* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Heliosphere wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
Kuiper belt wikipedia , lookup
Chelyabinsk meteor wikipedia , lookup
Tunguska event wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Halley's Comet wikipedia , lookup
Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 wikipedia , lookup
Comet Hale–Bopp wikipedia , lookup
Stardust (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
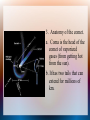
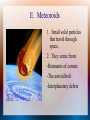
Minor Members of the Solar System Today you will learn: 1. What other objects, besides the planets, orbit around the sun. 2. The difference between asteroids, meteors, and comets. Introduction In 2001, the NEAR Shoemaker was the first visitor on asteroid Eros. This space probe found that it has dust and rocks on its surface. I. Asteroids A. Asteroids are called microplanets or “flying mountains” because they are small rocky bodies. 1. They can be 1000 km wide or the size of a grain of sand. Asteroids (cont) 2. They lie between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter and their orbital period is 3-6 years. 3. Astronomers hypothesize that the astroids are remnants of a planet that was 1/1000 the size of Earth. B. Comets 1. Comets are pieces of rocky and metallic materials held together by frozen gases (water, methane, ammonia, carbon dioxide) 2. They travel in elongated orbitals. a. Take 200 to 100,000 yrs to orbit the sun. 3. Anatomy of the comet. a. Coma is the head of the comet of vaporized gases (from getting hot from the sun). b. It has two tails that can extend for millions of km. Comets (cont) c. One tail is made of dust, the other is made of ionized gases from the solar wind. d. The tail always points away from the sun. e. Once far from the sun, it becomes “cold” and doesn't have a tail anymore. C. Famous Comets 1. Haily's Comet: orbits every 76 years. a. Has tail that is 1.6 million km long. b. Been recorded 29 times since 240 BC. c. It passed by Earth last in 1986. Famous Comets (cont) 2. Hale-Bopp comet: passed through Earth's orbit in 1997. a. Brightest comet to pass Earth and could be seen by the naked eye. b. 100 x brighter than Hailey's comet. D. Source for Comets 1. Comets with short orbital periods come from the Kuiper Belt. a. The Kuiper Belt lies outside of Neptune. (Pluto was believed to come from here) 2. Comets with long orbital periods come from the Oort Cloud. a. This is a sphere of comets that surrounds the solar system. E. Meteoroids 1. Small solid particles that travel through space. 2. They come from: -Remnants of comets -The astroid belt -Interplanetary debris F. Meteors 1. When a meteoroid enters Earth's atmosphere, it burns up due to the friction of the atmosphere's particles. 2. Meteor showers occur when multiple meteors enter Earth's atmosphere. Meteors (cont) 3. The Perseid meteor shower occurs around August 12 every year. 4. It is believed to be caused by the remnants of a comet that passed in 1862. G. Meteorites 1. When a meteor actually hits Earth's surface. 2. In northern Arizona, is the Meteor Crater, which is 1 mile wide and ½ mile deep. The Meteor Crater in Arizona