* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Benchmark SC.B.1.2.2: The student recognizes various forms
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Renewable portfolio standard (United States) wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
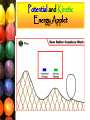
DISCLAIMER This Presentation may contain Copyrighted Material, DO NOT DISTRIBUTE Benchmark SC.B.1.2.2: The student recognizes various forms of energy (e.g., heat, light, and electricity) Ophir Ortiz Outline Outline • • • • • • • Energy Definition Vocabulary Forms of Energy- Light GLE Forms of Energy- Heat GLE Forms of Energy- Sound GLE Potential and Kinetic Energy GLE Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy GLE • Frequency, wavelength, and energy GLE Vocabulary Biomass Renewable energy source. Includes: wood, municipal solid waste (garbage), and agricultural waste (i.e., corn cobs and wheat straw). Coal Non-renewable energy source; produced from decayed animals and plants Electricity flow of electrons Electrons the particles in atoms that carry negative charges Energy the ability or capacity to do work Units: Joules (J) Frequency how often something happens in a given period of time Geothermal power Renewable energy; comes from heat energy buried beneath the surface of the earth Heat form of energy that is transferred by a difference in temperature Vocabulary (cont’d) Kinetic energy energy of motion Natural gas Obtained by drilling into the earth; formed from fossils millions of years old that were deposited in the earth. This is a source of non-renewable energy. Non-renewable energy Takes millions of years to produce more; the supply can run out. Examples: coal, natural gas, oil Nuclear process in which atoms are split- this produces heat, and this heat is used to spin turbines that produce electricity; source of non-renewable energy Oil This is a non-renewable source of energy that takes millions of years to produce. Potential energy Energy of position Renewable energy Examples: solar energy, wind, geothermal; this type of energy can be produced quickly Solar energy Form of renewable energy; comes from the sun What is ENERGY??? • Energy is defined as “the ability to do work” • When we eat, our bodies transform the energy stored in the food into energy to do work • When we run or walk, we "burn" food energy in our bodies • When we think or read or write, we are also doing work What is ENERGY??? • Energy can be found in a number of different forms. It can be – chemical energy – electrical energy – heat (thermal energy) – light (radiant energy) – mechanical energy – nuclear energy. Energy • Energy makes everything happen and can be divided into two types: • Stored energy is called potential energy. • Moving energy is called kinetic energy. • With a pencil, try this example to know the two types of energy. • Put the pencil at the edge of the desk and push it off to the floor. The moving pencil uses kinetic energy. • Now, pick up the pencil and put it back on the desk. You used your own energy to lift and move the pencil. Moving it higher than the floor adds energy to it. As it rests on the desk, the pencil has potential energy. The higher it is, the further it could fall. That means the pencil has more potential energy. Potential and Kinetic Energy Applet Potential and Kinetic Energy Activity Downhill Activity Two cylinders that look the same may roll down a hill at different rates. In this activity, two cylinders are rolled down a ramp • Washers are arranged inside the cylinders (outside of the rim for one cylinder, center of the rim for the second cylinder) • Due to the mass distribution, the rims with the mass along the sides will have to use more of its Potential Energy just to get moving, and this is why it will be slower than the other rim Source:http://www.exploratorium.edu/snacks/downhill_race.html Forms of Energy: Light What is light? • It's a kind of energy called "electromagnetic (EM) radiation" – More information on electromagnetic radiation in the appendix • light is the part WE can see, the part that makes the rainbow Light Activity: Lets Make a Rainbow!! MATERIALS: • glass jar or a large drinking glass • small mirror • flashlight • dark room with white walls PROCESS: • Fill the jar or glass with water. • Place the mirror inside the water filled jar or glass. • Tilt the mirror slightly upward. • In a very dark room with white walls, shine the flashlight onto the mirror. • A rainbow will appear! (Note: If no rainbow appears at first, just change the angle of the light from the flashlight or change the angle of the mirror.) EXPLANATION: • The mirror reflects light that passes back through the water, traveling at an angle. The water bends, or refracts, the light. As the light bends, it separates into the colors of the rainbow...red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. http://www.weatherwizkids.com/rainbow1.htm Forms of Energy: Heat • Heat is another form of energy. • At absolute zero (-273°C) the particles do not vibrate. • When we heat something we make the particles move faster. • The thermometer is a tool used to measure heat energy Hyperlinked Image Activity: How to Make a Thermometer http://www.wattsonschools.com/pdf/ue-2.pdf Forms of Energy: Sound • Sound energy is the energy of vibrating particles. • When you pluck a guitar string you are giving it kinetic energy. • The vibrating string makes the air around it vibrate. • You can hear these vibrations because the vibrating air (sound waves) travel to your ear and make your eardrum vibrate. Hyperlinked Image Renewable and NonRenewable Sources of Energy • We use many different energy sources to do work for us. • Energy sources are classified into two groups: renewable energy source- this type of energy can be made again and again and • non-renewable energy- this type of energy can run out because it takes millions of years to make more Sources of Energy Brain POP Video Renewable Energy Sources http://www.eia.doe.gov/kids/energyfacts/sources/whatsenergy.html Renewable Energy Sources • Renewable energy sources include solar energy, which comes from the sun and can be turned into electricity and heat. • Wind, geothermal energy from inside the earth, biomass from plants, and hydropower and ocean energy from water are also renewable energy sources. Biomass Energy • Biomass is matter usually thought of as garbage (i.e., dead trees, tree branches, woodchips, bark, sawdust) • This “garbage” can be used to produce electricity, heat, compost material or fuels • How biomass works: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The waste (scraps) gathered in a truck The truck transports the waste to a biomass power plant The biomass is burned in a furnace The heat is used to boil water in the boiler The energy in the steam is used to turn turbines and generators Biomass Energy Flash Movie Hyperlinked Image Hydro-Power! What is Hydro-Power? ٭Water is another very important renewable energy resource ٭Hydro-power is energy that comes from the force of moving water ٭A turbine converts the kinetic energy of falling water into mechanical energy ٭Then a generator converts the mechanical energy from the turbine into electrical energy Alexander Hydroelectric Plant on the Wisconsin River Hydroelectric Plant http://www.wvic.com/hydro-works.htm Hydro-Power Activity Objective: The students will learn the concept of “water pressure”, and how this relates to the production of hydropower. Materials: • Half gallon paper milk carton (empty and washed out) • Gallon of water • Awl or 10p nail • Masking tape • Ruler • Magic marker • Pair of scissors • Pad of paper and pencil to take notes http://www.energyquest.ca.gov/projects/hydro-power.html Renewable Energy Source: Hydrogen • Hydrogen, a renewable energy source, is the most plentiful gas in the universe! • Hydrogen is an energy carrier for the future. It is a clean fuel that can be used in places where it’s hard to use electricity. Sending electricity a long way costs four times as much as shipping hydrogen by pipeline. • Renewable energy sources—like solar and wind—can’t produce energy all the time. • Hydrogen can store the energy until it’s needed and can be moved to where it’s needed. Hydrogen as a Fuel Hydrogen Activity • The objective of this experiment is to produce hydrogen by using electrolysis Link to webpage: http://www.energyquest.ca.gov/projects/split_h2o.html Non-Renewable Energy Sources http://www.eia.doe.gov/kids/energyfacts/sources/whatsenergy.html Non-Renewable Energy Sources • We get most of our energy from nonrenewable energy sources, which include the fossil fuels -- oil, natural gas, and coal. • They're called fossil fuels because they were formed over millions and millions of years by the action of heat from the Earth's core and pressure from rock and soil on the remains (or "fossils") of dead plants and animals. Energy Sources Produce Electricity • Renewable and non-renewable energy sources are used to produce electricity • We use electricity everyday, for example: When you do things like play video games Make a milkshake in your blender Watch TV Surf the Net and turn on the light in your bedroom Electricity • Electricity is the flow of electrical power or charge • It is caused by the movement of electrons Electric Circuits Activity http://www.andythelwell.com/blobz/ Activity: Make a Battery from a Lemon • In this activity, you will make a voltaic battery out of a lemon • A voltaic battery changes chemical energy to electrical energy http://www.energyquest.ca.gov/projects/lemon.html Electricity ActivityHow Much Does it Cost? The objective of this activity is to introduce to the student the concept of conserving energy by investigating the cost of using electricity, and how different electrical device require different amounts of electricity. This activity also discusses the units used for electricity. http://whyfiles.larc.nasa.gov/text/kids/Problem_Board/problems/electricity/cost2.html Non-Renewable Source of Energy: Coal • Coal is used to make electricity • Coal is a nonrenewable energy source because it takes millions of years to create. • The energy in coal comes from the energy stored (Potential Energy) by plants that lived hundreds of millions of years ago, when the earth was partly covered with swampy forests. Sources of Energy Activity Chocolate Chip cookie mining http://www.eia.doe.gov/kids/classactivities/CookieMining_PriElem.pdf Wavelength, Frequency, and Energy • Light is a form of energy • Energy can be described by the wavelength and frequency • Wavelength is measured in meters (m) • Frequency is measured in Hertz (Hz) Relationship: • Long wavelength- low frequency • Short wavelength- high frequency Wavelength, Frequency, and Energy Applet