Gland a. Consists of two lobes, one on each side of the trachea b. Produces thyroxine c. Thyroxine: maintains metabolism; regulates rate of oxygen use by cells Pancreas 1. Long, soft organ in the posterior abdominal wall, behind the stomach 2.Pancreatic islets secrete glucagons & insulin a. Glucagons – involved in carbohydrate metabolism; released when glucose level in blood is low * causes liver to convert glycogen into glucose and releases the glucose into the bloodstream b. Insulin – causes most of the body’s cells to take in glucose * When insulin is low or absent, glucose is not taken up by most body cells and the body begins to use fat as an energy source 3. Disorder: Diabetes Adrenal Glands 1. Paired; one on upper portion of each kidney 2. Secretes adrenaline a. Adrenaline increases heart rate & opens up the airways (bronchioles) in the lungs (fight / flight hormone) Ovaries 1. Produce 2 groups of sex hormones 2. Both contribute to the development & function of female reproductive organs and sex characteristics a. Estrogens promote: * breast development * fat distribution in hips, legs, & breasts * maturation of reproductive organs b. Progesterone causes uterine lining to thicken in preparation for pregnancy Testes 1. Testosterone is produced by the testes 2. Produced during embryonic development & stops shortly after birth; resumes production during puberty 2. Responsible for: a. Growth & development of male reproductive structures b. Increased skeletal & muscular growth c. Enlargement of larynx (voice changes) d. Growth & distribution of body hair Name that Gland & Its Main Hormone (s) Pituitary gland Thyroid gland Growth hormone Thyroxine Adrenal glands Adrenaline Pancreas Ovaries Testes Insulin & glucagon Estrogen & progesterone Testosterone