* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9.01 - Neuroscience & Behavior Fall 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Neurostimulation wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
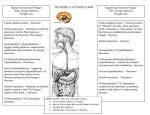
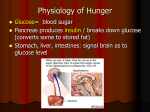
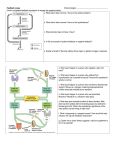
9.01 - Neuroscience & Behavior Fall 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Instructor: Professor Gerald Schneider 9.01 Study Questions Lectures 36-37: Motivation 2 1) Is it true that the choices that an animal (or a person) makes are guided by drives? In what sense? 2) The conclusion from studies of hunger elicited by electrical stimulation of the lateral hypothalamus: “Hunger acts as a ________ that eating will be ___________________.” 3) Describe two experiments showing that drive and reward are separately represented in the brain. 4) Activation of what pathway in the brain is accompanied by pleasure (and thus, reward). 5) What are the two major kinds of aggression in cats that can be elicited from electrical stimulation of the hypothalamus? How can we be sure that the kind that corresponds to predatory aggression is not due to increased hunger? 6) Describe an experiment that indicates connections to the motor system by the hypothalamic neurons involved in attack behavior. 7) How critical is the hypothalamus for control of attack behavior in the cat? Or, for temperature regulation? 8) How do we know that forebrain structures are also very important in the control of aggressive behavior? Give an example of such a forebrain structure. 9) How might androgens act to increase aggression? 10) How does the brain resolve the problem of more than one simultaneously activated drive state? 11) Describe an experimental set-up for obtaining fear conditioning in a rat. (The one described in the lecture results in learning that is dependent on the amygdala.)