* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Title Goes Here - Binus Repository
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Brand loyalty wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Brand equity wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Brand ambassador wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Emotional branding wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Customer satisfaction wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
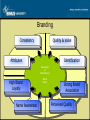
Matakuliah Tahun : V0222 - Penjualan dan Pemasaran Hotel : 2009 - 2010 Designing and Managing Products Pertemuan 6 “Profit is payment you get when you take advantage of change.” -Joseph Schumpeter“Being fed a decent meal in a casual environment is a commodity in far more supply than demand.” -Barry M. Cohen- What is a Product? • A product is anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use or consumption that might satisfy a want or need • Includes physical objects, services, places, organizations, and ideas Product Levels Core Product Facilitating Products Supporting Products Core Competency Core Product • What the buyer is really buying • Every product is a package of problem-solving services Facilitating Products • Goods or services that must be present for the guest to use the core product Supporting Products • Extra products offered to add value to the core product and help to differentiate it from the competition Augmented Product • The augmented product includes accessibility, atmosphere, customer interaction with the service organization, customer participation, and customers’ interaction with each other. Core Competency Review • Supporting products offer a competitive advantage only if they are properly planned and implemented • They must meet or exceed customer expectations to have a positive effect Atmosphere: The Physical Environment • Can be the customer’s reason for choosing, or not choosing, to do business with an establishment • Multidimensional – Visual, aural, olfactory, tactile Product levels (Adapted from C. Gonroos, “Developing the Service Offering— A Source of Competitive Advantage,” in Add Value to Your Service, C. Surprenant, ed., Chicago: American Marketing Association, 1987, p. 83.) Customer Interaction with the Service Delivery System • Joining stage is when the customer makes the initial inquiry contact • Consumption phase takes place when the service is consumed • Detachment phase is when the customer is through using a product and departs Customer Interaction with Other Customers • Hospitality organizations must manage the interaction of customers to ensure that some do not negatively affect the experience of others Customer Coproduction • Increase capacity • Improve customer satisfaction • Reduce costs Brand Decisions A brand is a name, term, sign, symbol, design, or a combination of these elements that is intended to identify the goods or services of a seller and differentiate them from competitors Brand • Brands are among a company’s most valuable assets • A Brand represents what the company is and what it stands for • A Brand implies trust , consistency, and a defined set of expectations • The strongest brands own a place in the customer’s mind Branding Consistency Quality & Value Attributes Identification Advantages of Brand Names High Brand Loyalty Name Awareness Brand Equity Strong Brand Association Perceived Quality Conditions that Support Branding • The product is easy to identify by brand or trademark • The product is perceived as the best value for the price • Quality and standards are easy to maintain • The demand for the general product class is large enough to support a regional, national, or international chain • There are economies of scale Leveraging Brand Equity • Cobranding • Partnerships New Product Development • Product life cycle – Product is born – Passes through several phases – Eventually dies as younger products come along that better serve consumer needs New Product Development Process Marketing Strategy Development Concept Development and Testing Business Analysis Product Development Idea Screening Market Testing Idea Generation Commercialization Idea Generation • • • • • Internal Sources Customers Competitors Distributors and Suppliers Other Sources Idea Screening The purpose of screening is to spot good ideas and drop poor ones as quickly as possible Concept Development and Testing • A product idea envisions a possible product that company managers might offer to the market • A product concept is a detailed version of the idea stated in meaningful consumer terms • A product image is the way that consumers picture an actual or potential product • The task is to develop an idea into alternative product concepts, determine how attractive each is to customers, and choose the best one • Concept testing occurs within a group of target consumers Marketing Strategy Includes information such as the target market and product positioning as well as both short and long term projections in terms of sales, profits and costs Business Analysis Business analysis involves a review of the sales, costs, and profit projections to determine whether they satisfy the company’s objectives Test Marketing The product and marketing program are introduced into realistic market settings Product Development • The prototype must: – Have the key features described in the product concept statement, as perceived by the customer – Performs safely under normal use – Be produced for the budgeted costs Commercialization In launching a new product, a company must make four decisions: When? Where? To whom? and How? Product Development Through Acquisition • A method of product development that reduces the risk considerably for large companies that have the assets to purchase and then develop a fledgling chain Product Development • Product development begins when the company finds and develops a new product idea • During development, sales are zero and the company’s investment costs add up Product Life Cycle Sales and Profits Over the Product’s Life From Inception to Demise Sales and Profits ($) Sales Profits Time Product Development Losses/ Investments ($) Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Product Deletion Process (Martin Bell, Marketing Concepts and Strategy, 3rd ed., p.267, 1979, Houghton Mifflin Company; used by permission, Mrs.. Marcellette (Bell) Chapman. ) Key Terms • • • • • • • • • • Augmented products Aural Brand Consumption phase Core product Customization Decline Detachment phase Drop Facilitating products • • • • • • • • • • Growth Introduction Joining Maturity Olfactory Phase-out Product concept Product development Product idea Product image