* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Écouché in the Second World War wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
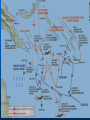
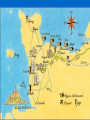
Chapter 12: America and World War II 1941 - 1945 Section 1: Mobilizing for War Industry: Because FDR had already partially mobilized the economy... it was easier to truly mobilize the country, economy, and military quickly FDR gave incentives to industry • • • No more bidding for contracts NOW- cost-plus contracts Pay production cost + % of costs as profit • More you make, faster you make it → more profit you get $$$ Expensive system, BUT got jeeps and tanks out quickly because of transformation of auto industry Auto industry manufacture 1/3 of military equip. during war Financing the War Reconstruction Finance Corporation • Loans to companies to help them convert to producing war goods • War Production Board (WPB) Set priorities and production goals for raw materials and supplies Supervised production of $185 billion in military weapons and supplies in 3 years; dysfunctional Office of War Mobilization (OWM) handled disputes Military Mobilization Selective Service and Training Act (June 1940) • Peacetime draft Draftees outnumbered supplies and facilities http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q78COT wT7nE Double V Campaign ”Double V” for African Americans • Victory in War, Victory over Segregation (at home) and Racism abroad (remember Jesse Owens?) In segregated units, often w/ white cmdrs • Separated for everything • Often given non-combat jobs Pittsburgh Courier “Double V” campaign 99th Pursuit Squadron- Tuskegee Airman • They were sent into combat, as were other Af. Amer. units later in the war 1943-military bases integrated 1948-military fully integrated Women in the War Women join the military! Often administrative and clerical jobs • *to release a man for combat WAAC's (auxiliary corps) → later WAC's (army) WAVE's (Navy)- WASP's (Air) Could move planes across Atlantic, nurses, transport, lab techs + more Section 2: The Early Battles: Japan Right after attacking Pearl Harbor, Japan attacked airfields in Philippines. • • • • • 2 days later J. landed. Amer. and Filipinos outnumbered. MacArthur forced to retreat (he left!). Bataan Death March- 65 miles. 78,000 marched. 24,000 died. May 1942-Philippines fell. The Early Battles: Japan Doolittle’s Raid- April 18, 1942 • Bombs fell on Japan • B- 25s had to land in China • Japan changed strategy • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gaDBEE2fe0k&feature=related Problem for Japan: We had broken Japanese code! Key to our successes! • Get control of S. coast of New Guinea. • Cut off Amer. supply lines to Australia • 3 carriers assigned to the mission Pacific Theatre Battle of the Coral Sea (1st battle in history fought entirely from aircraft carriers.) • Lexington sank • Yorktown crippled • But Japan called off landing on New Guinea. • Early May, 1942 Pacific Theatre Japanese Plan: Take Midway Island • Last Amer. base in No. Pacific • West of Hawaii. • Lure Amer. to attack and then annihilate them • All other carriers sent to Midway. Battle of Midway • U.S. was waiting. • 1st Wave - J. attacked island. Ak- ak guns ready. 38 planes down. • 2nd wave - U.S. countered. Planes caught J. w/ fuel, bombs exposed on board. Sank 3 carriers w/in minutes *Major turning point June 1942 • J. Navy lost 4 of its largest carriers, stopped J. advance in Pacific • 362 Amer.; 3,057 J. dead In Europe Vs. Germany: • Stalin wanted a western front, but Churchill and FDR decided to attack the periphery instead • → Invade Morocco and Algeria (Africa!) • U.S./Brit. plan: Morocco, why? 1. Give troops experience 2. Help Brits. hold on to Suez Canal (vital for supplies and materials) African Front Germans under Rommel (the Desert Fox) Brilliant strategist, although... forced to retreat • U.S. under Patton- also brilliant Problems/Challenges w/ Desert Warfare • hot and dry, sandstorms, • when wet → impassable, • high visibility, tanks made huge dust clouds • critters Nov. 1942- • U.S. Captured Casablanca, Algiers • went E. into Tunisia; • Brit. went W. into Libya. Plan: Trap Rommel 1st U.S. Battle vs. German Forces Battle of Kasserine Pass • 7,000 casualties; lost 200 tanks But, U.S. and Brit. persisted. May 13, 1943 Last Ger. forces in Africa surrendered Battle of the Atlantic German subs picking on cargo ships • Oil and gas hit hard, rationed → long oil pipeline built • Convoy systemimproved success • Built lots of ships to replace losses Stalingrad Ger. vs. USSR: Stalingrad Hitler felt only way to defeat USSR was by hitting their economy • May 1942- ordered army to Capture oil fields, industries and farmlands in S. Russia and Ukraine Attack Stalingrad- major RR, Volga R. Entered Stalingrad in Mid- Sept. Had to hold ground at all costs. Lost thousands fighting house to house Nov- Soviet reinforcements arrived. • Trapped 250,000 Gers. • Battle end in Jan. • 91,000 Ger. surrendered, but only 5,000 of them survived Gulags, etc. *Turning point- Put Germans the defensive. Section 3: Life on the Home Front For Women: “Rosie the Riveter” Women now did traditionally male manufacturing jobs • • • • ”I can make money.” ”I can do things I never thought I could do.” → permanently changed workplace http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HofnGQwPgqs&list=PL8dPuuaLjXtMwme pBjTSG593eG7ObzO7s Home Front: Hispanics 1942-1964 Bracero Program • farmers in SW had labor shortage • 1942-Bracero Program brought Mex. farm-workers in to help w/harvest • 200,000 came 1st year. Zoot Suit Riots • pg. 590, • → excessive material in the clothing = “unpatriotic” • rumors of attacks → sailors and soldiers attacked Mex. Amer. neighborhoods and zoot suits outlawed in LA • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nDEfhS-r_68 Home Front: African Americans A. Philip Randolph threatened a march on D.C. to demand jobs for African Americans → FDR issued Exec. Order 8802 = “No racial discrimination in workplace” but...still- last hired, first fired severe housing discrimination Great Migration resumed Home Front: For Everyone War created new jobs Doubled avg. family income Migration Prices rose, short supply Rationing → meat, sugar, gas, rubber, etc. • • • • • Blue and Red coupons Victory gardens Recycling Collection of vital items Blackouts War bonds, e-bonds In Oregon: http://www.oregonlive.com/portland/index.ssf/2015/03/vanport_survivors_are_dying_ha.html#incart_2box Japanese-American Relocation West Coast problems- fear/ suspicion of Japanese Americans FDR caved in to pressure- Executive order 9066, removed all JapaneseAmer. on West Coast to internment camps 10 of them: CA, AZ, UT, ID, WY, CO, AR Conditions in the Camps Lived in horse barns, cramped conditions Food lines -”foreign” food ignorance/ignoring customs Lost houses, businesses, etc. in home cities Korematsu vs. United States Went to Sup. Ct. Relocation was constitutional b/c it was based on “military urgency”- not race Racism Everywhere! Italian and German immigrants also harassed, lost jobs, had curfews, police searches, forced relocation, internment Propaganda The Other Side of the Story… But many minorities served in military • All-Japanese 100th Battalion- integrated into the 442nd Regimental Combat Team (most highly decorated unit in WWII) Navajo Code Talkers Mex-Americans fought in all theatres Section 4: Pushing the Axis Back Tehran Conference • Iran • Late 1943 Plans: • • • • Invade France Break up Ger. after war USSR help vs. Japan UN for after war Strategy for the Pacific • 1.Island hopping to Japan • 2. MacArthur's troops go thru Solomon Islands, capture N Coast of New Guinea, retake Phil.s Island Hopping Problems Ctrl Pacific Problem- many islands are coral reef atolls. Makes amphibious landing difficult and dangerous • Boats get struck, soldiers wade to shore. • Ex.- Tarawa Atoll, Central Pacific under Nimitz Amphibious landing At least 20 ships ran aground 1,000 died (5,000 landed). Amphibious Assault Vehicles Success w/ LVT- a boat w/ tank tracks “The Alligator”amphibious tractor- amphtrac Several different models Then Kwajalein Atoll • Landing with all amphtracs - much better Ctrl Marianas Pacific Gained Marshall Islands, then onto the Marianas • U.S. invaded Saipan, Tinian, Guam • June - Aug. 1944 • We controlled; used as bases for B-29’s in order to launch bombing runs on Japan Southwestern Pacific SW Pacific under MacArthur Guadalcanal -Aug. '42- early '43Rabawl- Japanese Base Hollandia - on N. coast of New Guinea Morotai - last stop before Phil.s Leyte Gulf Philippines We goofed! Largest naval battle in history 3-4 days Oct. 1944 1st Kamikaze attacks “Divine winds” March 1945: MacArthur captured Manila. • Guerrilla warfare til end of war. I told you I would return! SW Pacific Casablanca Conference Jan, '43 FDR and Churchill • Decide upon “Sicily and bombing of Germany” as strategy to hopefully end the war Next Phase in War: Europe On Germany • Step up bombing of strategic points (military, industrial, economic system) • → oil shortage, wrecked RR system, destroyed aircraft factories, allied total control of air (before D-Day) on “the soft underbelly”invading Sicily In approx. 1 month, w/ Patton and tanks from West; Montgomery, from South: Ger. surr. Attack on Sicily = crisis in Italy. • King had Mussolini arrested; negotiated w/ Allies for surrender. • Ger. fight but Italy fell- May 2, 1945, hard to keep control Operation Overlord Eisenhower in ctrl. Invade at Normandy, France D-Day- June 6th, 1944 In favor- Low tide at dawn, moonlight, break in weather, sm. window of opportunity Timing is bad- heavy cloud cover, strong winds, high waves 7,000 ships, 100,000 troops, 23,000 paratroopers, 13,000 aircraft, 11,912 tons of explosives Beaches Utah – went rather smoothly, sandy beach which made German defenses weaker; there was a wall on the beach; 23,000 landed Omaha – 34,000 + were to land, BUT decimated (cliffs, misinformation about who was there) • • • • Amer, Brit, France (naval support) 10 ships sunk before arriving Lost 50+ tanks before nightfall Losses: 1200 German; 9,387 (+1557 MIA) by nightfall Gold – 25,000 landed; pushed Nazis back 6 miles by nightfall Sword – British Infantry Division; 29,000 men, 223 tanks; German defense was weak; Panzers counter-attacked Juno – 359 Allies died; Canadians and UK. U.S., Brit, Canadian forces suffered high casualties, but invasion successful! Allowed ground and air presence in France; went inland from there. Section 5: The War Ends We advanced in France, but tough going! French Resistance: • Staged a rebellion in Paris • Acts of sabotage on German holdings in Fr. Railroads Factories • Collected intelligence Battle of the Bulge We won! • 100,000 German casualties • Lost tanks, aircraft Germans left with little to prevent allies from entering Germany Dec. 16, 1944 – Jan. 16, 1945 American Hero: http://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=ZX2PbzV 1go8 Nuts! Soviets Pester Germany USSR picked on German troops in Soviet Union • Drove Germany back across Poland • U.S. and USSR troops squeezed German troops in Germany FDR Dies April 12th, 1945 Truman sworn in • VE Day within a month • Fight with Japan, however, only intensifying http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Objoad6rG6U &list=PL8dPuuaLjXtMwmepBjTSG593eG7ObzO7s Hitler Commits Suicide Suicide on April 30th/ May 1st Successor tried to surrender to U.S., Gr. Brit. Eisenhower replied “Unconditional Surrender” May 7th, 1945: Surrender May 8th, 1945: VE Day (Victory in Europe Day) To End the War with Japan Bombing Japan, but not accurate enough to cause enough damage. Need a closer base = Iwo Jima • Nasty topography • Japanese had great defenses • 6,800 Marines died • 19 February–26 March 1945 • “Operation Detachment “ Napalm Bombs on Tokyo Napalm bombs on Tokyo • 80,000 died; 250,000 bldgs. Destroyed • By June of 1945, 6 most important industrial cities been firebombed; • 67 cities hit by end of war Okinawa Belief…Japan won’t surrender until it is invaded. U.S. goes for Okinawa • 1 April – 21 June 1945 Japan had fortified mountains • 12,000 Americans died by June 22, 1945 Casualties and losses U.S. 12,513 killed 38,916 wounded, 33,096 noncombat losses Japan About 95,000+ killed 7,400–10,755 captured Estimated 42,000–150,000 civilians killed Emperor Hirohito Wanted to surrender Unconditional surrender would include removal of Emperor “No.” Several cabinet members resigned. How To End the War??? YES? NO? VJ Day August 15th, 1945 Japan surrendered Building a New World Immediately after the war… • Help Japan clean up MacArthur put in charge United Nations • Plans made before war was over • 39 countries made plans General Assembly: every member nation has 1 vote Security Council: 11 member (now 15) 5 permanent: Gr. Brit., France, China, USSR, US Veto power • April 25, 1945: 50 countries got together, write charter, vote on budget Nuremberg Trials International Military Tribunal (IMT) Nuremberg (Germany) • Put Nazi leaders on trial for war crimes • 22 leaders in first round: 3 acquitted 7 prison sentence 12 death by hanging • 24 more executed • 107 more in prison Tokyo Trials 25 Japanese leaders charged • NOT the emperor • 18 in prison • Rest hanged Test! The usual Essays: • Zoot suiters: What? Why anger so many Americans? • Different points of view/debate over use of atomic bomb. Why did Truman finally decide to use it?