* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Week 4 - cda college
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
E-governance wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Online shopping wikipedia , lookup
Yield management wikipedia , lookup
Michael Aldrich wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
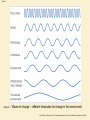
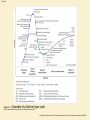
Slide 4.1 Chapter 4 E-environment Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.2 Learning outcomes • Identify the different elements of an organization macro-environment that impact on an organizations e-business and e-marketing strategy • Assess the impact of legal, privacy and ethical constraints or opportunities on a company • Assess the role of macro-economic factors such as governmental e-business policies, economics, taxation and legal constraints. Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.3 Management issues • What are the constraints placed on developing and implementing an e-business strategy by the e-environment? • How can trust and privacy be assured for the customer while seeking to achieve marketing objectives of customer acquisition and retention? • Assessment of the business relevance of technological innovation. Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.4 Activity 4.1 Introduction to social, legal and ethical issues • List all the social, legal and ethical issues that the manager of a sell-side e-commerce web site needs to consider to avoid damaging relationships with users of his or her site or which may leave the company facing prosecution. • You can base your answer on issues which may concern you, your friends or family when you access a web site. Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.5 SLEPT Framework • Social-influence consumer perception of Internet use for e-commerce • Legal & Ethical-determine what can be promoted and sold online • Economic-affect spending patterns • Political-Determine the adoption and the future of Internet • Technological-offer new opportunities Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.6 Figure 4.1 ‘Waves of change’ – different timescales for change in the environment Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.7 SLEPT Framework • E-Commerce Manager has to monitor the changes of the Macro-environment (also called environment scan) • Among the 5 factor type, Legal factor is one of the most important. • P.195, Table 4.2 Lists the Key legal issues that have direct impact on e-commerce Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.8 Factors Govern E-commerce Adoption • • • • • • Cost of Access Value proposition Ease of use Security and trust Fear of the unknown Skills Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.9 Webographics – – – – – – – Usage location Access device Connection speed ISP Experience level Usage type-work, social, entertainment, etc. Usage level-hours or minutes / month Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.10 Variation in broadband subscribers per 100 inhabitants, by technology, December 2007 Figure 4.2 Source: OECD (www.oecd.org/sti/ict/broadband) Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.11 Influences of Online Channel • Finding products and services online is a popular web activity • Online research occurs at every phase of purchase, even for offline purchases Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.12 Figure 4.3 Percentage by category who bought offline after researching online Source: BrandNewWorld: AOL UK / Anne Molen (Cranfield School of Management) /Henley Centre, 2004 Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.13 Motivation for Using Online Services Community Survey Entertainment Download Product trial Search Information Interaction Make purchases Exploration Games News Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.14 E-commerce-Psychographic Segmentation • Ref. Box 4.1 on pp. 202-203 Online Consumer Type 1999 2004 Realistic Enthusiasts 15% 14% Confident brand shoppers 16% 18% Carefree spenders 15% 19% Cautious Shoppers 20% 14% Bargain hunter 16% 21% Unfulfilled 17% 14% Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.15 Trust in Different Information Sources • The role of social media and friends in influencing sales was highlighted by this research http://eiaa.net/ftp/casestudiesppt/EIAA_Online _Shoppers_Report.pdf – Search engines (76%) – Personal recommendations (72%) Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.16 Trust in Different Information Sources – – – – – – – – Price comparison web sites (61%) Web sites of well-known brands (59%) Newspapers/magazines (58%) Customer web site reviews (58%) Expert web site reviews (57%) Retailer web sites (57%) Sales people in shops (50%) Content provided by ISPs (38%). Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.17 Figure 4.4 Development of experience in Internet usage Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.18 Figure 4.5 Variation in purchase rates of online products and services in Europe Source: European Interactive Advertising Association (www.eiaa.net), Mediascope Eupore 2008 Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.19 Business as Online Buyers B2B Profiles • The % of companies with access by the right personnel • Influenced online—may not buy online but affected by online information • Purchase online Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.20 E-Business Adoption by SMEs SMEs have a lower adoption rate in comparison to larger enterprises. They can be classified into 4 categories – – – – Developers Communicators Web presence Transactors Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.21 Variation in use of e-commerce services between SMEs and larger enterprises Figure 4.6 Source: European Commission (2007) Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.22 E-Business Adoption by SMEs Assessing the risk and reward for SME adoption • Revenue • Reputation • Strategic importance • Regulatory compliance Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.23 Privacy and Trust in E-Commerce • • • • • What are ethical standards? Why is it so important for e-commerce? What’s privacy? Why privacy a big deal for e-commerce? Identity fraud in Canadahttp://www.safecanada.ca/identitytheft_e.asp Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.24 Personal Data and E-Commerce Online businesses and e-marketer typical need these data – – – – – Contact info Profile info—segmentation Access platform Behavioural info on a single site Behavioural Info on multiple sites • Anything else? Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.25 Table 4.6 Types of information collected online and related technologies Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.26 Table 4.6 Types of information collected online and related technologies (Continued) Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.27 Ethical issues and data protection • Ethical issues concerned with personal information ownership have been usefully summarized by Mason (1986) into four areas: 1. Privacy – what information is held about the individual? 2. Accuracy – is it correct? 3. Property – who owns it and how can ownership be transferred? 4. Accessibility – who is allowed to access this information, and under which conditions? Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.28 Table 4.2 Significant laws which control digital marketing Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.29 Table 4.2 Significant laws which control digital marketing (Continued) Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.30 Ethics – Fletcher’s view • Fletcher (2001) provides an alternative perspective, raising these issues of concern for both the individual and the marketer: 1. Transparency – who is collecting what information? 2. Security – how is information protected once collected by a company? 3. Liability – who is responsible if data is abused? Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.31 The eight principles for data protection • • • • • • Fairly and lawfully processed processed for limited purposes adequate, relevant and not excessive accurate not kept longer than necessary processed in accordance with the data subject's rights • secure • not transferred to countries without adequate protection www.dataprotection.gov.uk Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.32 Ethical issues and data protection • In Canada, Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) establishes principles for collection, use, and disclosure of personal information. http://laws.justice.gc.ca/en/showdoc/cs/P-8.6///en?page=1 • Provinces have parallel legislation Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.33 Standard information collected about web site visitors from the DaveChaffey.com site Figure 4.7 Source: Feedjit Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.34 Information flows that need to be understood for compliance with data protection legislation Figure 4.8 Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.35 Other E-Commerce Legislation • Market e-commerce business o Domain name and brand/trademark protection o Using competitor name in meta-tag and payper-click advertising o Accessibility law Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.36 Figure 4.9 Comparison of number of blog postings for three consumer brands Source: Blogpulse (www.blogpulse.com), reprinted by permission of Nielsen Buzzmetrics Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.37 Other E-Commerce Legislation • • • • • Forming Electronic Contracts Country of origin principle Distance selling law Making and accepting payment Others—ref. pp. 226-227 Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.38 E-Commerce & Green Environment • Do you think e-commerce have positive effect on environment? • Read the Box 4.6 on page 228 Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.39 Figure 4.10 HSBC virtual forest Source: www.hsbc.co.uk Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.40 Taxation • What do you know about the e-commerce taxes? Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.41 Taxation Tax Jurisdiction • In general, taxes are collected in the jurisdiction where consumption take place • This applies to EU and Canada • The US federal government doesn’t collect taxes for online purchases • States may have different legislations Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.42 Taxation • Canadian merchants must collect Federal taxes (H/GST) for any order in the county, and Provincial taxes for orders made in any region that they have a physical location. • If you are a merchants outside of Canada shipping to Canada, with no physical presence in Canada, you do not have collect any taxes • http://www.ecomnet.ca/?p=87 Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.43 Freedom Restriction Legislation • Read p. 232 Activity 4.4 • Discuss the questions Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.44 Economic & Competitive Factors • The e-commerce potential would be determined by the economic health and competitive environment of the country. • A 4-layer model was proposed to assess such e-economy environment by Booz Allen Hamilton (2002) Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.45 Figure 4.11 A framework describing the e-economy Source: Booz Allen Hamilton (2002). International E-Economy: Benchmarking The World’s Most Effective Policy for the E-Economy. Report published 19 November, London. www.e-envoy.gov.uk/oee/oee/nsf/sections/summit_benchmarking/$file/indexpage.htm Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.46 Localization • Singh and Pereira (2005) provide an evaluation framework for the level of localization: – Standardized web sites (not localized). A single site serves all customer segments (domestic and international) Many sites, especially small business sites fall into this category – Semi-localized web sites. A single site serves all customers; however, there will be contact information about foreign subsidiaries available for international customers. Many sites fall into this category http://scotiabank.com/ – Localized web sites. Country-specific web sites with language translation for international customers, wherever relevant. 3M (www.3m.com) has adapted the web sites for many countries to local language versions. Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.47 Localization (Continued) • Highly localized web sites. Country-specific web sites with language translation; they also include other localization efforts in terms of time, date, postcode, currency formats, etc. Dell (www.dell.com) provides highly localized web sites • Culturally customized web sites.Web sites reflecting complete ‘immersion’ in the culture of target customer segments; as such, targeting a particular country may mean providing multiple web sites for that country depending on the dominant cultures present. Durex (www.durex.com) is a good example of a culturally customized web site Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.48 Localization • Why localize a website? Is it important? • What to be considered for localization? Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.49 B2B International E-Trading • Large organizations are doing fairly well. • How about SMEs? • What’s your opinion on SME B2B international trading? • Complete Activity 4.5 on p. 237 Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.51 Technological issues • Rate of change – Which new technologies should we adopt? • Monitoring for new techniques • Evaluation – are we early adopters? • Re-skilling and training Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.52 Figure 4.12 Diffusion–adoption curve Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.53 Figure 4.13 Example of a Gartner hype cycle Source: Gartner (2005) Gartner’s Hype Cycle Special Report for 2005 Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.54 Identifying Emerging Technologies • Technology networking—monitoring, scouting, and sharing • Crowd-sourcing—facilitate access to ideas from customers, partners, inventors, etc. e.g., innocentive.com • Technology hunting—structured review of start-up companies for new tech capability • Technology mining—search the published documentations. E.g., googlealert Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.55 Figure 4.14 InnoCentive Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.56 Figure 4.15 Alternative responses to changes in technology Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.57 Summary • What are the SLEPT factors? • How could they affect e-commerce? • What’s a strategy to adopt in coping with the SLEPT factors? Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.58 Lab Exercise • Read the Box 4.3 on p.217. Compare to PIPEDA of Canada to see any similarity and differences Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009 Slide 4.59 Next Class Read pp. 256-259 of the Econsultancy Interview and answer/discus these questions – What type of business does Standard Life do? – What’s their online business target % in their whole business? – Can you find a favorite Canadian company to see what a typical % of their business are done online? – What are the key challenges in implementing the online business? – What’s the relationship between the online and other channels? – What can we learn from this interview? Dave Chaffey, E-Business and E-Commerce Management, 4th Edition, © Marketing Insights Limited 2009