* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WWII the Tide Turns
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Propaganda of Fascist Italy wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Italian Empire wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Torch wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Italian Social Republic wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Italian resistance movement wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
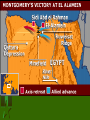
WWII The Tide Turns: Allies in Victory Overview • • • • • • • The entrance of the United States to the War El Alamein The Invasion of Italy The Red Army pushes the Germans back D-Day and the Invasion of France Nazi’s are Defeated The War in the Pacific – Hiroshima and Nagasaki The U.S. Enters the War • The U.S. enters the war. Britain, France, Russia are now on one side. • The 8th Air Force is deployed to Britain and the bombing campaign of Germany from England starts. • U.S. forces deploy to North Africa, Patton defeats Rommel and the British find new victories. El Alamein, Egypt • Field Marshal Montgomery beats Rommel’s Panzers and protects the route to the Suez Canal. • This defeat signals the beginning of the end for the German War Machine Invasion of Italy • July 1943: U.S. and British forces invade Italy from two points, Anzio and Salerno. • Tired of the fascist dictator, Mussolini is overthrown from within and the new Italian government signs the armistice. • Although Allies faced heavy German resistance in Italy, they continued to move up the peninsula to retake the entire country. • Mussolini is taken into the streets, beaten and hanged for all to see. Benito Mussolini and his Wife Stalingrad • Hitler orders a new offensive in Russia. • After surrounding the city named after Stalin, the Germans moved into the city. • The Russians then countered the Germans by surrounding them and began to starve them out. • 300,000 Germans were killed, wounded or captured at Stalingrad. Invasion of France • June 6, 1944 D-Day Invasion on the Normandy coast of France. • Allied paratroopers dropped in behind enemy lines to help secure the beaches. • 176,000 allied troops landed on Omaha, Utah, Gold, Sword and Juno beaches marking the largest amphibious assault in history The Nazi’s are Defeated • The Allies advanced through Europe, Russia from the east and the U.S. – British forces from the west. • Allied bombers destroyed German cities and industrial complexes to reduce the 3rd Reich’s ability to wage war. The city of Dresden was reduced to rubble and engulfed in a firestorm after bombers struck it day and night. • On May 8th, 1945 V-E Day was declared when Russians overtook Berlin, finding that Hitler had committed suicide in his command bunker. Defeat of Japan • The United States finally makes headway using a technique called island-hopping. • The Battles of Midway and Coral Sea were turning points of the war in the pacific. • Bloody battles on Iwo Jima and Tarawa made it clear that the Japanese were not giving up. America decides on the Pacific • An invasion of Japan would cost thousands, if not more than hundreds of thousands of lives. • The Japanese used the Kamikaze (Suicide attack) to shock troops and increase damage to ships. • President Truman makes a decision about Japan and the War. Hiroshima • August 6th 1945 – an American plane (The Enola Gay) dropped an atomic bomb on the mid-sized city of Hiroshima. • Over 70,000 people are instantly killed. • Four square miles were reduced to nothing. Nagasaki • August 9th, after refusal to surrender by the Japanese, the United States dropped a second atomic bomb on the city of Nagasaki. • Over 40,000 killed instantly • On September 2, 1945 on the deck of the U.S.S Missouri, Japan surrenders to the United States.